Physicochemical Properties
| Molecular Formula | C65H112N22O13 |
| Molecular Weight | 1409.72439289093 |
| CAS # | 1021346-05-3 |
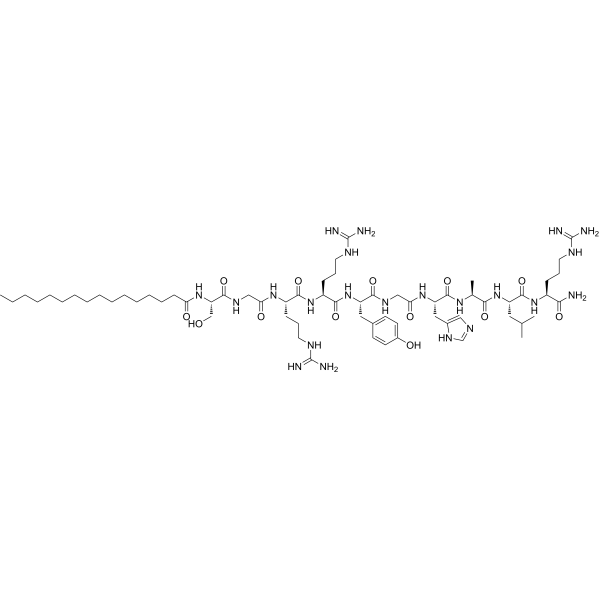
| Sequence | {Pal}-Ser-Gly-Arg-Arg-Tyr-Gly-His-Ala-Leu-Arg-NH2 |
| SequenceShortening | {Pal}-SGRRYGHALR-NH2 |
| Appearance | Typically exists as solid at room temperature |
| HS Tariff Code | 2934.99.9001 |
| Storage |
Powder-20°C 3 years 4°C 2 years In solvent -80°C 6 months -20°C 1 month |
| Shipping Condition | Room temperature (This product is stable at ambient temperature for a few days during ordinary shipping and time spent in Customs) |
Biological Activity
| Targets | PAR4[1] |
| ln Vitro | P4pal10 is a pepducin with a peptide sequence identical to part of the third intracellular loop of the protease activated receptor 4 (PAR4) which acts as a PAR4 antagonist. P4pal10 has no agonist activity as measured by platelet aggregation, intracellular Ca2+ release or InsP production, but preincubation of human platelets with P4pal10 completely blocks aggregation in response to PAR4 activators. Infusion of P4Pal10 into mice extends bleeding time and protects against systemic platelet activation, and in rat models of myocardial injury, P4pal10 treatment before ischemia significantly decreases infarct size when given before, during, and after ischemia. P4Pal10 also inhibits signaling downstream of the Galphai-coupled FPR2. |
| ln Vivo | We evaluated a potential role for proteinase-activated receptor 4 (PAR(4)) in a rodent paw inflammation model, with a focus on two main features of inflammation: (1) oedema and (2) granulocyte recruitment. 2 A PAR(4) antagonist (Pepducin P4pal-10; palmitoyl-SGRRYGHALR-NH(2)) reduced both the oedema and granulocyte recruitment induced by a localized administration of carrageenan in the rat hind paw, pointing to a key role for PAR(4) in this inflammation model. 3 Further, intraplantar injection in the mouse hind paw of a PAR(4) agonist (AYPGKF-NH(2)), but not its standard PAR(4)-inactive peptide control (YAPGKF-NH(2)), caused an inflammatory reaction characterized by oedema (increased paw thickness) and granulocyte recruitment (increased paw myeloperoxidase activity). The PAR(4) agonist-induced effects were inhibited in mice pretreated with pepducin P4pal10. 4 These PAR(4) agonist-mediated effects were not affected by pretreatment with inhibitors of either NO production or prostaglandin release (L-NAME and indomethacin, respectively). 5 However, selective immuno-depletion of neutrophils significantly reduced PAR(4) agonist-induced oedema formation. 6 Moreover, AYPGKF-NH(2)-induced oedema was also reduced by pretreatment with either a kinin B(2) receptor antagonist (icatibant) or a tissue or plasma kallikrein inhibitor (FE999024 and FE999026, respectively), but not with a kinin B(1) receptor antagonist (SSR240612). 7 We conclude: (1) that PAR(4) plays an important role in the inflammatory response as it mediates some of the hallmarks of inflammation and (2) that PAR(4)-mediated oedema is dependent on the recruitment of neutrophils and components of the kallikrein-kinin system.[1] |
| References |
[1]. Neutrophils and the kallikrein-kinin system in proteinase-activated receptor 4-mediated inflammation in rodents. Br J Pharmacol. 2005 Nov;146(5):670-8. |
Solubility Data
| Solubility (In Vitro) | May dissolve in DMSO (in most cases), if not, try other solvents such as H2O, Ethanol, or DMF with a minute amount of products to avoid loss of samples |
| Solubility (In Vivo) |
Note: Listed below are some common formulations that may be used to formulate products with low water solubility (e.g. < 1 mg/mL), you may test these formulations using a minute amount of products to avoid loss of samples. Injection Formulations (e.g. IP/IV/IM/SC) Injection Formulation 1: DMSO : Tween 80: Saline = 10 : 5 : 85 (i.e. 100 μL DMSO stock solution → 50 μL Tween 80 → 850 μL Saline) *Preparation of saline: Dissolve 0.9 g of sodium chloride in 100 mL ddH ₂ O to obtain a clear solution. Injection Formulation 2: DMSO : PEG300 :Tween 80 : Saline = 10 : 40 : 5 : 45 (i.e. 100 μL DMSO → 400 μLPEG300 → 50 μL Tween 80 → 450 μL Saline) Injection Formulation 3: DMSO : Corn oil = 10 : 90 (i.e. 100 μL DMSO → 900 μL Corn oil) Example: Take the Injection Formulation 3 (DMSO : Corn oil = 10 : 90) as an example, if 1 mL of 2.5 mg/mL working solution is to be prepared, you can take 100 μL 25 mg/mL DMSO stock solution and add to 900 μL corn oil, mix well to obtain a clear or suspension solution (2.5 mg/mL, ready for use in animals). Injection Formulation 4: DMSO : 20% SBE-β-CD in saline = 10 : 90 [i.e. 100 μL DMSO → 900 μL (20% SBE-β-CD in saline)] *Preparation of 20% SBE-β-CD in Saline (4°C,1 week): Dissolve 2 g SBE-β-CD in 10 mL saline to obtain a clear solution. Injection Formulation 5: 2-Hydroxypropyl-β-cyclodextrin : Saline = 50 : 50 (i.e. 500 μL 2-Hydroxypropyl-β-cyclodextrin → 500 μL Saline) Injection Formulation 6: DMSO : PEG300 : castor oil : Saline = 5 : 10 : 20 : 65 (i.e. 50 μL DMSO → 100 μLPEG300 → 200 μL castor oil → 650 μL Saline) Injection Formulation 7: Ethanol : Cremophor : Saline = 10: 10 : 80 (i.e. 100 μL Ethanol → 100 μL Cremophor → 800 μL Saline) Injection Formulation 8: Dissolve in Cremophor/Ethanol (50 : 50), then diluted by Saline Injection Formulation 9: EtOH : Corn oil = 10 : 90 (i.e. 100 μL EtOH → 900 μL Corn oil) Injection Formulation 10: EtOH : PEG300:Tween 80 : Saline = 10 : 40 : 5 : 45 (i.e. 100 μL EtOH → 400 μLPEG300 → 50 μL Tween 80 → 450 μL Saline) Oral Formulations Oral Formulation 1: Suspend in 0.5% CMC Na (carboxymethylcellulose sodium) Oral Formulation 2: Suspend in 0.5% Carboxymethyl cellulose Example: Take the Oral Formulation 1 (Suspend in 0.5% CMC Na) as an example, if 100 mL of 2.5 mg/mL working solution is to be prepared, you can first prepare 0.5% CMC Na solution by measuring 0.5 g CMC Na and dissolve it in 100 mL ddH2O to obtain a clear solution; then add 250 mg of the product to 100 mL 0.5% CMC Na solution, to make the suspension solution (2.5 mg/mL, ready for use in animals). Oral Formulation 3: Dissolved in PEG400 Oral Formulation 4: Suspend in 0.2% Carboxymethyl cellulose Oral Formulation 5: Dissolve in 0.25% Tween 80 and 0.5% Carboxymethyl cellulose Oral Formulation 6: Mixing with food powders Note: Please be aware that the above formulations are for reference only. InvivoChem strongly recommends customers to read literature methods/protocols carefully before determining which formulation you should use for in vivo studies, as different compounds have different solubility properties and have to be formulated differently. (Please use freshly prepared in vivo formulations for optimal results.) |
| Preparing Stock Solutions | 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | |
| 1 mM | 0.7094 mL | 3.5468 mL | 7.0936 mL | |
| 5 mM | 0.1419 mL | 0.7094 mL | 1.4187 mL | |
| 10 mM | 0.0709 mL | 0.3547 mL | 0.7094 mL |