Physicochemical Properties
| Molecular Formula | C15H14O4 |
| Molecular Weight | 258.27 |
| Exact Mass | 258.089 |
| CAS # | 21255-69-6 |
| PubChem CID | 89472 |
| Appearance | White to off-white solid powder |
| Density | 1.329g/cm3 |
| Boiling Point | 483.3ºC at 760mmHg |
| Flash Point | 260.2ºC |
| Vapour Pressure | 5.76E-10mmHg at 25°C |
| Index of Refraction | 1.652 |
| LogP | 2.789 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 3 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 4 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 3 |
| Heavy Atom Count | 19 |
| Complexity | 309 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| InChi Key | JDJPNKPFDDUBFV-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
| InChi Code | InChI=1S/C15H14O4/c1-9(10-2-4-11(16)5-3-10)15(19)13-7-6-12(17)8-14(13)18/h2-9,16-18H,1H3 |
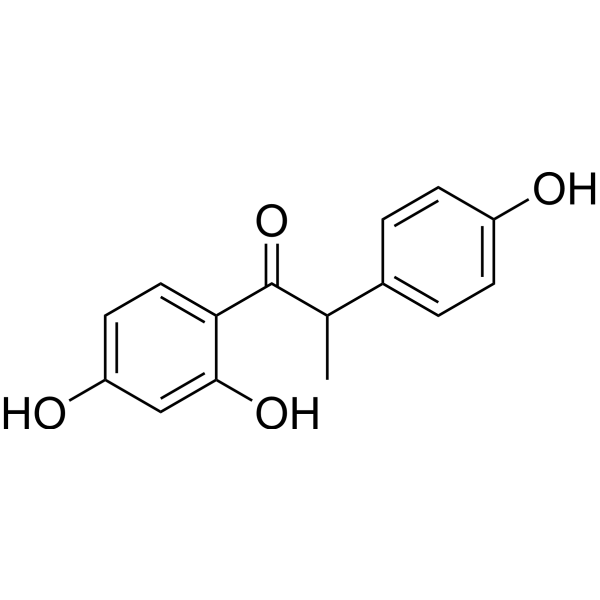
| Chemical Name | 1-(2,4-dihydroxyphenyl)-2-(4-hydroxyphenyl)propan-1-one |
| HS Tariff Code | 2934.99.9001 |
| Storage |
Powder-20°C 3 years 4°C 2 years In solvent -80°C 6 months -20°C 1 month |
| Shipping Condition | Room temperature (This product is stable at ambient temperature for a few days during ordinary shipping and time spent in Customs) |
Biological Activity
| Targets | Microbial Metabolite |
| ln Vitro | Higher doses of O-Desmethylangolensin (O-DMA) (about 30% reduction at 75 μM) impede the development of HepG2 cells [2]. |
| Toxicity/Toxicokinetics |
Toxicity Summary O-desmethylangolensin (ODMA) exerts androgen receptor antagonistic activity and agonistic activity towards estrogen receptor (ER)-α and ERβ. The structure of ODMA is somewhat similar to estrogen. (A15413) |
| References |
[1]. Metabolomics reveals differences between three daidzein metabolizing phenotypes in adults with cardiometabolic risk factors. Mol Nutr Food Res. 2017 Jan;61(1). [2]. The antioxidant activity of daidzein metabolites, O‑desmethylangolensin and equol, in HepG2 cells. Mol Med Rep. 2014 Jan;9(1):328-32. |
| Additional Infomation |
O-Desmethylangolensin is a stilbenoid. O-Desmethylangolensin (ODMA) is a metabolite of the soy isoflavone daidzein by intestinal bacteria in approximately 80-90% of persons. Studies suggest beneficial health effects associated with daidzein-metabolizing phenotypes, and there is some small association between ODMA production and some phenotypes. Few dietary factors are associated with daidzein-metabolizing phenotypes. However, it remains unclear why some, but not all, persons harbor ODMA-producing bacteria. ODMA production is inversely associated with age, height, weight, and body mass index. In addition, Asians are less likely than whites to be ODMA producers, and former smokers were more likely than never smokers to be ODMA producers. Investigators have attempted to identify the bacteria involved in ODMA production, and several candidate bacteria were associated, but not definitely identified. ODMA production is correlated with the abundance of methanogens, indicating that the metabolic fate of daidzein may be related to intestinal H(2) metabolism. (A3192, A3193). |
Solubility Data
| Solubility (In Vitro) | DMSO: 62.5 mg/mL (241.99 mM) |
| Solubility (In Vivo) |
Solubility in Formulation 1: ≥ 2.08 mg/mL (8.05 mM) (saturation unknown) in 10% DMSO + 40% PEG300 + 5% Tween80 + 45% Saline (add these co-solvents sequentially from left to right, and one by one), clear solution. For example, if 1 mL of working solution is to be prepared, you can add 100 μL of 20.8 mg/mL clear DMSO stock solution to 400 μL PEG300 and mix evenly; then add 50 μL Tween-80 to the above solution and mix evenly; then add 450 μL normal saline to adjust the volume to 1 mL. Preparation of saline: Dissolve 0.9 g of sodium chloride in 100 mL ddH₂ O to obtain a clear solution. Solubility in Formulation 2: ≥ 2.08 mg/mL (8.05 mM) (saturation unknown) in 10% DMSO + 90% (20% SBE-β-CD in Saline) (add these co-solvents sequentially from left to right, and one by one), clear solution. For example, if 1 mL of working solution is to be prepared, you can add 100 μL of 20.8 mg/mL clear DMSO stock solution to 900 μL of 20% SBE-β-CD physiological saline solution and mix evenly. Preparation of 20% SBE-β-CD in Saline (4°C,1 week): Dissolve 2 g SBE-β-CD in 10 mL saline to obtain a clear solution. Solubility in Formulation 3: ≥ 2.08 mg/mL (8.05 mM) (saturation unknown) in 10% DMSO + 90% Corn Oil (add these co-solvents sequentially from left to right, and one by one), clear solution. For example, if 1 mL of working solution is to be prepared, you can add 100 μL of 20.8 mg/mL clear DMSO stock solution to 900 μL of corn oil and mix evenly. (Please use freshly prepared in vivo formulations for optimal results.) |
| Preparing Stock Solutions | 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | |
| 1 mM | 3.8719 mL | 19.3596 mL | 38.7192 mL | |
| 5 mM | 0.7744 mL | 3.8719 mL | 7.7438 mL | |
| 10 mM | 0.3872 mL | 1.9360 mL | 3.8719 mL |