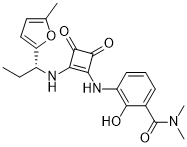
Navarixin (formerly known as MK-7123; SCH527123; PS291822) is a novel potent and specific allosteric antagonist of CXCR1 and CXCR2 with antitumor and anti-inflammatory activity and is able to sensitize cells to oxaliplatin in preclinical colon cancer models. Its Kd values are 41 nM for cynomolgus CXCR1 and 0.20 nM, 0.20 nM, and 0.08 nM for cynomolgus monkey CXCR2, mouse, and rat, respectively. Navarixin exhibited reversible and saturable binding to CXCR1 and CXCR2. Navarixin exhibited good affinity towards CXCR1 (K(d) = 3.9 +/- 0.3 nM); however, it is selective towards CXCR2 (K(d) = 0.049 +/- 0.004 nM). All of the information combined indicates that Navarixin is a new, strong, and targeted CXCR2 antagonist that may be used therapeutically to treat a range of inflammatory diseases.
Physicochemical Properties
| Molecular Formula | C21H23N3O5 | |
| Molecular Weight | 397.43 | |
| Exact Mass | 397.164 | |
| Elemental Analysis | C, 63.47; H, 5.83; N, 10.57; O, 20.13 | |
| CAS # | 473727-83-2 | |
| Related CAS # | 862464-58-2 (hydrate); 473727-83-2 | |
| PubChem CID | 9865554 | |
| Appearance | White to off-white solid powder | |
| LogP | 2.975 | |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 3 | |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 7 | |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 7 | |
| Heavy Atom Count | 29 | |
| Complexity | 704 | |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 1 | |
| SMILES | O=C1C(C(NC2=CC=CC(C(N(C)C)=O)=C2O)=C1N[C@H](CC)C3=CC=C(O3)C)=O |
|
| InChi Key | RXIUEIPPLAFSDF-CYBMUJFWSA-N | |
| InChi Code | InChI=1S/C21H23N3O5/c1-5-13(15-10-9-11(2)29-15)22-16-17(20(27)19(16)26)23-14-8-6-7-12(18(14)25)21(28)24(3)4/h6-10,13,22-23,25H,5H2,1-4H3/t13-/m1/s1 | |
| Chemical Name | 2-hydroxy-N,N-dimethyl-3-[[2-[[(1R)-1-(5-methylfuran-2-yl)propyl]amino]-3,4-dioxocyclobuten-1-yl]amino]benzamide | |
| Synonyms |
|
|
| HS Tariff Code | 2934.99.9001 | |
| Storage |
Powder-20°C 3 years 4°C 2 years In solvent -80°C 6 months -20°C 1 month |
|
| Shipping Condition | Room temperature (This product is stable at ambient temperature for a few days during ordinary shipping and time spent in Customs) |
Biological Activity
| Targets | 125I-CXCL8-CXCR2 ( IC50 = 0.97 nM ); Cynomolgus CXCR2 ( Kd = 0.08 nM ); Mouse CXCR2 ( Kd = 0.2 nM ); Rat CXCR2 ( Kd = 0.2 nM ); 125I-CXCL8-CXCR1 ( IC50 = 43 nM ); Cynomolgus CXCR1 ( Kd = 41 nM ) | |
| ln Vitro |
|
|
| ln Vivo |
|
|
| Enzyme Assay | Navarixin, formerly known as MK-7123, SCH527123, or PS291822, is a novel, potent, and specific allosteric antagonist of CXCR1 and CXCR2 that exhibits antitumor activity. In preclinical models of colon cancer, it has the ability to sensitize cells to oxaliplatin. Its Kd values are 41 nM for cynomolgus CXCR1 and 0.20 nM, 0.20 nM, and 0.08 nM for cynomolgus monkey CXCR2, mouse, and rat, respectively. Navarixin exhibited reversible and saturable binding to CXCR1 and CXCR2. | |
| Cell Assay | The assay buffer (phenol red free-RPMI 1640 supplemented with 2% FBS) is used to resuspend recombinant cells at a density of 1×106/mL. The same assay buffer containing 5% FBS is used to resuscend human neutrophils at a density of 2 × 106/mL. High affinity is only exhibited by CXCL1 by CXCR2; however, CXCL8 exhibits high affinity for both CXCR1 and CXCR2. Filter is placed over the bottom wells of disposable microchemotaxis plates after 30 μL of chemoattractants diluted in assay buffer are poured into them. Navarixin (1–300 nM) is preincubated for 90 minutes in a CO2 incubator with cells. On each spot on the filter, cell aliquots (25 μL) are applied. After incubation, the filters are taken out (90 minutes for BaF/3 cells and 30 minutes for PMN in a CO2 incubator). A Microlite luminometer plate is used to observe the migrated cells in the bottom wells. Each well is then filled with 25 μL of ATPlite one-step. The luminescence intensity is measured with a luminometer following a 10-minute incubation period at room temperature. | |
| Animal Protocol |
Mice: The mice utilized are male BALB/c strains weighing 20–25 grams. Isotonic (0.9%) saline (50 μL) is injected intraperitoneally into control mice. When administered orally by gavage two hours prior to and four hours following each intranasal administration of lipopolysaccharide (LPS), napraxixin (0.1–10 mg/kg, p.o.) is suspended in 0.4% methylcellulose. 0.4% methylcellulose (10 mL/kg) is given to control animals. Four Navarixin or vehicle dosages are administered in total[1]. Rats: We utilize male 200 g Sprague-Dawley rats. A volume of 100 μL of isotonic saline is given to control animals. Orally administered two hours prior to the LPS challenge, navixin (0.1-3 mg/kg, p.o.) is suspended in a 0.4% methylcellulose vessel. 10 mL/kg of oral methylcellulose is given to control rats. In these experiments, either the vehicle or Navarixin is administered once[1]. |
|
| References |
[1]. Pharmacological characterization of Sch527123, a potent allosteric CXCR1/CXCR2 antagonist. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2007 Aug;322(2):477-85. [2]. A novel, orally active CXCR1/2 receptor antagonist, Sch527123, inhibits neutrophil recruitment, mucus production, and goblet cell hyperplasia in animal models of pulmonary inflammation. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2007 Aug;322(2):486-93. [3]. The CXCR2 antagonist, SCH-527123, shows antitumor activity and sensitizes cells to NSC 266046 in preclinical colon cancer models. Mol Cancer Ther. 2012 Jun;11(6):1353-64. |
|
| Additional Infomation | See also: Navarixin (annotation moved to). |
Solubility Data
| Solubility (In Vitro) |
|
|||
| Solubility (In Vivo) |
Solubility in Formulation 1: ≥ 2.5 mg/mL (6.29 mM) (saturation unknown) in 10% DMSO + 40% PEG300 + 5% Tween80 + 45% Saline (add these co-solvents sequentially from left to right, and one by one), clear solution. For example, if 1 mL of working solution is to be prepared, you can add 100 μL of 25.0 mg/mL clear DMSO stock solution to 400 μL PEG300 and mix evenly; then add 50 μL Tween-80 to the above solution and mix evenly; then add 450 μL normal saline to adjust the volume to 1 mL. Preparation of saline: Dissolve 0.9 g of sodium chloride in 100 mL ddH₂ O to obtain a clear solution. Solubility in Formulation 2: 2.5 mg/mL (6.29 mM) in 10% DMSO + 90% (20% SBE-β-CD in Saline) (add these co-solvents sequentially from left to right, and one by one), suspension solution; with ultrasonication. For example, if 1 mL of working solution is to be prepared, you can add 100 μL of 25.0 mg/mL clear DMSO stock solution to 900 μL of 20% SBE-β-CD physiological saline solution and mix evenly. Preparation of 20% SBE-β-CD in Saline (4°C,1 week): Dissolve 2 g SBE-β-CD in 10 mL saline to obtain a clear solution. Solubility in Formulation 3: ≥ 2.5 mg/mL (6.29 mM) (saturation unknown) in 10% DMSO + 90% Corn Oil (add these co-solvents sequentially from left to right, and one by one), clear solution. For example, if 1 mL of working solution is to be prepared, you can add 100 μL of 25.0 mg/mL clear DMSO stock solution to 900 μL of corn oil and mix evenly. Solubility in Formulation 4: ≥ 2.5 mg/mL (6.29 mM) (saturation unknown) in 5% DMSO + 40% PEG300 + 5% Tween80 + 50% Saline (add these co-solvents sequentially from left to right, and one by one), clear solution. Preparation of saline: Dissolve 0.9 g of sodium chloride in 100 mL ddH₂ O to obtain a clear solution. Solubility in Formulation 5: ≥ 2.5 mg/mL (6.29 mM) (saturation unknown) in 5% DMSO + 95% (20% SBE-β-CD in Saline) (add these co-solvents sequentially from left to right, and one by one), clear solution.Preparation of 20% SBE-β-CD in Saline (4°C,1 week): Dissolve 2 g SBE-β-CD in 10 mL saline to obtain a clear solution. (Please use freshly prepared in vivo formulations for optimal results.) |
| Preparing Stock Solutions | 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | |
| 1 mM | 2.5162 mL | 12.5808 mL | 25.1617 mL | |
| 5 mM | 0.5032 mL | 2.5162 mL | 5.0323 mL | |
| 10 mM | 0.2516 mL | 1.2581 mL | 2.5162 mL |