Physicochemical Properties
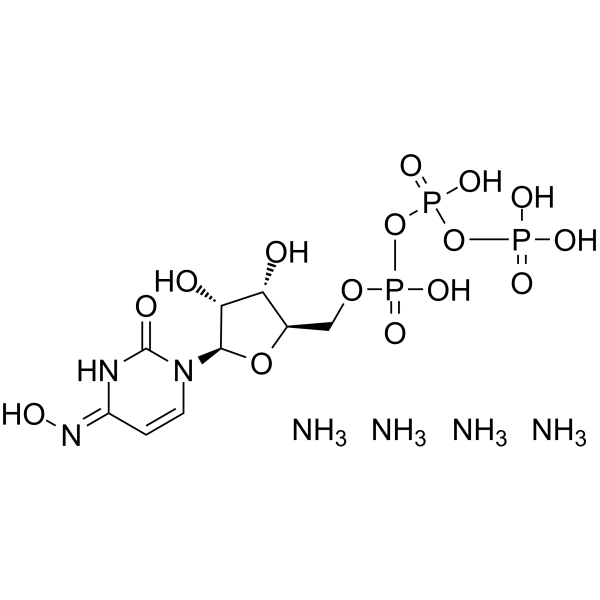
| Molecular Formula | C9H28N7O15P3 |
| Molecular Weight | 567.28 |
| Related CAS # | NHC-triphosphate;34973-27-8;NHC-triphosphate tetrasodium |
| Appearance | White to off-white solid powder |
| HS Tariff Code | 2934.99.9001 |
| Storage |
Powder-20°C 3 years 4°C 2 years In solvent -80°C 6 months -20°C 1 month Note: (1). This product requires protection from light (avoid light exposure) during transportation and storage.(2). Please store this product in a sealed and protected environment (e.g. under nitrogen), avoid exposure to moisture. |
| Shipping Condition | Room temperature (This product is stable at ambient temperature for a few days during ordinary shipping and time spent in Customs) |
Biological Activity
| ln Vitro | HCV replicon cells are treated with 10 μM 3H-labeled NHC in an intracellular metabolism test. After 1, 2, and 8 hours of incubation, intracellular nucleotide levels are measured. NHC is quickly transformed into the mono-, di-, and triphosphate forms; within 8 hours, NHC-TP can reach 71.12 pM[1]. In the absence of NHC-triphosphate tetraammonium (NHC-TP) (3-5 μM), full-length polymerization products result, and it may be a poor substitute substrate. Furthermore, in cell-free HCV NS5B polymerization events, an evident electrophoretic shift is seen, and the molecular weight of the polymerization product increases by 16 (one extra oxygen) upon insertion of NHC-TP rather than CTP[1]. NHC (10–50 μM; 4 h) or a McGuigan phosphoramidate prodrug of NHC are cultured in Huh-7 cells. LC-MS/MS is used to evaluate the intracellular levels of the primary chemicals and phosphorylated metabolites. While NHC-triphosphate tetraammonium continues to be the most prevalent metabolite, trace levels of NHC-monophosphate (MP) and NHC-diphosphate (DP) are also visible[2]. The metabolite NHC-triphosphate tetraammonium (NHC-TP) may act as a nonobligate chain terminator and directly target the viral polymerase. Through chain termination or mutagenesis, it inhibits early negative-strand RNA synthesis in a significant way. This can potentially obstruct the proper assembly of replicase complexes. |
| References |
[1]. Ribonucleoside analogue that blocks replication of bovine viral diarrhea and hepatitis C viruses in culture.Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2003 Jan;47(1):244-54. [2]. Characterization of β-d- N4-Hydroxycytidine as a Novel Inhibitor of Chikungunya Virus. |
Solubility Data
| Solubility (In Vitro) |
H2O :~200 mg/mL (~352.56 mM) DMSO :~170 mg/mL (~299.68 mM) |
| Solubility (In Vivo) |
Solubility in Formulation 1: ≥ 4.25 mg/mL (7.49 mM) (saturation unknown) in 10% DMSO + 40% PEG300 + 5% Tween80 + 45% Saline (add these co-solvents sequentially from left to right, and one by one), clear solution. For example, if 1 mL of working solution is to be prepared, you can add 100 μL of 42.5 mg/mL clear DMSO stock solution to 400 μL PEG300 and mix evenly; then add 50 μL Tween-80 to the above solution and mix evenly; then add 450 μL normal saline to adjust the volume to 1 mL. Preparation of saline: Dissolve 0.9 g of sodium chloride in 100 mL ddH₂ O to obtain a clear solution. Solubility in Formulation 2: ≥ 4.25 mg/mL (7.49 mM) (saturation unknown) in 10% DMSO + 90% Corn Oil (add these co-solvents sequentially from left to right, and one by one), clear solution. For example, if 1 mL of working solution is to be prepared, you can add 100 μL of 42.5 mg/mL clear DMSO stock solution to 900 μL of corn oil and mix evenly. Solubility in Formulation 3: 100 mg/mL (176.28 mM) in PBS (add these co-solvents sequentially from left to right, and one by one), clear solution; with ultrasonication. (Please use freshly prepared in vivo formulations for optimal results.) |
| Preparing Stock Solutions | 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | |
| 1 mM | 1.7628 mL | 8.8140 mL | 17.6280 mL | |
| 5 mM | 0.3526 mL | 1.7628 mL | 3.5256 mL | |
| 10 mM | 0.1763 mL | 0.8814 mL | 1.7628 mL |