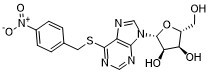
NBMPR( NBTI) is a nucleoside analog that competitively inhibits the equilibrative nucleoside transporter 1 (Kd = 0.1-1.0 nM, IC50s = 4.6 and 3.6 nM in rat and human, respectively). NBMPR is commonly used to selectively block nucleoside transport mediated by equilibrative nucleoside transporters 1 (ENT1) and 2 (ENT2), at concentrations of 0.10 μM and 0.10 mM, respectively. ABCG2 activity is eliminated by NBMPR at a concentration of 0.10 mM.
Physicochemical Properties
| Molecular Formula | C17H17N5O6S |
| Molecular Weight | 419.41178 |
| Exact Mass | 419.089 |
| Elemental Analysis | C, 48.68; H, 4.09; N, 16.70; O, 22.89; S, 7.64 |
| CAS # | 38048-32-7 |
| PubChem CID | 65407 |
| Appearance | Solid powder |
| Density | 1.8±0.1 g/cm3 |
| Boiling Point | 770.2±70.0 °C at 760 mmHg |
| Melting Point | 187-190 °C(lit.) |
| Flash Point | 419.6±35.7 °C |
| Vapour Pressure | 0.0±2.8 mmHg at 25°C |
| Index of Refraction | 1.808 |
| LogP | 1.2 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 3 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 10 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 5 |
| Heavy Atom Count | 29 |
| Complexity | 577 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 4 |
| SMILES | OC[C@@H]1[C@H]([C@H]([C@H](N2C=NC3=C2N=CN=C3SCC4=CC=C([N+]([O-])=O)C=C4)O1)O)O |
| InChi Key | DYCJFJRCWPVDHY-LSCFUAHRSA-N |
| InChi Code | InChI=1S/C17H17N5O6S/c23-5-11-13(24)14(25)17(28-11)21-8-20-12-15(21)18-7-19-16(12)29-6-9-1-3-10(4-2-9)22(26)27/h1-4,7-8,11,13-14,17,23-25H,5-6H2/t11-,13-,14-,17-/m1/s1 |
| Chemical Name | (2R,3S,4R,5R)-2-(hydroxymethyl)-5-[6-[(4-nitrophenyl)methylsulfanyl]purin-9-yl]oxolane-3,4-diol |
| Synonyms | NSC-296962; NSC 296962; NSC296962; NBMPR; NBTI; S-4-nitrophenylmethyl-6-thioinosine |
| HS Tariff Code | 2934.99.9001 |
| Storage |
Powder-20°C 3 years 4°C 2 years In solvent -80°C 6 months -20°C 1 month Note: Please store this product in a sealed and protected environment (e.g. under nitrogen), avoid exposure to moisture. |
| Shipping Condition | Room temperature (This product is stable at ambient temperature for a few days during ordinary shipping and time spent in Customs) |
Biological Activity
| Targets | ENT1 transporter |
| ln Vitro | Rats were sleep-deprived for 3 or 6 h using gentle handling. After 6 h one group was allowed to sleep for 2 h. NBMPR binding was determined from BF and cortex by incubating tissue extracts with [3H] NBMPR. The in situ hybridization was carried out on 20 microm cryosections using [35S]dATP-labelled oligonucleotide probe for ENT1 mRNA. The NBMPR binding was significantly decreased in the BF, but not in the cortex, after 6 h sleep deprivation when compared with the time-matched controls, suggesting a decline in adenosine transport. The expression of ENT1 mRNA did not change during prolonged wakefulness or recovery sleep in either cortex or the BF, although circadian variations were measured in both areas. We conclude that the regional decrease in adenosine transport could contribute to the gradual accumulation of extracellular adenosine in the basal forebrain during prolonged wakefulness.[1] |
| ln Vivo | Nucleoside transport inhibitors that cross the blood-brain barrier may be able to potentiate the neuroprotective effects of adenosine. We tested whether nitrobenzylthioinosine (NBMPR) crosses the blood-brain barrier in three types of experiments. First, intravenous injection of [3H]NBMPR and [14C]sucrose was performed. Brain volume of distribution and brain delivery were greater for [3H]NBMPR than for [14C]sucrose. Second, rats were injected intraperitoneally with NBMPR 5'-monophosphate (NBMPR-P), a prodrug form of NBMPR, or vehicle. Perchloric acid extracts of brains from rats treated with NBMPR-P inhibited [3H]NBMPR binding in competition binding assays nearly 3-fold more than extracts from brains of vehicle-treated animals. Third, cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) extracted from rats treated with NBMPR-P (10 mg/kg i.p.) contained 24.1 +/- 4.4 nM NBMPR while levels were undetectable in CSF from vehicle-treated rats. From these data, we conclude that NBMPR crosses the blood-brain barrier.[2] |
| References |
[1]. Nitrobenzylthioinosine (NBMPR) binding and nucleoside transporter ENT1 mRNA expression after prolonged wakefulness and recovery sleep in the cortex and basal forebrain of rat. J Sleep Res. 2003 Dec;12(4):299-304. [2]. Ability of nitrobenzylthioinosine to cross the blood-brain barrier in rats. Neurosci Lett. 1996 Nov 29;219(3):191-4. [3]. [3H]nitrobenzylthioinosine is a photoaffinity probe for adenosine uptake sites in brain. Eur J Pharmacol. 1982 Dec 3;85(3-4):359-60. |
| Additional Infomation | NBMPR is a purine nucleoside. |
Solubility Data
| Solubility (In Vitro) | DMSO: 50~84 mg/mL (119.2~200.3 mM) |
| Solubility (In Vivo) |
Solubility in Formulation 1: ≥ 2.08 mg/mL (4.96 mM) (saturation unknown) in 10% DMSO + 40% PEG300 + 5% Tween80 + 45% Saline (add these co-solvents sequentially from left to right, and one by one), clear solution. For example, if 1 mL of working solution is to be prepared, you can add 100 μL of 20.8 mg/mL clear DMSO stock solution to 400 μL PEG300 and mix evenly; then add 50 μL Tween-80 to the above solution and mix evenly; then add 450 μL normal saline to adjust the volume to 1 mL. Preparation of saline: Dissolve 0.9 g of sodium chloride in 100 mL ddH₂ O to obtain a clear solution. Solubility in Formulation 2: ≥ 2.08 mg/mL (4.96 mM) (saturation unknown) in 10% DMSO + 90% (20% SBE-β-CD in Saline) (add these co-solvents sequentially from left to right, and one by one), clear solution. For example, if 1 mL of working solution is to be prepared, you can add 100 μL of 20.8 mg/mL clear DMSO stock solution to 900 μL of 20% SBE-β-CD physiological saline solution and mix evenly. Preparation of 20% SBE-β-CD in Saline (4°C,1 week): Dissolve 2 g SBE-β-CD in 10 mL saline to obtain a clear solution. Solubility in Formulation 3: ≥ 2.08 mg/mL (4.96 mM) (saturation unknown) in 10% DMSO + 90% Corn Oil (add these co-solvents sequentially from left to right, and one by one), clear solution. For example, if 1 mL of working solution is to be prepared, you can add 100 μL of 20.8 mg/mL clear DMSO stock solution to 900 μL of corn oil and mix evenly. (Please use freshly prepared in vivo formulations for optimal results.) |
| Preparing Stock Solutions | 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | |
| 1 mM | 2.3843 mL | 11.9215 mL | 23.8430 mL | |
| 5 mM | 0.4769 mL | 2.3843 mL | 4.7686 mL | |
| 10 mM | 0.2384 mL | 1.1922 mL | 2.3843 mL |