Physicochemical Properties
| Molecular Formula | C11H15NO |
| Molecular Weight | 177.24 |
| Exact Mass | 177.115 |
| CAS # | 3376-24-7 |
| PubChem CID | 638877 |
| Appearance | White to off-white solid powder |
| Density | 1.0±0.1 g/cm3 |
| Boiling Point | 283.3±23.0 °C at 760 mmHg |
| Melting Point | 71-75ºC |
| Flash Point | 118.5±15.4 °C |
| Vapour Pressure | 0.0±0.6 mmHg at 25°C |
| Index of Refraction | 1.552 |
| LogP | 1.25 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 0 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 1 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 2 |
| Heavy Atom Count | 13 |
| Complexity | 185 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
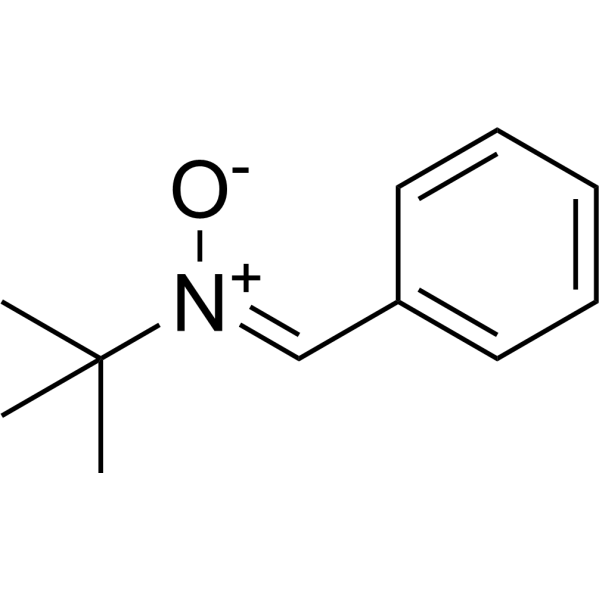
| SMILES | CC(C)(C)/[N+](=C/C1=CC=CC=C1)/[O-] |
| InChi Key | IYSYLWYGCWTJSG-XFXZXTDPSA-N |
| InChi Code | InChI=1S/C11H15NO/c1-11(2,3)12(13)9-10-7-5-4-6-8-10/h4-9H,1-3H3/b12-9- |
| Chemical Name | N-tert-butyl-1-phenylmethanimine oxide |
| HS Tariff Code | 2934.99.9001 |
| Storage |
Powder-20°C 3 years 4°C 2 years In solvent -80°C 6 months -20°C 1 month |
| Shipping Condition | Room temperature (This product is stable at ambient temperature for a few days during ordinary shipping and time spent in Customs) |
Biological Activity
| Targets | COX-2 Reactive oxygen species (ROS) |
| ln Vitro | The formation of intracellular ROS caused by 2,2'-azobis (2-amidinopropane) dihydrochloride (AAPH) is significantly reduced when treated with N-tert-Butyl-α-phenylnitrone (PBN) at concentrations ranging from 25 to 100 µM. Additionally, AAPH-induced cytotoxicity, matrix disintegration, and apoptosis are attenuated by N-tert-Butyl-α-phenylnitrone. N-tert-Butyl-α-phenylnitrone inhibits the activation of the ERK/MAPK pathway caused by AAPH. There is potential for studying intervertebral disc degeneration (IDD) with N-tert-Butyl-α-phenylnitrone[1]. |
| ln Vivo | Treatment with N-tert-Butyl-α-phenylnitrone (PBN; 100 mg/kg; intraperitoneal injection; twice daily; C57Bl/6 mice) eliminates the lipid peroxidation, nitrotyrosine residue levels, and GSH depletion caused by LPS and reduces the occurrence of external malformations[2]. |
| Animal Protocol |
Animal/Disease Models: C57Bl/6 mice induced by lipopolysaccharide (LPS)[2] Doses: 100 mg/kg Route of Administration: intraperitoneal (ip) injection; twice a day (on gestational day 8) Experimental Results: Abolished LPS -induced lipid peroxidation, nitrotyrosine residues, and GSH depletion. |
| References |
[1]. PBN Protects NP Cells From AAPH-induced Degenerative Changes by Inhibiting the ERK1/2 Pathway. Connect Tissue Res. 2020 Mar 30;1-10. [2]. Reactive Oxygen Species Contribute to Lipopolysaccharide-Induced Teratogenesis in Mice. Toxicol Sci. 2008 May;103(1):149-57. [3]. Inhibition of NF-kappaB, iNOS mRNA, COX2 mRNA, and COX Catalytic Activity by phenyl-N-tert-butylnitrone (PBN). Biochim Biophys Acta. 1998 Nov 19;1448(1):77-84. [4]. R A Floyd. Antioxidants, Oxidative Stress, and Degenerative Neurological Disorders. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1999 Dec;222(3):236-45. |
Solubility Data
| Solubility (In Vitro) | DMSO: 100 mg/mL (564.21 mM) |
| Solubility (In Vivo) |
Solubility in Formulation 1: ≥ 2.5 mg/mL (14.11 mM) (saturation unknown) in 10% DMSO + 40% PEG300 + 5% Tween80 + 45% Saline (add these co-solvents sequentially from left to right, and one by one), clear solution. For example, if 1 mL of working solution is to be prepared, you can add 100 μL of 25.0 mg/mL clear DMSO stock solution to 400 μL PEG300 and mix evenly; then add 50 μL Tween-80 to the above solution and mix evenly; then add 450 μL normal saline to adjust the volume to 1 mL. Preparation of saline: Dissolve 0.9 g of sodium chloride in 100 mL ddH₂ O to obtain a clear solution. Solubility in Formulation 2: ≥ 2.5 mg/mL (14.11 mM) (saturation unknown) in 10% DMSO + 90% (20% SBE-β-CD in Saline) (add these co-solvents sequentially from left to right, and one by one), clear solution. For example, if 1 mL of working solution is to be prepared, you can add 100 μL of 25.0 mg/mL clear DMSO stock solution to 900 μL of 20% SBE-β-CD physiological saline solution and mix evenly. Preparation of 20% SBE-β-CD in Saline (4°C,1 week): Dissolve 2 g SBE-β-CD in 10 mL saline to obtain a clear solution. Solubility in Formulation 3: ≥ 2.5 mg/mL (14.11 mM) (saturation unknown) in 10% DMSO + 90% Corn Oil (add these co-solvents sequentially from left to right, and one by one), clear solution. For example, if 1 mL of working solution is to be prepared, you can add 100 μL of 25.0 mg/mL clear DMSO stock solution to 900 μL of corn oil and mix evenly. (Please use freshly prepared in vivo formulations for optimal results.) |
| Preparing Stock Solutions | 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | |
| 1 mM | 5.6421 mL | 28.2103 mL | 56.4207 mL | |
| 5 mM | 1.1284 mL | 5.6421 mL | 11.2841 mL | |
| 10 mM | 0.5642 mL | 2.8210 mL | 5.6421 mL |