Physicochemical Properties
| Molecular Formula | C7H11N3O |
| Molecular Weight | 153.18174 |
| Exact Mass | 153.09 |
| CAS # | 673-49-4 |
| PubChem CID | 69602 |
| Appearance | White to off-white solid powder |
| Density | 1.153g/cm3 |
| Boiling Point | 501.7ºC at 760 mmHg |
| Melting Point | 147-149ºC(lit.) |
| Flash Point | 257.2ºC |
| Index of Refraction | 1.533 |
| LogP | 0.479 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 2 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 2 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 3 |
| Heavy Atom Count | 11 |
| Complexity | 138 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
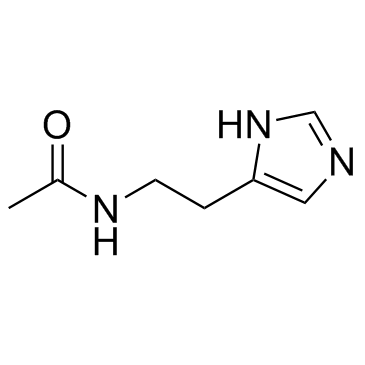
| SMILES | CC(NCCC1=CN=CN1)=O |
| InChi Key | XJWPISBUKWZALE-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
| InChi Code | InChI=1S/C7H11N3O/c1-6(11)9-3-2-7-4-8-5-10-7/h4-5H,2-3H2,1H3,(H,8,10)(H,9,11) |
| Chemical Name | N-[2-(1H-imidazol-5-yl)ethyl]acetamide |
| Synonyms | N-Acetylhistamine; N-Omega-acetylhistamine |
| HS Tariff Code | 2934.99.9001 |
| Storage |
Powder-20°C 3 years 4°C 2 years In solvent -80°C 6 months -20°C 1 month |
| Shipping Condition | Room temperature (This product is stable at ambient temperature for a few days during ordinary shipping and time spent in Customs) |
Biological Activity
| Targets | Human Endogenous Metabolite |
| ln Vitro | N-acetylhistamine is a crucial indicator for anaphylactoid reactions[1]. |
| References |
[1]. Metabolomics analysis of anaphylactoid reaction reveals its mechanism in a rat model. Asian Pac J Allergy Immunol. 2017 Dec;35(4):224-232. |
| Additional Infomation |
N-acetylhistamine is a member of the class of acetamides that is acetamide comprising histamine having an acetyl group attached to the side-chain amino function. It has a role as a human metabolite. It is a member of acetamides and a member of imidazoles. It is functionally related to a histamine. N-Acetylhistamine has been reported in Drosophila melanogaster, Euglena gracilis, and other organisms with data available. |
Solubility Data
| Solubility (In Vitro) | DMSO: ≥ 100 mg/mL (~652.8 mM) |
| Solubility (In Vivo) |
Solubility in Formulation 1: ≥ 2.5 mg/mL (16.32 mM) (saturation unknown) in 10% DMSO + 40% PEG300 + 5% Tween80 + 45% Saline (add these co-solvents sequentially from left to right, and one by one), clear solution. For example, if 1 mL of working solution is to be prepared, you can add 100 μL of 25.0 mg/mL clear DMSO stock solution to 400 μL PEG300 and mix evenly; then add 50 μL Tween-80 to the above solution and mix evenly; then add 450 μL normal saline to adjust the volume to 1 mL. Preparation of saline: Dissolve 0.9 g of sodium chloride in 100 mL ddH₂ O to obtain a clear solution. Solubility in Formulation 2: ≥ 2.5 mg/mL (16.32 mM) (saturation unknown) in 10% DMSO + 90% (20% SBE-β-CD in Saline) (add these co-solvents sequentially from left to right, and one by one), clear solution. For example, if 1 mL of working solution is to be prepared, you can add 100 μL of 25.0 mg/mL clear DMSO stock solution to 900 μL of 20% SBE-β-CD physiological saline solution and mix evenly. Preparation of 20% SBE-β-CD in Saline (4°C,1 week): Dissolve 2 g SBE-β-CD in 10 mL saline to obtain a clear solution. Solubility in Formulation 3: ≥ 2.5 mg/mL (16.32 mM) (saturation unknown) in 10% DMSO + 90% Corn Oil (add these co-solvents sequentially from left to right, and one by one), clear solution. For example, if 1 mL of working solution is to be prepared, you can add 100 μL of 25.0 mg/mL clear DMSO stock solution to 900 μL of corn oil and mix evenly. (Please use freshly prepared in vivo formulations for optimal results.) |
| Preparing Stock Solutions | 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | |
| 1 mM | 6.5283 mL | 32.6413 mL | 65.2827 mL | |
| 5 mM | 1.3057 mL | 6.5283 mL | 13.0565 mL | |
| 10 mM | 0.6528 mL | 3.2641 mL | 6.5283 mL |