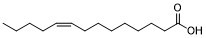
Myristoleic acid (Oleomyristic Acid) is a naturally occurring cytotoxic agent from Serenoa repens with anticancer activity. It induces apoptosis and necrosis in human prostatic LNCaP cells. Myristoleic acid is capable of blocking the formation of large multinucleated osteoclasts and bone resorption likely through suppressing activation of Src and Pyk2.
Physicochemical Properties
| Molecular Formula | C14H26O2 |
| Molecular Weight | 226.36 |
| Exact Mass | 226.193 |
| CAS # | 544-64-9 |
| PubChem CID | 5281119 |
| Appearance | Colorless to light yellow liquid(Density:0.9 g/cm3) |
| Density | 0.9±0.1 g/cm3 |
| Boiling Point | 338.9±0.0 °C at 760 mmHg |
| Melting Point | -4.5--4ºC(lit.) |
| Flash Point | 206.5±14.4 °C |
| Vapour Pressure | 0.0±1.5 mmHg at 25°C |
| Index of Refraction | 1.465 |
| LogP | 5.57 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 1 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 2 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 11 |
| Heavy Atom Count | 16 |
| Complexity | 185 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| SMILES | CCCC/C=C\CCCCCCCC(=O)O |
| InChi Key | YWWVWXASSLXJHU-WAYWQWQTSA-N |
| InChi Code | InChI=1S/C14H26O2/c1-2-3-4-5-6-7-8-9-10-11-12-13-14(15)16/h5-6H,2-4,7-13H2,1H3,(H,15,16)/b6-5- |
| Chemical Name | (Z)-tetradec-9-enoic acid |
| Synonyms | cis-9-Tetradecenoate; Myristoleic Acid; Oleomyristic Acid |
| HS Tariff Code | 2934.99.9001 |
| Storage |
Powder-20°C 3 years 4°C 2 years In solvent -80°C 6 months -20°C 1 month Note: Please store this product in a sealed and protected environment, avoid exposure to moisture. |
| Shipping Condition | Room temperature (This product is stable at ambient temperature for a few days during ordinary shipping and time spent in Customs) |
Biological Activity
| ln Vitro | Myristoleic acid causes apoptosis in LNCaP cells (100 μg/mL, 89.5%) as well as necrosis (100 μg/mL, 81.8%)[1]. Particularly at later stages of differentiation, myristoleic acid inhibited the formation of osteoclasts induced by RANKL in vitro [2]. |
| ln Vivo | Mice treated with myristoleic acid (2 mg/kg, IP every 24 h) for 4 days are able to avoid osteoclast development and bone loss caused by RANKL[2]. |
| Cell Assay |
Cell Proliferation Assay[1] Cell Types: Human prostatic carcinoma LNCaP cells. Tested Concentrations: 0, 50, 100, 150, 200, 250 μg/mL. Incubation Duration: 24 h. Experimental Results: When LNCaP cells were treated with 130 μg/mL extract or 100 μg/mL myristoleic acid for 24 hr, the proportion of apoptotic cells was 16.5 and 8.8%, and that of necrotic one was 46.8 and 81.8%, respectively. |
| Animal Protocol |
Animal/Disease Models: C57BL/6 mice at 5 weeks[2]. Doses: 0.2, 2 mg/kg Route of Administration: IP every 24 h for 4 days. Experimental Results: Co-administration of myristoleic acid suppressed generation of TRAP-positive osteoclasts induced by sRANKL and attenuated the increases in osteoclastic indices of Oc.S/BS, N.Oc/B . Pm and ES/BS in a dose-dependent manner. |
| References |
[1]. Xiaoyan Gao, et al. Ozone initiated heterogeneous oxidation of unsaturated carboxylic acids by ATR-FTIR spectroscopy. Spectrochim Acta A Mol Biomol Spectrosc. 2019 May 5;214:177-183. [2]. Jun-Oh Kwon, et al. Myristoleic acid inhibits osteoclast formation and bone resorption by suppressing the RANKL activation of Src and Pyk2. Eur J Pharmacol. 2015 Dec 5;768:189-98. |
| Additional Infomation |
Myristoleic acid is a tetradecenoic acid in which the double bond is at the 9-10 position and has Z configuration. Myristoleic acid has been isolated from Serenoa repens and has cytotoxic and apoptosis-inducing effects. It has a role as an apoptosis inducer, a plant metabolite and an EC 3.1.1.1 (carboxylesterase) inhibitor. It is a tetradecenoic acid and a long-chain fatty acid. It is a conjugate acid of a myristoleate. Myristoleic acid has been reported in Hoya crassipes, Hoya pseudolanceolata, and other organisms with data available. Myristoleic acid is a metabolite found in or produced by Saccharomyces cerevisiae. |
Solubility Data
| Solubility (In Vitro) | DMSO : ≥ 100 mg/mL (~441.77 mM) |
| Solubility (In Vivo) |
Note: Listed below are some common formulations that may be used to formulate products with low water solubility (e.g. < 1 mg/mL), you may test these formulations using a minute amount of products to avoid loss of samples. Injection Formulations (e.g. IP/IV/IM/SC) Injection Formulation 1: DMSO : Tween 80: Saline = 10 : 5 : 85 (i.e. 100 μL DMSO stock solution → 50 μL Tween 80 → 850 μL Saline) *Preparation of saline: Dissolve 0.9 g of sodium chloride in 100 mL ddH ₂ O to obtain a clear solution. Injection Formulation 2: DMSO : PEG300 :Tween 80 : Saline = 10 : 40 : 5 : 45 (i.e. 100 μL DMSO → 400 μLPEG300 → 50 μL Tween 80 → 450 μL Saline) Injection Formulation 3: DMSO : Corn oil = 10 : 90 (i.e. 100 μL DMSO → 900 μL Corn oil) Example: Take the Injection Formulation 3 (DMSO : Corn oil = 10 : 90) as an example, if 1 mL of 2.5 mg/mL working solution is to be prepared, you can take 100 μL 25 mg/mL DMSO stock solution and add to 900 μL corn oil, mix well to obtain a clear or suspension solution (2.5 mg/mL, ready for use in animals). Injection Formulation 4: DMSO : 20% SBE-β-CD in saline = 10 : 90 [i.e. 100 μL DMSO → 900 μL (20% SBE-β-CD in saline)] *Preparation of 20% SBE-β-CD in Saline (4°C,1 week): Dissolve 2 g SBE-β-CD in 10 mL saline to obtain a clear solution. Injection Formulation 5: 2-Hydroxypropyl-β-cyclodextrin : Saline = 50 : 50 (i.e. 500 μL 2-Hydroxypropyl-β-cyclodextrin → 500 μL Saline) Injection Formulation 6: DMSO : PEG300 : castor oil : Saline = 5 : 10 : 20 : 65 (i.e. 50 μL DMSO → 100 μLPEG300 → 200 μL castor oil → 650 μL Saline) Injection Formulation 7: Ethanol : Cremophor : Saline = 10: 10 : 80 (i.e. 100 μL Ethanol → 100 μL Cremophor → 800 μL Saline) Injection Formulation 8: Dissolve in Cremophor/Ethanol (50 : 50), then diluted by Saline Injection Formulation 9: EtOH : Corn oil = 10 : 90 (i.e. 100 μL EtOH → 900 μL Corn oil) Injection Formulation 10: EtOH : PEG300:Tween 80 : Saline = 10 : 40 : 5 : 45 (i.e. 100 μL EtOH → 400 μLPEG300 → 50 μL Tween 80 → 450 μL Saline) Oral Formulations Oral Formulation 1: Suspend in 0.5% CMC Na (carboxymethylcellulose sodium) Oral Formulation 2: Suspend in 0.5% Carboxymethyl cellulose Example: Take the Oral Formulation 1 (Suspend in 0.5% CMC Na) as an example, if 100 mL of 2.5 mg/mL working solution is to be prepared, you can first prepare 0.5% CMC Na solution by measuring 0.5 g CMC Na and dissolve it in 100 mL ddH2O to obtain a clear solution; then add 250 mg of the product to 100 mL 0.5% CMC Na solution, to make the suspension solution (2.5 mg/mL, ready for use in animals). Oral Formulation 3: Dissolved in PEG400 Oral Formulation 4: Suspend in 0.2% Carboxymethyl cellulose Oral Formulation 5: Dissolve in 0.25% Tween 80 and 0.5% Carboxymethyl cellulose Oral Formulation 6: Mixing with food powders Note: Please be aware that the above formulations are for reference only. InvivoChem strongly recommends customers to read literature methods/protocols carefully before determining which formulation you should use for in vivo studies, as different compounds have different solubility properties and have to be formulated differently. (Please use freshly prepared in vivo formulations for optimal results.) |
| Preparing Stock Solutions | 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | |
| 1 mM | 4.4177 mL | 22.0887 mL | 44.1774 mL | |
| 5 mM | 0.8835 mL | 4.4177 mL | 8.8355 mL | |
| 10 mM | 0.4418 mL | 2.2089 mL | 4.4177 mL |