Maytansinoid DM4, a naturally occuring maytansine analogue, is a highly potent/cytotoxic antitubulin agent with anticancer properties. Maytansinoids have been shown to be able to disrupt microtubule function. Maytansinoid DM4 can be used for the preparation of antibody drug conjugates such as Anetumab ravtansine (BAY 94-9343) and Indatuximab ravtansine (BT062).
Physicochemical Properties
| Molecular Formula | C38H54N3O10SCL |
| Molecular Weight | 780.371 |
| Exact Mass | 779.322 |
| Elemental Analysis | C, 58.49; H, 6.98; Cl, 4.54; N, 5.38; O, 20.50; S, 4.11 |
| CAS # | 796073-69-3 |
| Related CAS # | DM4-d6 |
| PubChem CID | 11686439 |
| Appearance | White to light yellow solid powder |
| Density | 1.29±0.1 g/cm3 |
| Boiling Point | 943.2±65.0 °C |
| Melting Point | 185-187 °C (decomp) |
| LogP | 5.396 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 3 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 11 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 9 |
| Heavy Atom Count | 53 |
| Complexity | 1430 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 8 |
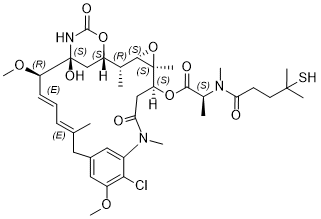
| SMILES | C[C@]12[C@@H](OC(=O)[C@H](C)N(C)C(=O)CCC(S)(C)C)CC(=O)N(C)C3C(=C(C=C(C=3)CC(C)=CC=C[C@@H](OC)[C@@]3(NC(O[C@@H](C3)[C@@H](C)[C@@H]1O2)=O)O)OC)Cl |c:32,34,&1:1,2,6,35,38,42,44,46| |
| InChi Key | JFCFGYGEYRIEBE-YVLHJLIDSA-N |
| InChi Code | InChI=1S/C38H54ClN3O10S/c1-21-12-11-13-28(49-10)38(47)20-27(50-35(46)40-38)22(2)33-37(6,52-33)29(51-34(45)23(3)41(7)30(43)14-15-36(4,5)53)19-31(44)42(8)25-17-24(16-21)18-26(48-9)32(25)39/h11-13,17-18,22-23,27-29,33,47,53H,14-16,19-20H2,1-10H3,(H,40,46)/b13-11+,21-12+/t22-,23+,27+,28-,29+,33+,37+,38+/m1/s1 |
| Chemical Name | (14S,16S,32S,33S,2R,4S,10E,12E,14R)-86-chloro-14-hydroxy-85,14-dimethoxy-33,2,7,10-tetramethyl-12,6-dioxo-7-aza-1(6,4)-oxazinana-3(2,3)-oxirana-8(1,3)-benzenacyclotetradecaphane-10,12-dien-4-yl N-(4-mercapto-4-methylpentanoyl)-N-methyl-L-alaninate |
| Synonyms | Maytansinoid DM4; DM4, Ravtansine, Soravtansine |
| HS Tariff Code | 2934.99.9001 |
| Storage |
Powder-20°C 3 years 4°C 2 years In solvent -80°C 6 months -20°C 1 month |
| Shipping Condition | Room temperature (This product is stable at ambient temperature for a few days during ordinary shipping and time spent in Customs) |
Biological Activity
| ln Vitro | A novel thiol-containing powerful maytansinoid is DM4, a structural analogue of maytansine. A cytotoxic maytansinoid medication is DM4. It is synthesized to form disulfide bonds between maytansinoids and antibodies. Maytansinoids potently suppress microtubule dynamics, causing a mitotic block and consequent apoptotic cell death. They do this by inhibiting tubulin polymerization and microtubule assembly and by enhancing microtubule destabilization[1]. |
| References |
[1]. P-gp activity is a critical resistance factor against AVE9633 and DM4 cytotoxicity in leukaemia cell lines, but not a major mechanism of chemoresistance in cells from acute myeloid leukaemia patients. BMC Cancer. 2009 Jun 23;9:199. [2]. Schönfeld K, Zuber C, Pinkas J, Häder T, Bernöster K, Uherek C. Indatuximab ravtansine (BT062) combination treatment in multiple myeloma: pre-clinical studies. J Hematol Oncol. 2017 Jan 11;10(1):13. doi: 10.1186/s13045-016-0380-0. PubMed PMID: 28077160; PubMed Central PMCID: PMC5225632. |
| Additional Infomation |
Ravtansine is an organic molecular entity. Ravtansine is a tubulin-binding maytansinoid. Ravtansine binds to tubulin at the maytansine-binding site, which disrupts microtubule assembly/disassembly dynamics and inhibits mitosis. An ansa macrolide isolated from the MAYTENUS genus of East African shrubs. See also: Maytansine (annotation moved to). |
Solubility Data
| Solubility (In Vitro) | DMSO : ~100 mg/mL (~128.14 mM ) |
| Solubility (In Vivo) |
Solubility in Formulation 1: ≥ 2.5 mg/mL (3.20 mM) (saturation unknown) in 10% DMSO + 40% PEG300 + 5% Tween80 + 45% Saline (add these co-solvents sequentially from left to right, and one by one), clear solution. For example, if 1 mL of working solution is to be prepared, you can add 100 μL of 25.0 mg/mL clear DMSO stock solution to 400 μL PEG300 and mix evenly; then add 50 μL Tween-80 to the above solution and mix evenly; then add 450 μL normal saline to adjust the volume to 1 mL. Preparation of saline: Dissolve 0.9 g of sodium chloride in 100 mL ddH₂ O to obtain a clear solution. Solubility in Formulation 2: 2.5 mg/mL (3.20 mM) in 10% DMSO + 90% (20% SBE-β-CD in Saline) (add these co-solvents sequentially from left to right, and one by one), suspension solution; with ultrasonication. For example, if 1 mL of working solution is to be prepared, you can add 100 μL of 25.0 mg/mL clear DMSO stock solution to 900 μL of 20% SBE-β-CD physiological saline solution and mix evenly. Preparation of 20% SBE-β-CD in Saline (4°C,1 week): Dissolve 2 g SBE-β-CD in 10 mL saline to obtain a clear solution. Solubility in Formulation 3: ≥ 2.5 mg/mL (3.20 mM) (saturation unknown) in 10% DMSO + 90% Corn Oil (add these co-solvents sequentially from left to right, and one by one), clear solution. For example, if 1 mL of working solution is to be prepared, you can add 100 μL of 25.0 mg/mL clear DMSO stock solution to 900 μL of corn oil and mix evenly.. Solubility in Formulation 4: 10% DMSO+ 40% PEG300+ 5% Tween-80+ 45% saline: ≥ 2.5 mg/mL (3.20 mM) (Please use freshly prepared in vivo formulations for optimal results.) |
| Preparing Stock Solutions | 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | |
| 1 mM | 1.2814 mL | 6.4072 mL | 12.8144 mL | |
| 5 mM | 0.2563 mL | 1.2814 mL | 2.5629 mL | |
| 10 mM | 0.1281 mL | 0.6407 mL | 1.2814 mL |