Physicochemical Properties
| Molecular Formula | C22H32O4 |
| Exact Mass | 360.23 |
| CAS # | 1268720-28-0 |
| Related CAS # | Maresin 1-d5 |
| PubChem CID | 60201795 |
| Appearance | Colorless to light yellow liquid |
| Density | 1.0±0.1 g/cm3 |
| Boiling Point | 559.4±50.0 °C at 760 mmHg |
| Flash Point | 306.2±26.6 °C |
| Vapour Pressure | 0.0±3.4 mmHg at 25°C |
| Index of Refraction | 1.546 |
| LogP | 3.81 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 3 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 4 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 14 |
| Heavy Atom Count | 26 |
| Complexity | 524 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 2 |
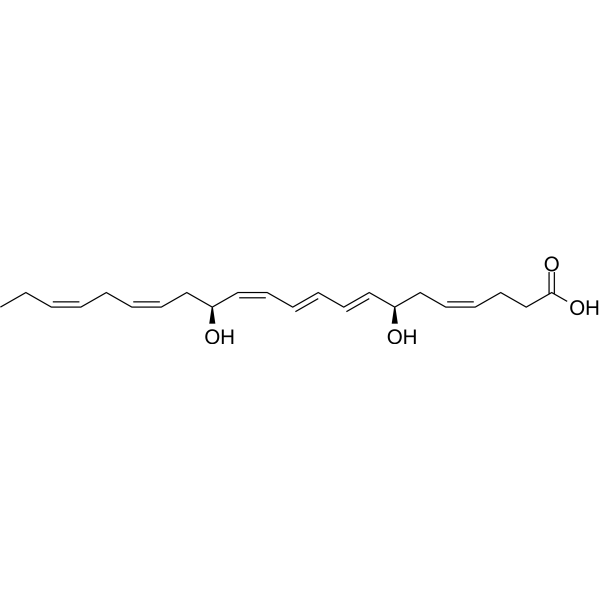
| SMILES | CC/C=C\C/C=C\C[C@@H](/C=C\C=C\C=C\[C@@H](C/C=C\CCC(=O)O)O)O |
| InChi Key | HLHYXXBCQOUTGK-FHCQLJOMSA-N |
| InChi Code | InChI=1S/C22H32O4/c1-2-3-4-5-6-10-15-20(23)16-11-7-8-12-17-21(24)18-13-9-14-19-22(25)26/h3-4,6-13,16-17,20-21,23-24H,2,5,14-15,18-19H2,1H3,(H,25,26)/b4-3-,8-7+,10-6-,13-9-,16-11-,17-12+/t20-,21-/m0/s1 |
| Chemical Name | (4Z,7R,8E,10E,12Z,14S,16Z,19Z)-7,14-dihydroxydocosa-4,8,10,12,16,19-hexaenoic acid |
| HS Tariff Code | 2934.99.9001 |
| Storage |
Powder-20°C 3 years 4°C 2 years In solvent -80°C 6 months -20°C 1 month |
| Shipping Condition | Room temperature (This product is stable at ambient temperature for a few days during ordinary shipping and time spent in Customs) |
Biological Activity
| ln Vitro | Maresin 1 (MaR1, 300 nM) decreases neutrophil migration and reactive oxygen species generation in addition to lowering IL-1β, TNF-α, IL-6, and INF-γ production [3]. |
| ln Vivo | Maresin 1 (MaR1) decreases inflammation and chemotherapy-induced neuropathic pain in rats[2], inhibits TRPV1 currents in neurons in a dose-dependent manner, and blocks capsaicin (100 nM)-induced inward currents (IC50=0.49 nM). Mice are protected against acute DSS-induced colitis by maresin 1 (MaR1, 0.1, 0.3, and 1 μg/animal, ev). In an acute regimen of DSS-induced colitis, maresin 1 (0.3 and 1 μg/animal, ev) therapy dramatically reduced macroscopic damage[3]. |
| Cell Assay |
Cell Viability Assay[3] Cell Types: Neutrophils (2 ╳105 cells/well). Tested Concentrations: 300 nM. Incubation Duration: 30 min. Experimental Results: Adherent cells are stimulated for 24 h with LPS (1 mg/ml) in the presence or absence of MaR1 (300 nM) in a final volume of 250 ml/well[3]. |
| Animal Protocol |
Animal/Disease Models: Male CD1 mice (8-10 wk of age) (colitis was induced by DSS)[3]. Doses: 0.1, 0.3, and 1 μg/animal. Route of Administration: Intraocular route one time/day from day 0 to day 7. Experimental Results: MaR1 (0.3 and 1 mg/animal) Dramatically reduces MPO levels in mouse colon tissue. |
| References |
[1]. Maresin 1, a Specialized Proresolving Mediator, Stimulates Intracellular [Ca 2+ ] and Secretion in Conjunctival Goblet Cells. J Cell Physiol. 2020 Jun 8. [2]. Macrophage Proresolving Mediator Maresin 1 Stimulates Tissue Regeneration and Controls Pain. [3]. Maresin 1, a Proresolving Lipid Mediator Derived From omega-3 Polyunsaturated Fatty Acids, Exerts Protective Actions in Murine Models of Colitis. J Immunol. 2013 Oct 15;191(8):4288-98. |
| Additional Infomation |
(7R,14S)-dihydroxy-(4Z,8E,10E,12Z,16Z,19Z)-docosahexaenoic acid is a dihydroxydocosahexaenoic acid that is (4Z,8E,10E,12Z,16Z,19Z)-docosahexaenoic acid in which the two hydroxy substituents are located at the 7R- and 14S-positions. It has a role as an anti-inflammatory agent, a human xenobiotic metabolite, a hepatoprotective agent and a specialised pro-resolving mediator. It is a dihydroxydocosahexaenoic acid and a secondary allylic alcohol. It is functionally related to an all-cis-docosa-4,7,10,13,16,19-hexaenoic acid. Maresin 1 is a polyunsaturated dihydroxydocosahexaenoic acid that is a metabolite of docosahexaenoic acid (DHA), with potential analgesic, anti-inflammatory, and protective activities. |
Solubility Data
| Solubility (In Vitro) | May dissolve in DMSO (in most cases), if not, try other solvents such as H2O, Ethanol, or DMF with a minute amount of products to avoid loss of samples |
| Solubility (In Vivo) |
Note: Listed below are some common formulations that may be used to formulate products with low water solubility (e.g. < 1 mg/mL), you may test these formulations using a minute amount of products to avoid loss of samples. Injection Formulations (e.g. IP/IV/IM/SC) Injection Formulation 1: DMSO : Tween 80: Saline = 10 : 5 : 85 (i.e. 100 μL DMSO stock solution → 50 μL Tween 80 → 850 μL Saline) *Preparation of saline: Dissolve 0.9 g of sodium chloride in 100 mL ddH ₂ O to obtain a clear solution. Injection Formulation 2: DMSO : PEG300 :Tween 80 : Saline = 10 : 40 : 5 : 45 (i.e. 100 μL DMSO → 400 μLPEG300 → 50 μL Tween 80 → 450 μL Saline) Injection Formulation 3: DMSO : Corn oil = 10 : 90 (i.e. 100 μL DMSO → 900 μL Corn oil) Example: Take the Injection Formulation 3 (DMSO : Corn oil = 10 : 90) as an example, if 1 mL of 2.5 mg/mL working solution is to be prepared, you can take 100 μL 25 mg/mL DMSO stock solution and add to 900 μL corn oil, mix well to obtain a clear or suspension solution (2.5 mg/mL, ready for use in animals). Injection Formulation 4: DMSO : 20% SBE-β-CD in saline = 10 : 90 [i.e. 100 μL DMSO → 900 μL (20% SBE-β-CD in saline)] *Preparation of 20% SBE-β-CD in Saline (4°C,1 week): Dissolve 2 g SBE-β-CD in 10 mL saline to obtain a clear solution. Injection Formulation 5: 2-Hydroxypropyl-β-cyclodextrin : Saline = 50 : 50 (i.e. 500 μL 2-Hydroxypropyl-β-cyclodextrin → 500 μL Saline) Injection Formulation 6: DMSO : PEG300 : castor oil : Saline = 5 : 10 : 20 : 65 (i.e. 50 μL DMSO → 100 μLPEG300 → 200 μL castor oil → 650 μL Saline) Injection Formulation 7: Ethanol : Cremophor : Saline = 10: 10 : 80 (i.e. 100 μL Ethanol → 100 μL Cremophor → 800 μL Saline) Injection Formulation 8: Dissolve in Cremophor/Ethanol (50 : 50), then diluted by Saline Injection Formulation 9: EtOH : Corn oil = 10 : 90 (i.e. 100 μL EtOH → 900 μL Corn oil) Injection Formulation 10: EtOH : PEG300:Tween 80 : Saline = 10 : 40 : 5 : 45 (i.e. 100 μL EtOH → 400 μLPEG300 → 50 μL Tween 80 → 450 μL Saline) Oral Formulations Oral Formulation 1: Suspend in 0.5% CMC Na (carboxymethylcellulose sodium) Oral Formulation 2: Suspend in 0.5% Carboxymethyl cellulose Example: Take the Oral Formulation 1 (Suspend in 0.5% CMC Na) as an example, if 100 mL of 2.5 mg/mL working solution is to be prepared, you can first prepare 0.5% CMC Na solution by measuring 0.5 g CMC Na and dissolve it in 100 mL ddH2O to obtain a clear solution; then add 250 mg of the product to 100 mL 0.5% CMC Na solution, to make the suspension solution (2.5 mg/mL, ready for use in animals). Oral Formulation 3: Dissolved in PEG400 Oral Formulation 4: Suspend in 0.2% Carboxymethyl cellulose Oral Formulation 5: Dissolve in 0.25% Tween 80 and 0.5% Carboxymethyl cellulose Oral Formulation 6: Mixing with food powders Note: Please be aware that the above formulations are for reference only. InvivoChem strongly recommends customers to read literature methods/protocols carefully before determining which formulation you should use for in vivo studies, as different compounds have different solubility properties and have to be formulated differently. (Please use freshly prepared in vivo formulations for optimal results.) |