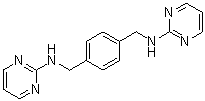MSX-122 is a novel, potent and orally bioavailable inhibitor/partial antagonist of CXCR4 which inhibits CXCR4/CXCL12 actions with an IC50 of 10 nM. It may have antiviral and anticancer properties. By binding to CXCR4, MSX-122 inhibits CXCR4's ability to interact with stromal derived factor-1 (SDF-1), which reduces the migration and proliferation of tumor cells.
Physicochemical Properties
| Molecular Formula | C16H16N6 |
| Molecular Weight | 292.338441848755 |
| Exact Mass | 292.144 |
| Elemental Analysis | C, 65.74; H, 5.52; N, 28.75 |
| CAS # | 897657-95-3 |
| Related CAS # | 897657-95-3 |
| PubChem CID | 11687907 |
| Appearance | White solid powder |
| LogP | 2.636 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 2 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 6 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 6 |
| Heavy Atom Count | 22 |
| Complexity | 263 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| SMILES | N1C(NCC2C=CC(CNC3N=CC=CN=3)=CC=2)=NC=CC=1 |
| InChi Key | PXZXYRKDDXKDTK-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
| InChi Code | InChI=1S/C16H16N6/c1-7-17-15(18-8-1)21-11-13-3-5-14(6-4-13)12-22-16-19-9-2-10-20-16/h1-10H,11-12H2,(H,17,18,21)(H,19,20,22) |
| Chemical Name | N-[[4-[(pyrimidin-2-ylamino)methyl]phenyl]methyl]pyrimidin-2-amine |
| Synonyms | MSX 122; MSX122; MSX-122 |
| HS Tariff Code | 2934.99.9001 |
| Storage |
Powder-20°C 3 years 4°C 2 years In solvent -80°C 6 months -20°C 1 month |
| Shipping Condition | Room temperature (This product is stable at ambient temperature for a few days during ordinary shipping and time spent in Customs) |
Biological Activity
| Targets | CXCR4/CXCL12 ( IC50 ~10 nM ) |
| ln Vitro | MSX-122, which has an IC50 of approximately 10 nM, is a partial antagonist of CXCR4, blocking CXCR4/CXCL12 actions. When the corresponding ligands, CCR3/CCL5 and CCR5/CCL5, mediate the reduction of cAMP, MSX-122 exhibits no inhibition. Invasion of 78% MDA-MB-231 cells is potently blocked by MSX-122 (100 nM). But in the calcium flux assay, MSX-122 is inert and does not inhibit T-tropic HIV infection[1]. |
| ln Vivo | MSX-122 (10 mg/kg, i.p.) inhibits inflammation induced by carrageenan and lung fibrosis induced by bleomycin in mice. In an animal model of breast cancer metastasis used in experiments, MSX-122 (4 mg/kg, i.p., daily) prevents metastasis. Moreover, the number of hepatic micrometastases is significantly reduced by MSX-122 (10 mg/kg i.p., daily)[1]. |
| Cell Assay | MSX-122 is preincubated at 1, 10, 100, and 1000 nM on MDA-MB-231 cells grown in an 8-well slide chamber for the binding affinity assay. Following an incubation period with 50 nM biotinylated TN14003 and a fixation step using 4% formaldehyde, the cells are then stained with rhodamine. |
| Animal Protocol | Mice: Female nude mice aged six to eight weeks are injected via the tail vein with 1.5×1066 MDA-MB-231 breast cancer cells mixed with the compound (1 µM, less than 5 min preincubation) (10/group). The mice in the treated group are injected intraperitoneally (i.p.) with 4 mg/kg MSX-122ms (salt form) every day starting the next day. Thirty-five days after the tumor cell injection, the animals are killed. Complete lung tissues are taken and sectioned for H&E histochemistry and real-time RT-PCR for human CXCR4 in order to assess the metastatic tumor area in five fields per section under a microscope. The results are confirmed by repeating these experiments. For the head and neck cancer animal model, metastatic subclones of 686LN-Ms cells are injected in the same way as MDA-MB-231 cells. [18F]FDG-PET is performed. In the mouse model for uveal melanoma micrometastasis, 1×106 wild-type OMM2.3 cells expressing HGF/TGF-β/CXCR4/MMP2 are injected into the posterior chamber of the right eye of each mouse on day 0. On day three, mice are given 10 mg/kg MSX-122 intraperitoneally (i.p.) in 0.1 mL of 45% CD volume per day, while the control group receives 0.1 mL of 45% CD injections only. Day 7: Tumor-bearing eyes are removed. Histological techniques are used to monitor tumor growth. The number of hepatic micrometastases is counted under a microscope on day 28, after hepatic tissues have been extracted, preserved in 10% formalin, processed, and stained with H&E. The average number of micrometastases per section is calculated by microscopically examining six sections through the liver's center for the presence of micrometastases (<100 µm diameter). For each group, ten mice are used. A table summarizing animal experiments for three metastasis models can be found in the Data S3[1]. |
| References |
[1]. Development of a unique small molecule modulator of CXCR4. PLoS One. 2012;7(4):e34038. |
| Additional Infomation |
MSX-122 has been used in trials studying the treatment of Solid Tumors. CXCR4 Inhibitor Q-122 is an orally bioavailable inhibitor of CXCR4 with potential antineoplastic and antiviral activities. CXCR4 inhibitor MSX-122 binds to the chemokine receptor CXCR4, preventing the binding of stromal derived factor-1 (SDF-1) to the CXCR4 receptor and receptor activation, which may result in decreased tumor cell proliferation and migration. CXCR4, a chemokine receptor belonging to the GPCR (G protein-coupled receptor) gene family, plays an important role in chemotaxis and angiogenesis and is upregulated in several tumor cell types; it is also a co-receptor for HIV entry into T cells. |
Solubility Data
| Solubility (In Vitro) | DMSO: 3~4 mg/mL (10.3~13.7 mM) |
| Solubility (In Vivo) |
Solubility in Formulation 1: ≥ 0.4 mg/mL (1.37 mM) (saturation unknown) in 10% DMSO + 40% PEG300 + 5% Tween80 + 45% Saline (add these co-solvents sequentially from left to right, and one by one), clear solution. For example, if 1 mL of working solution is to be prepared, you can add 100 μL of 4.0 mg/mL clear DMSO stock solution to 400 μL PEG300 and mix evenly; then add 50 μL Tween-80 to the above solution and mix evenly; then add 450 μL normal saline to adjust the volume to 1 mL. Preparation of saline: Dissolve 0.9 g of sodium chloride in 100 mL ddH₂ O to obtain a clear solution. Solubility in Formulation 2: ≥ 0.4 mg/mL (1.37 mM) (saturation unknown) in 10% DMSO + 90% (20% SBE-β-CD in Saline) (add these co-solvents sequentially from left to right, and one by one), clear solution. For example, if 1 mL of working solution is to be prepared, you can add 100 μL of 4.0 mg/mL clear DMSO stock solution to 900 μL of 20% SBE-β-CD physiological saline solution and mix evenly. Preparation of 20% SBE-β-CD in Saline (4°C,1 week): Dissolve 2 g SBE-β-CD in 10 mL saline to obtain a clear solution. Solubility in Formulation 3: ≥ 0.4 mg/mL (1.37 mM) (saturation unknown) in 10% DMSO + 90% Corn Oil (add these co-solvents sequentially from left to right, and one by one), clear solution. For example, if 1 mL of working solution is to be prepared, you can add 100 μL of 4.0 mg/mL clear DMSO stock solution to 900 μL of corn oil and mix evenly. Solubility in Formulation 4: 10 mg/mL (34.21 mM) in 0.5% CMC-Na/saline water (add these co-solvents sequentially from left to right, and one by one), suspension solution; with ultrasonication. Preparation of saline: Dissolve 0.9 g of sodium chloride in 100 mL ddH₂ O to obtain a clear solution. (Please use freshly prepared in vivo formulations for optimal results.) |
| Preparing Stock Solutions | 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | |
| 1 mM | 3.4207 mL | 17.1034 mL | 34.2067 mL | |
| 5 mM | 0.6841 mL | 3.4207 mL | 6.8413 mL | |
| 10 mM | 0.3421 mL | 1.7103 mL | 3.4207 mL |