Physicochemical Properties
| Molecular Formula | C24H25N3O3 |
| Molecular Weight | 403.482 |
| Exact Mass | 403.189 |
| Elemental Analysis | C, 71.44; H, 6.25; N, 10.41; O, 11.90 |
| CAS # | 931695-79-3 |
| Related CAS # | 931695-79-3 |
| PubChem CID | 23612552 |
| Appearance | Off-white to light yellow solid powder |
| Density | 1.3±0.1 g/cm3 |
| Boiling Point | 569.5±60.0 °C at 760 mmHg |
| Flash Point | 298.2±32.9 °C |
| Vapour Pressure | 0.0±1.6 mmHg at 25°C |
| Index of Refraction | 1.668 |
| LogP | 2.75 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 0 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 4 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 4 |
| Heavy Atom Count | 30 |
| Complexity | 695 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
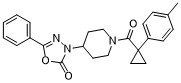
| SMILES | CC1=CC=C(C=C1)C2(CC2)C(=O)N3CCC(CC3)N4C(=O)OC(=N4)C5=CC=CC=C5 |
| InChi Key | WWJKJCDOYFKZBJ-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
| InChi Code | InChI=1S/C24H25N3O3/c1-17-7-9-19(10-8-17)24(13-14-24)22(28)26-15-11-20(12-16-26)27-23(29)30-21(25-27)18-5-3-2-4-6-18/h2-10,20H,11-16H2,1H3 |
| Chemical Name | 3-[1-[1-(4-methylphenyl)cyclopropanecarbonyl]piperidin-4-yl]-5-phenyl-1,3,4-oxadiazol-2-one |
| Synonyms | CCG 152883; CCG-152883; CCG152883; ML 191; ML-191; ML191; CID 23612552; 3-[1-[[1-(4-methylphenyl)cyclopropyl]-oxomethyl]-4-piperidinyl]-5-phenyl-1,3,4-oxadiazol-2-one; 3-[1-[1-(4-methylphenyl)cyclopropanecarbonyl]piperidin-4-yl]-5-phenyl-1,3,4-oxadiazol-2-one; MLS001116074; CCG-152883; SMR000625852; CID-23612552; CID23612552 |
| HS Tariff Code | 2934.99.9001 |
| Storage |
Powder-20°C 3 years 4°C 2 years In solvent -80°C 6 months -20°C 1 month |
| Shipping Condition | Room temperature (This product is stable at ambient temperature for a few days during ordinary shipping and time spent in Customs) |
Biological Activity
| Targets | GPR55 (EC50 = 1.076 µM in U2OS cells overexpressing GPR55) |
| ln Vitro | GPR55 is a class A G protein-coupled receptor (GPCR) that has been implicated in inflammatory pain, neuropathic pain, metabolic disorder, bone development, and cancer. Initially deorphanized as a cannabinoid receptor, GPR55 has been shown to be activated by non-cannabinoid ligands such as l-α-lysophosphatidylinositol (LPI). While there is a growing body of evidence of physiological and pathophysiological roles for GPR55, the paucity of specific antagonists has limited its study. In collaboration with the Molecular Libraries Probe Production Centers Network initiative, we identified a series of GPR55 antagonists using a β-arrestin, high-throughput, high-content screen of ~300000 compounds. This screen yielded novel, GPR55 antagonist chemotypes with IC50 values in the range of 0.16-2.72 μM [Heynen-Genel, S., et al. (2010) Screening for Selective Ligands for GPR55: Antagonists (ML191, ML192, ML193) (Bookshelf ID NBK66153; PMID entry 22091481)]. Importantly, many of the GPR55 antagonists were completely selective, with no agonism or antagonism against GPR35, CB1, or CB2 up to 20 μM. Using a model of the GPR55 inactive state, we studied the binding of an antagonist series that emerged from this screen. These studies suggest that GPR55 antagonists possess a head region that occupies a horizontal binding pocket extending into the extracellular loop region, a central ligand portion that fits vertically in the receptor binding pocket and terminates with a pendant aromatic or heterocyclic ring that juts out. Both the region that extends extracellularly and the pendant ring are features associated with antagonism. Taken together, our results provide a set of design rules for the development of second-generation GPR55 selective antagonists.[1] |
| Enzyme Assay |
Chemical Library Screening[1] A β-arrestin (see methods below), high-throughput, high-content screen (HCS) of 300,000 compounds was used here to identify potent GPR55 selective antagonists. This work was performed in collaboration with the Molecular Libraries Probe Production Centers Network program. For more details about this library of compounds, see http://mli.nih.gov/mli/compound-repository/mlsmr-compounds/. Compounds were screened for antagonism (PubChem AID 2026) at GPR55 (using LPI as the agonist), as well as for both agonism and antagonism at GPR35 (PubChem AIDs 2809, 2815), CB1 (PubChem AIDs 2814, 2835) and CB2 (PubChem AIDs 2822, 2836). A cell line permanently expressing a β-arrestin GFP biosensor and an enhanced receptor of interest (i.e., GPR55, GPR35, CB1 or CB2) were employed in the high content imaging assay. Assay protocol descriptions (according to AID number) are accessible at the PubChem website (http://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/). Potent GPR55 antagonist compounds that lacked agonism or antagonism at GPR35, CB1 or CB2, were further evaluated for inhibition of pERK activation and PKCβII translocation produced by the GPR55 agonists, LPI or ML186 (see methods below). A set of novel GPR55 antagonist molecular scaffolds were selected from the screen ML191 (CID23612552), ML192 (CID1434953) and M193(CID1261822), and the binding of each compound was explored using a computer model of the GPR55 inactive state. |
| Cell Assay |
Cell-based assays[1] Compounds LPI, ML191, ML192, ML193 and ML186 (MolPort) were dissolved in DMSO to 10mM. 10mM stock solutions were dissolved in Hanks’ balanced salt solution (HBSS) to working concentrations. β-Arrestin Translocation[1] U2OS cells permanently expressing HA-GPR55E and βarr2-GFP have been previously described. Cells were seeded onto glass coverslips at 80–85% confluence and placed in 24-well plates (BD Falcon ™). Cells were maintained at 37°C in 5% CO2 overnight. Cells were washed briefly with HBSS before drug application. Experiments were performed using HBSS as the assay buffer. Agonist-stimulated redistribution of βarr2-GFP was assessed following 40 min drug treatment at room temperature (RT). Cells were then fixed with 4% paraformaldehyde for 25 min at room temperature followed by three washes with PBS and one wash with double distilled water. The antagonism protocol included 15 min of pre-incubation with the antagonist, followed by a 40 min co-application with the agonist. PKCβII TranslocationAssay of GPR55 Activation [1] HEK 293 cells plated in 35-mm glass well Matek plastic dishes were transiently transfected with 175 μl of solution containing 1.5 μg/ml PKCβII-GFP cDNA or the PKC plasmid and 5 μg/ml human GPR55 cDNA in pCMV-Sport6 using a standard calcium phosphate protocol. Cells expressing GPR55 and PKCβII-GFP were utilized 24 h after transfection. Cells were washed with warm MEM and maintained at 37°C in 5% CO2 for 30–45 min after drug application. Inhibition of agonist -stimulated redistribution of PKCβII-GFP was assessed after drug treatment at room temperature. Extracellular signal-regulated kinase 1/2 assays [1] Extracellular signal-regulated kinase 1/2 phosphorylation was measured by immunoblotting, as previously described. GPR55E-expressing U2OS cells were grown to sub-confluence in 60-mm plates and serum-starved overnight before assay. Cells were rinsed once with HBSS and antagonists compounds were applied for 30 min prior to agonist application (LPI 10 μM, 10 min). Following drug treatment the cells were disrupted in a lysis buffer (50 mM Hepes, 150 mM NaCl, 1 mM EDTA, 1 mM EGTA, 10% glycerol, 1% Triton X-100, 10 μM MgCl2, 20mM p-nitrophenyl phosphate, 1 mM Na3VO4, 25mM NaF, and a protease inhibitor mixture (1:25, pH 7.5)). Lysates were immediately placed on ice for 10 min and then centrifuged at 16,000 × g for 30 min at 4°C. Supernatants, corresponding to the cytosolic fraction, were collected, and protein concentrations were determined by the Bradford assay using bovine serum albumin as a standard. Cytosolic fractions (20 μg) were separated on a 10% gel by SDS-PAGE followed by immunoblotting. Antibodies against doubly phosphorylated ERK1/2 (1:5000) were detected using a LI-COR Odyssey IR Imager. A polyclonal antibody against total ERK1/2 (1:1000) was used to confirm equal protein loading. Densitometric analysis was performed using LI-COR Odyssey IR Imager. The value obtained for both ERK1 and ERK2 was normalized to total ERK1/2 levels. The data were normalized to response achieved by 10 μM LPI, and presented as percentage inhibition. |
| References |
[1]. Identification of the GPR55 antagonist binding site using a novel set of high-potency GPR55 selective ligands. Biochemistry. 2013 Dec 31;52(52):9456-69. [2]. Screening for Selective Ligands for GPR55 - Antagonists. 2010 Oct 30. |
| Additional Infomation | 3-[1-[[1-(4-methylphenyl)cyclopropyl]-oxomethyl]-4-piperidinyl]-5-phenyl-1,3,4-oxadiazol-2-one is a member of acetamides. |
Solubility Data
| Solubility (In Vitro) | DMSO: ~125 mg/mL (~309.8 mM) |
| Solubility (In Vivo) |
Note: Listed below are some common formulations that may be used to formulate products with low water solubility (e.g. < 1 mg/mL), you may test these formulations using a minute amount of products to avoid loss of samples. Injection Formulations (e.g. IP/IV/IM/SC) Injection Formulation 1: DMSO : Tween 80: Saline = 10 : 5 : 85 (i.e. 100 μL DMSO stock solution → 50 μL Tween 80 → 850 μL Saline) *Preparation of saline: Dissolve 0.9 g of sodium chloride in 100 mL ddH ₂ O to obtain a clear solution. Injection Formulation 2: DMSO : PEG300 :Tween 80 : Saline = 10 : 40 : 5 : 45 (i.e. 100 μL DMSO → 400 μLPEG300 → 50 μL Tween 80 → 450 μL Saline) Injection Formulation 3: DMSO : Corn oil = 10 : 90 (i.e. 100 μL DMSO → 900 μL Corn oil) Example: Take the Injection Formulation 3 (DMSO : Corn oil = 10 : 90) as an example, if 1 mL of 2.5 mg/mL working solution is to be prepared, you can take 100 μL 25 mg/mL DMSO stock solution and add to 900 μL corn oil, mix well to obtain a clear or suspension solution (2.5 mg/mL, ready for use in animals). Injection Formulation 4: DMSO : 20% SBE-β-CD in saline = 10 : 90 [i.e. 100 μL DMSO → 900 μL (20% SBE-β-CD in saline)] *Preparation of 20% SBE-β-CD in Saline (4°C,1 week): Dissolve 2 g SBE-β-CD in 10 mL saline to obtain a clear solution. Injection Formulation 5: 2-Hydroxypropyl-β-cyclodextrin : Saline = 50 : 50 (i.e. 500 μL 2-Hydroxypropyl-β-cyclodextrin → 500 μL Saline) Injection Formulation 6: DMSO : PEG300 : castor oil : Saline = 5 : 10 : 20 : 65 (i.e. 50 μL DMSO → 100 μLPEG300 → 200 μL castor oil → 650 μL Saline) Injection Formulation 7: Ethanol : Cremophor : Saline = 10: 10 : 80 (i.e. 100 μL Ethanol → 100 μL Cremophor → 800 μL Saline) Injection Formulation 8: Dissolve in Cremophor/Ethanol (50 : 50), then diluted by Saline Injection Formulation 9: EtOH : Corn oil = 10 : 90 (i.e. 100 μL EtOH → 900 μL Corn oil) Injection Formulation 10: EtOH : PEG300:Tween 80 : Saline = 10 : 40 : 5 : 45 (i.e. 100 μL EtOH → 400 μLPEG300 → 50 μL Tween 80 → 450 μL Saline) Oral Formulations Oral Formulation 1: Suspend in 0.5% CMC Na (carboxymethylcellulose sodium) Oral Formulation 2: Suspend in 0.5% Carboxymethyl cellulose Example: Take the Oral Formulation 1 (Suspend in 0.5% CMC Na) as an example, if 100 mL of 2.5 mg/mL working solution is to be prepared, you can first prepare 0.5% CMC Na solution by measuring 0.5 g CMC Na and dissolve it in 100 mL ddH2O to obtain a clear solution; then add 250 mg of the product to 100 mL 0.5% CMC Na solution, to make the suspension solution (2.5 mg/mL, ready for use in animals). Oral Formulation 3: Dissolved in PEG400 Oral Formulation 4: Suspend in 0.2% Carboxymethyl cellulose Oral Formulation 5: Dissolve in 0.25% Tween 80 and 0.5% Carboxymethyl cellulose Oral Formulation 6: Mixing with food powders Note: Please be aware that the above formulations are for reference only. InvivoChem strongly recommends customers to read literature methods/protocols carefully before determining which formulation you should use for in vivo studies, as different compounds have different solubility properties and have to be formulated differently. (Please use freshly prepared in vivo formulations for optimal results.) |
| Preparing Stock Solutions | 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | |
| 1 mM | 2.4784 mL | 12.3922 mL | 24.7844 mL | |
| 5 mM | 0.4957 mL | 2.4784 mL | 4.9569 mL | |
| 10 mM | 0.2478 mL | 1.2392 mL | 2.4784 mL |