Physicochemical Properties
| Molecular Formula | C25H40N2O6S |
| Molecular Weight | 496.66 |
| Exact Mass | 496.26 |
| CAS # | 73836-78-9 |
| Related CAS # | Leukotriene D4-d5;1240398-17-7 |
| PubChem CID | 5280878 |
| Appearance | Colorless to light yellow liquid |
| Density | 1.1±0.1 g/cm3 |
| Boiling Point | 748.3±70.0 °C at 760 mmHg |
| Flash Point | 406.4±35.7 °C |
| Vapour Pressure | 0.0±5.7 mmHg at 25°C |
| Index of Refraction | 1.538 |
| LogP | 5.78 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 5 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 8 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 20 |
| Heavy Atom Count | 34 |
| Complexity | 706 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 3 |
| SMILES | S(C([H])([H])[C@@]([H])(C(N([H])C([H])([H])C(=O)O[H])=O)N([H])[H])[C@]([H])(/C(/[H])=C(\[H])/C(/[H])=C(\[H])/C(/[H])=C(/[H])\C([H])([H])/C(/[H])=C(/[H])\C([H])([H])C([H])([H])C([H])([H])C([H])([H])C([H])([H])[H])[C@]([H])(C([H])([H])C([H])([H])C([H])([H])C(=O)O[H])O[H] |
| InChi Key | YEESKJGWJFYOOK-IJHYULJSSA-N |
| InChi Code | InChI=1S/C25H40N2O6S/c1-2-3-4-5-6-7-8-9-10-11-12-13-16-22(21(28)15-14-17-23(29)30)34-19-20(26)25(33)27-18-24(31)32/h6-7,9-13,16,20-22,28H,2-5,8,14-15,17-19,26H2,1H3,(H,27,33)(H,29,30)(H,31,32)/b7-6-,10-9-,12-11+,16-13+/t20-,21-,22+/m0/s1 |
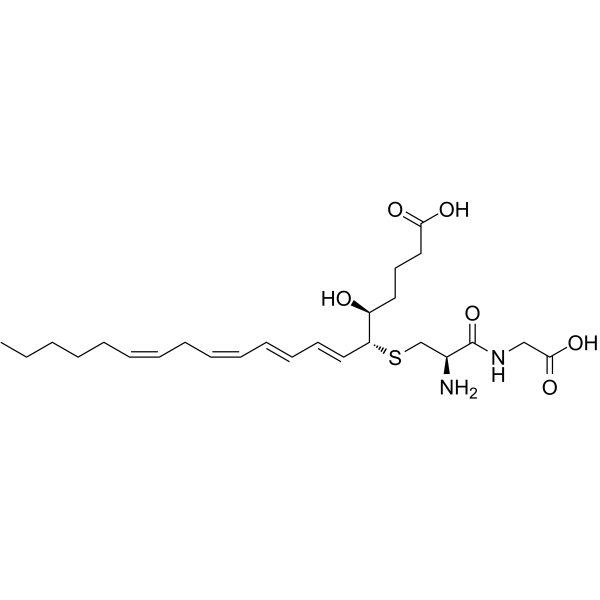
| Chemical Name | (5S,6R,7E,9E,11Z,14Z)-6-[(2R)-2-amino-3-(carboxymethylamino)-3-oxopropyl]sulfanyl-5-hydroxyicosa-7,9,11,14-tetraenoic acid |
| HS Tariff Code | 2934.99.9001 |
| Storage |
Powder-20°C 3 years 4°C 2 years In solvent -80°C 6 months -20°C 1 month |
| Shipping Condition | Room temperature (This product is stable at ambient temperature for a few days during ordinary shipping and time spent in Customs) |
Biological Activity
| Targets | Human Endogenous Metabolite |
| ln Vivo | In mice, intradermal injections of leukotriene D4 (1.5, 3, 6, 12, 24 µg/paw) result in edema and an increase in capillary permeability that is dose-dependent[2]. |
| Animal Protocol |
Animal/Disease Models: 21-24 g, Balb/c male mice[2] Doses: 1.5, 3, 6, 12, 24 µg/paw Route of Administration: Injected intradermally (10 µL was injected into the left hind paw) Experimental Results: Caused significant edematous response and dye extravasation at doses of 1.5-6 ~g/ paw. |
| References |
[1]. The effect of inhaled leukotriene D4 in humans. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1985 Mar;131(3):368-72. [2]. Phlogistic activity of leukotriene D4 in the mouse. Inflammation. 1986 Mar;10(1):1-7. |
| Additional Infomation |
Leukotriene D4 is a leukotriene that is (7E,9E,11Z,14Z)-icosa-7,9,11,14-tetraenoic acid substituted by a hydroxy group at position 5 (5S) and a L-cysteinylglycinyl group at position 6 (6R). It has a role as a human metabolite, a bronchoconstrictor agent and a mouse metabolite. It is an organic sulfide, a dipeptide and a leukotriene. It is functionally related to an icosa-7,9,11,14-tetraenoic acid. It is a conjugate acid of a leukotriene D4(1-). Leukotriene D4 has been used in trials studying the diagnostic of Asthma and Allergic Rhinitis. leukotriene D4 has been reported in Homo sapiens with data available. Leukotriene D4 is a leukotriene synthesized from leukotriene C4 secreted by basophils via removal of a glutamic acid group by cell surface proteases. Leukotriene D4 (LTD4) induces the contraction of smooth muscle cells, which results in bronchoconstriction and vasoconstriction, and increases vascular permeability. LTD4 can be further cleaved by cell surface proteases that remove a glycine group to form leukotriene E4. One of the biologically active principles of SRS-A. It is generated from LEUKOTRIENE C4 after partial hydrolysis of the peptide chain, i.e., cleavage of the gamma-glutamyl portion. Its biological actions include stimulation of vascular and nonvascular smooth muscle, and increases in vascular permeability. (From Dictionary of Prostaglandins and Related Compounds, 1990) |
Solubility Data
| Solubility (In Vivo) |
Note: Listed below are some common formulations that may be used to formulate products with low water solubility (e.g. < 1 mg/mL), you may test these formulations using a minute amount of products to avoid loss of samples. Injection Formulations (e.g. IP/IV/IM/SC) Injection Formulation 1: DMSO : Tween 80: Saline = 10 : 5 : 85 (i.e. 100 μL DMSO stock solution → 50 μL Tween 80 → 850 μL Saline) *Preparation of saline: Dissolve 0.9 g of sodium chloride in 100 mL ddH ₂ O to obtain a clear solution. Injection Formulation 2: DMSO : PEG300 :Tween 80 : Saline = 10 : 40 : 5 : 45 (i.e. 100 μL DMSO → 400 μLPEG300 → 50 μL Tween 80 → 450 μL Saline) Injection Formulation 3: DMSO : Corn oil = 10 : 90 (i.e. 100 μL DMSO → 900 μL Corn oil) Example: Take the Injection Formulation 3 (DMSO : Corn oil = 10 : 90) as an example, if 1 mL of 2.5 mg/mL working solution is to be prepared, you can take 100 μL 25 mg/mL DMSO stock solution and add to 900 μL corn oil, mix well to obtain a clear or suspension solution (2.5 mg/mL, ready for use in animals). Injection Formulation 4: DMSO : 20% SBE-β-CD in saline = 10 : 90 [i.e. 100 μL DMSO → 900 μL (20% SBE-β-CD in saline)] *Preparation of 20% SBE-β-CD in Saline (4°C,1 week): Dissolve 2 g SBE-β-CD in 10 mL saline to obtain a clear solution. Injection Formulation 5: 2-Hydroxypropyl-β-cyclodextrin : Saline = 50 : 50 (i.e. 500 μL 2-Hydroxypropyl-β-cyclodextrin → 500 μL Saline) Injection Formulation 6: DMSO : PEG300 : castor oil : Saline = 5 : 10 : 20 : 65 (i.e. 50 μL DMSO → 100 μLPEG300 → 200 μL castor oil → 650 μL Saline) Injection Formulation 7: Ethanol : Cremophor : Saline = 10: 10 : 80 (i.e. 100 μL Ethanol → 100 μL Cremophor → 800 μL Saline) Injection Formulation 8: Dissolve in Cremophor/Ethanol (50 : 50), then diluted by Saline Injection Formulation 9: EtOH : Corn oil = 10 : 90 (i.e. 100 μL EtOH → 900 μL Corn oil) Injection Formulation 10: EtOH : PEG300:Tween 80 : Saline = 10 : 40 : 5 : 45 (i.e. 100 μL EtOH → 400 μLPEG300 → 50 μL Tween 80 → 450 μL Saline) Oral Formulations Oral Formulation 1: Suspend in 0.5% CMC Na (carboxymethylcellulose sodium) Oral Formulation 2: Suspend in 0.5% Carboxymethyl cellulose Example: Take the Oral Formulation 1 (Suspend in 0.5% CMC Na) as an example, if 100 mL of 2.5 mg/mL working solution is to be prepared, you can first prepare 0.5% CMC Na solution by measuring 0.5 g CMC Na and dissolve it in 100 mL ddH2O to obtain a clear solution; then add 250 mg of the product to 100 mL 0.5% CMC Na solution, to make the suspension solution (2.5 mg/mL, ready for use in animals). Oral Formulation 3: Dissolved in PEG400 Oral Formulation 4: Suspend in 0.2% Carboxymethyl cellulose Oral Formulation 5: Dissolve in 0.25% Tween 80 and 0.5% Carboxymethyl cellulose Oral Formulation 6: Mixing with food powders Note: Please be aware that the above formulations are for reference only. InvivoChem strongly recommends customers to read literature methods/protocols carefully before determining which formulation you should use for in vivo studies, as different compounds have different solubility properties and have to be formulated differently. (Please use freshly prepared in vivo formulations for optimal results.) |
| Preparing Stock Solutions | 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | |
| 1 mM | 2.0134 mL | 10.0672 mL | 20.1345 mL | |
| 5 mM | 0.4027 mL | 2.0134 mL | 4.0269 mL | |
| 10 mM | 0.2013 mL | 1.0067 mL | 2.0134 mL |