Physicochemical Properties
| Molecular Formula | C15H20CL2N4O2 |
| Molecular Weight | 359.250901222229 |
| Exact Mass | 358.096 |
| CAS # | 2362527-67-9 |
| PubChem CID | 156024492 |
| Appearance | Colorless to light yellow ointment |
| LogP | 4.9 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 0 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 6 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 9 |
| Heavy Atom Count | 23 |
| Complexity | 417 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 1 |
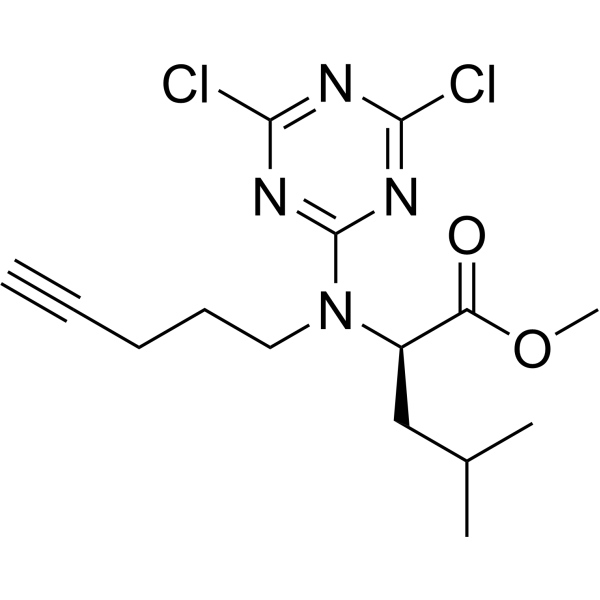
| SMILES | CC(C)C[C@H](C(=O)OC)N(CCCC#C)C1=NC(=NC(=N1)Cl)Cl |
| InChi Key | UTXOIMJGBZBFGA-LLVKDONJSA-N |
| InChi Code | InChI=1S/C15H20Cl2N4O2/c1-5-6-7-8-21(11(9-10(2)3)12(22)23-4)15-19-13(16)18-14(17)20-15/h1,10-11H,6-9H2,2-4H3/t11-/m1/s1 |
| Chemical Name | methyl (2R)-2-[(4,6-dichloro-1,3,5-triazin-2-yl)-pent-4-ynylamino]-4-methylpentanoate |
| HS Tariff Code | 2934.99.9001 |
| Storage |
Powder-20°C 3 years 4°C 2 years In solvent -80°C 6 months -20°C 1 month |
| Shipping Condition | Room temperature (This product is stable at ambient temperature for a few days during ordinary shipping and time spent in Customs) |
Biological Activity
| ln Vitro | Cellular defense against reactive electrophiles is mediated by glutathione S-Transferase Pi (GSTP1). GSTP1 activity is in vitro inhibited by LAS17 in a concentration-dependent manner[1]. Treatment with LAS17 (10 µM; serum-free survival 48 h) in 231MFP breast cancer cells reproduces the impairments in serum-free cell survival linked to genetic GSTP1 inactivation[2]. When 231MFP cells are treated with LAS17 (10 µM) and GSTP1 knockdown, the levels of phosphorylated AMPK and acetyl CoA carboxylase (ACC) rise[2]. A decrease in ATP, lactic acid, purine nucleotides, diacylated phospholipids, and alkylacyl ether lipids is also observed in 231MFP cells, while an increase is seen in acyl carnitines (ACs), ceramides, and lysophospholipids[2]. |
| ln Vivo | When treatment is started two days after subcutaneous cell injection, LAS17 (20 mg/kg ip, once daily) significantly inhibits the growth of 231MFP breast tumor xenografts in immune-deficient mice. When treatment is started sixteen days after tumor implantation, LAS17 even slows tumor growth without causing any noticeable toxicity or weight change[2]. |
| Cell Assay |
Cell Viability Assay[2] Cell Types: 231MFP breast cancer cells Tested Concentrations: 10 µM Incubation Duration: 48 hrs (hours) Experimental Results: Recapitulated the serum-free cell survival impairments observed with genetic inactivation of GSTP1. Western Blot Analysis[2] Cell Types: 231MFP cells Tested Concentrations: 10 µM Incubation Duration: Experimental Results: LAS17- Treated 231MFP cells show increased levels of phosphorylated AMPK and ACC. |
| Animal Protocol |
Animal/Disease Models: Severe combined immunodeficiency (SCID) mice bearing 231MFP tumor xenograft[2] Doses: 20 mg/kg (prepared in PBS:ethanol: PEG40 (18: 1:1)) Route of Administration: Daily administration ip, once per day Experimental Results: Dramatically impaired 231MFP breast tumor xenograft growth. |
| References |
[1]. A tyrosine-reactive irreversible inhibitor for glutathione S-transferase Pi (GSTP1). Mol Biosyst. 2016 May 24;12(6):1768-71. [2]. GSTP1 Is a Driver of Triple-Negative Breast Cancer Cell Metabolism and Pathogenicity. Cell Chem Biol. 2016 May 19;23(5):567-578. |
Solubility Data
| Solubility (In Vitro) | DMSO: 100 mg/mL (278.36 mM) |
| Solubility (In Vivo) |
Note: Listed below are some common formulations that may be used to formulate products with low water solubility (e.g. < 1 mg/mL), you may test these formulations using a minute amount of products to avoid loss of samples. Injection Formulations (e.g. IP/IV/IM/SC) Injection Formulation 1: DMSO : Tween 80: Saline = 10 : 5 : 85 (i.e. 100 μL DMSO stock solution → 50 μL Tween 80 → 850 μL Saline) *Preparation of saline: Dissolve 0.9 g of sodium chloride in 100 mL ddH ₂ O to obtain a clear solution. Injection Formulation 2: DMSO : PEG300 :Tween 80 : Saline = 10 : 40 : 5 : 45 (i.e. 100 μL DMSO → 400 μLPEG300 → 50 μL Tween 80 → 450 μL Saline) Injection Formulation 3: DMSO : Corn oil = 10 : 90 (i.e. 100 μL DMSO → 900 μL Corn oil) Example: Take the Injection Formulation 3 (DMSO : Corn oil = 10 : 90) as an example, if 1 mL of 2.5 mg/mL working solution is to be prepared, you can take 100 μL 25 mg/mL DMSO stock solution and add to 900 μL corn oil, mix well to obtain a clear or suspension solution (2.5 mg/mL, ready for use in animals). Injection Formulation 4: DMSO : 20% SBE-β-CD in saline = 10 : 90 [i.e. 100 μL DMSO → 900 μL (20% SBE-β-CD in saline)] *Preparation of 20% SBE-β-CD in Saline (4°C,1 week): Dissolve 2 g SBE-β-CD in 10 mL saline to obtain a clear solution. Injection Formulation 5: 2-Hydroxypropyl-β-cyclodextrin : Saline = 50 : 50 (i.e. 500 μL 2-Hydroxypropyl-β-cyclodextrin → 500 μL Saline) Injection Formulation 6: DMSO : PEG300 : castor oil : Saline = 5 : 10 : 20 : 65 (i.e. 50 μL DMSO → 100 μLPEG300 → 200 μL castor oil → 650 μL Saline) Injection Formulation 7: Ethanol : Cremophor : Saline = 10: 10 : 80 (i.e. 100 μL Ethanol → 100 μL Cremophor → 800 μL Saline) Injection Formulation 8: Dissolve in Cremophor/Ethanol (50 : 50), then diluted by Saline Injection Formulation 9: EtOH : Corn oil = 10 : 90 (i.e. 100 μL EtOH → 900 μL Corn oil) Injection Formulation 10: EtOH : PEG300:Tween 80 : Saline = 10 : 40 : 5 : 45 (i.e. 100 μL EtOH → 400 μLPEG300 → 50 μL Tween 80 → 450 μL Saline) Oral Formulations Oral Formulation 1: Suspend in 0.5% CMC Na (carboxymethylcellulose sodium) Oral Formulation 2: Suspend in 0.5% Carboxymethyl cellulose Example: Take the Oral Formulation 1 (Suspend in 0.5% CMC Na) as an example, if 100 mL of 2.5 mg/mL working solution is to be prepared, you can first prepare 0.5% CMC Na solution by measuring 0.5 g CMC Na and dissolve it in 100 mL ddH2O to obtain a clear solution; then add 250 mg of the product to 100 mL 0.5% CMC Na solution, to make the suspension solution (2.5 mg/mL, ready for use in animals). Oral Formulation 3: Dissolved in PEG400 Oral Formulation 4: Suspend in 0.2% Carboxymethyl cellulose Oral Formulation 5: Dissolve in 0.25% Tween 80 and 0.5% Carboxymethyl cellulose Oral Formulation 6: Mixing with food powders Note: Please be aware that the above formulations are for reference only. InvivoChem strongly recommends customers to read literature methods/protocols carefully before determining which formulation you should use for in vivo studies, as different compounds have different solubility properties and have to be formulated differently. (Please use freshly prepared in vivo formulations for optimal results.) |
| Preparing Stock Solutions | 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | |
| 1 mM | 2.7836 mL | 13.9179 mL | 27.8358 mL | |
| 5 mM | 0.5567 mL | 2.7836 mL | 5.5672 mL | |
| 10 mM | 0.2784 mL | 1.3918 mL | 2.7836 mL |