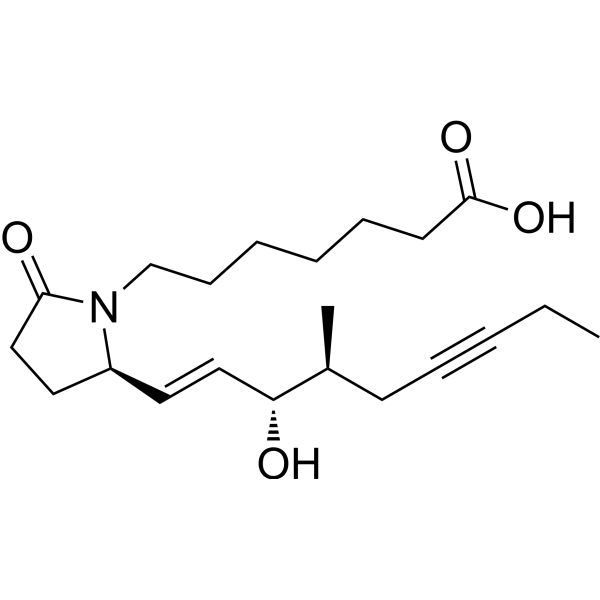
Physicochemical Properties
| Molecular Formula | C21H33NO4 |
| Molecular Weight | 363.491026639938 |
| Exact Mass | 363.24 |
| CAS # | 1628759-75-0 |
| PubChem CID | 72706947 |
| Appearance | Typically exists as solid at room temperature |
| LogP | 2.9 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 2 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 4 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 11 |
| Heavy Atom Count | 26 |
| Complexity | 543 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 3 |
| SMILES | CCC#CC[C@H](C)[C@@H](/C=C/[C@H]1CCC(=O)N1CCCCCCC(=O)O)O |
| InChi Key | CBIUADIJQPJQEZ-VIDOSBHOSA-N |
| InChi Code | InChI=1S/C21H33NO4/c1-3-4-7-10-17(2)19(23)14-12-18-13-15-20(24)22(18)16-9-6-5-8-11-21(25)26/h12,14,17-19,23H,3,5-6,8-11,13,15-16H2,1-2H3,(H,25,26)/b14-12+/t17-,18-,19+/m0/s1 |
| Chemical Name | 7-[(2R)-2-[(E,3S,4S)-3-hydroxy-4-methylnon-1-en-6-ynyl]-5-oxopyrrolidin-1-yl]heptanoic acid |
| HS Tariff Code | 2934.99.9001 |
| Storage |
Powder-20°C 3 years 4°C 2 years In solvent -80°C 6 months -20°C 1 month |
| Shipping Condition | Room temperature (This product is stable at ambient temperature for a few days during ordinary shipping and time spent in Customs) |
Biological Activity
| Targets | EP4 2.35 nM (Ki) EP4 3 nM (IC50) |
| ln Vitro | The rat EP4 receptor's Ki is 1.11 nM, while the rat EP4 receptor's cAMP levels and rat EP4 receptor's CREB activation have EC50 values of 2.66 nM and 0.17 nM, respectively. KMN-80 is tested for both EP4 receptor binding and rat EP2 and EP4 receptor activation[1]. On day nine, the ALP enzyme activity is measured and BMCs, which are isolated from young female rats, are treated once during plating with different doses of KMN-80. ALP EC50 values for KMN-80 (0-100 nM) exhibit significant differences from those corresponding to PGE2 and PGE1, with EC50 values of 82.1 nM and 29.3 nM, respectively, for the activation of ALP enzyme activity in young female rat BMCs, old female rat BMCs, and young male rat BMCs[1]. In EP4-transfected HEK293 cells, KMN-80 has been demonstrated to increase secreted alkaline phosphatase gene reporter activity with an EC50 value of 0.19 nM, exhibiting >5,000 and 50,000-fold selectivity against EP2 and TP, respectively[2]. While the EP4 agonist L-902,688 is highly cytotoxic at similar concentrations in these cells, KMN-80 can induce the differentiation of bone marrow stem cells from both young and old rats into osteoblasts in vitro (EC50s=20 and 153 nM, respectively) and exhibits favorable tolerability up to at least 10 μM[2]. With Ki values of 880 nM and 2.349 nM for hEP3 and hEP4, respectively, KMN-80 binds to human EP receptor subtypes[2]. |
| References |
[1]. M Li, et al. Prostaglandin E(2) Receptors in Bone Formation. Int Orthop [2]. Thomas A Owen, et al. KMN-159, a Novel EP 4 Receptor Selective Agonist, Stimulates Osteoblastic Differentiation in Cultured Whole Rat Bone Marrow. Gene. 2020 Jul 20;748:144668. |
Solubility Data
| Solubility (In Vitro) | May dissolve in DMSO (in most cases), if not, try other solvents such as H2O, Ethanol, or DMF with a minute amount of products to avoid loss of samples |
| Solubility (In Vivo) |
Note: Listed below are some common formulations that may be used to formulate products with low water solubility (e.g. < 1 mg/mL), you may test these formulations using a minute amount of products to avoid loss of samples. Injection Formulations (e.g. IP/IV/IM/SC) Injection Formulation 1: DMSO : Tween 80: Saline = 10 : 5 : 85 (i.e. 100 μL DMSO stock solution → 50 μL Tween 80 → 850 μL Saline) *Preparation of saline: Dissolve 0.9 g of sodium chloride in 100 mL ddH ₂ O to obtain a clear solution. Injection Formulation 2: DMSO : PEG300 :Tween 80 : Saline = 10 : 40 : 5 : 45 (i.e. 100 μL DMSO → 400 μLPEG300 → 50 μL Tween 80 → 450 μL Saline) Injection Formulation 3: DMSO : Corn oil = 10 : 90 (i.e. 100 μL DMSO → 900 μL Corn oil) Example: Take the Injection Formulation 3 (DMSO : Corn oil = 10 : 90) as an example, if 1 mL of 2.5 mg/mL working solution is to be prepared, you can take 100 μL 25 mg/mL DMSO stock solution and add to 900 μL corn oil, mix well to obtain a clear or suspension solution (2.5 mg/mL, ready for use in animals). Injection Formulation 4: DMSO : 20% SBE-β-CD in saline = 10 : 90 [i.e. 100 μL DMSO → 900 μL (20% SBE-β-CD in saline)] *Preparation of 20% SBE-β-CD in Saline (4°C,1 week): Dissolve 2 g SBE-β-CD in 10 mL saline to obtain a clear solution. Injection Formulation 5: 2-Hydroxypropyl-β-cyclodextrin : Saline = 50 : 50 (i.e. 500 μL 2-Hydroxypropyl-β-cyclodextrin → 500 μL Saline) Injection Formulation 6: DMSO : PEG300 : castor oil : Saline = 5 : 10 : 20 : 65 (i.e. 50 μL DMSO → 100 μLPEG300 → 200 μL castor oil → 650 μL Saline) Injection Formulation 7: Ethanol : Cremophor : Saline = 10: 10 : 80 (i.e. 100 μL Ethanol → 100 μL Cremophor → 800 μL Saline) Injection Formulation 8: Dissolve in Cremophor/Ethanol (50 : 50), then diluted by Saline Injection Formulation 9: EtOH : Corn oil = 10 : 90 (i.e. 100 μL EtOH → 900 μL Corn oil) Injection Formulation 10: EtOH : PEG300:Tween 80 : Saline = 10 : 40 : 5 : 45 (i.e. 100 μL EtOH → 400 μLPEG300 → 50 μL Tween 80 → 450 μL Saline) Oral Formulations Oral Formulation 1: Suspend in 0.5% CMC Na (carboxymethylcellulose sodium) Oral Formulation 2: Suspend in 0.5% Carboxymethyl cellulose Example: Take the Oral Formulation 1 (Suspend in 0.5% CMC Na) as an example, if 100 mL of 2.5 mg/mL working solution is to be prepared, you can first prepare 0.5% CMC Na solution by measuring 0.5 g CMC Na and dissolve it in 100 mL ddH2O to obtain a clear solution; then add 250 mg of the product to 100 mL 0.5% CMC Na solution, to make the suspension solution (2.5 mg/mL, ready for use in animals). Oral Formulation 3: Dissolved in PEG400 Oral Formulation 4: Suspend in 0.2% Carboxymethyl cellulose Oral Formulation 5: Dissolve in 0.25% Tween 80 and 0.5% Carboxymethyl cellulose Oral Formulation 6: Mixing with food powders Note: Please be aware that the above formulations are for reference only. InvivoChem strongly recommends customers to read literature methods/protocols carefully before determining which formulation you should use for in vivo studies, as different compounds have different solubility properties and have to be formulated differently. (Please use freshly prepared in vivo formulations for optimal results.) |
| Preparing Stock Solutions | 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | |
| 1 mM | 2.7511 mL | 13.7555 mL | 27.5111 mL | |
| 5 mM | 0.5502 mL | 2.7511 mL | 5.5022 mL | |
| 10 mM | 0.2751 mL | 1.3756 mL | 2.7511 mL |