JNJ-42041935 is a novel, potent, competitive, reversible, and selective inhibitor of prolyl hydroxylase PHD with pKi values of 7.91±0.04, 7.29 ±0.05, and 7.65±0.09 for PHD1, PHD2, and PHD3, respectively. The hypoxia-inducible factor (HIF) prolyl hydroxylase (PHD) enzymes represent novel targets for the treatment of anemia, ulcerative colitis, and ischemic and metabolic disease inter alia. JNJ-42041935 is a new pharmacological tool, which can be used to investigate PHD inhibition and demonstrate that PHD inhibitors offer great promise for the treatment of inflammation-induced anemia.
Physicochemical Properties
| Molecular Formula | C12H6N4O3F3CL |
| Molecular Weight | 346.649 |
| Exact Mass | 346.008 |
| Elemental Analysis | C, 41.58; H, 1.74; Cl, 10.23; F, 16.44; N, 16.16; O, 13.85 |
| CAS # | 1193383-09-3 |
| PubChem CID | 45102710 |
| Appearance | White to off-white solid powder |
| Density | 1.8±0.1 g/cm3 |
| Boiling Point | 555.9±60.0 °C at 760 mmHg |
| Flash Point | 290.0±32.9 °C |
| Vapour Pressure | 0.0±1.6 mmHg at 25°C |
| Index of Refraction | 1.674 |
| LogP | 3.72 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 2 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 8 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 3 |
| Heavy Atom Count | 23 |
| Complexity | 469 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
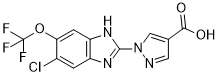
| SMILES | OC(C(C=N1)=CN1C2=NC3=CC(Cl)=C(OC(F)(F)F)C=C3N2)=O |
| InChi Key | FXHHASJVTYRJHH-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
| InChi Code | InChI=1S/C12H6ClF3N4O3/c13-6-1-7-8(2-9(6)23-12(14,15)16)19-11(18-7)20-4-5(3-17-20)10(21)22/h1-4H,(H,18,19)(H,21,22) |
| Chemical Name | 1-(5-chloro-6-(trifluoromethoxy)-1H-benzo[d]imidazol-2-yl)-1H-pyrazole-4-carboxylic acid |
| Synonyms | JNJ-42041935; JNJ 42041935; JNJ42041935. |
| HS Tariff Code | 2934.99.9001 |
| Storage |
Powder-20°C 3 years 4°C 2 years In solvent -80°C 6 months -20°C 1 month |
| Shipping Condition | Room temperature (This product is stable at ambient temperature for a few days during ordinary shipping and time spent in Customs) |
Biological Activity
| Targets |
JNJ-42041935 targets hypoxia-inducible factor prolyl hydroxylase (PHD) enzymes (pK(I) = 7.3-7.9) [1] |
| ln Vitro |
The most potent PHD2181–417-fold was JNJ-42041935, which had a pIC50 value of 7.0±0.03. The full-length PHD1, PHD2, and PHD3 enzymes (pKi values of 7.91±0.04, 7.29 ±0.05, and 7.65±0.09, respectively) are also inhibited by JNJ-42041935 [1]. 1. JNJ-42041935 acts as a potent inhibitor of PHD enzymes with a pK(I) value ranging from 7.3 to 7.9; it functions as a reversible, selective inhibitor and competes with 2-oxoglutarate for binding to PHD enzymes, demonstrating high specificity for the target enzymes in in vitro enzyme activity assays [1] |
| ln Vivo |
In a pathway-induced cooling model, JNJ-42041935 was utilized to assess the effects of intermittent high-dose (50 μg/kg ip) exogenous erythropoietin hemostatic agent with the circulating inhibitor PHD. The anemia that was produced was successfully corrected by JNJ-42041935 (100 μMol/kg, once day for 14 days), but erythropoietin promotion had no impact. JNJ-42041935 (100 μMol/kg face) was administered for five days in a row. The rise in reticulocytes was twofold, hemoglobin was increased by 2.3 g/dl, and hematocrit increased by 9%. After administering 300 μMol/kg JNJ-42041935 topically, mice's peritoneal bioluminescence increased by 2.2 ± 0.3 times compared to vehicle controls treated with luciferase [1]. 1. In a rat model of inflammation-induced anemia, JNJ-42041935 administered at a dose of 100 μmol/kg once daily for 14 days effectively reversed the inflammation-induced anemia; in contrast, intermittent high doses (50 μg/kg via intraperitoneal injection) of an exogenous erythropoietin receptor agonist showed no therapeutic effect on this type of anemia in the same model [1] |
| Enzyme Assay |
1. The inhibitory activity of JNJ-42041935 against PHD enzymes was evaluated through a series of enzyme activity assays: first, the binding affinity of the compound to PHD enzymes was determined by measuring the pK(I) value (7.3-7.9); then, the competitive nature of the inhibition was assessed by investigating the interaction between JNJ-42041935 and 2-oxoglutarate, a key cofactor for PHD enzymes; additionally, the reversibility and selectivity of JNJ-42041935 towards PHD enzymes were verified by comparing its inhibitory effects on PHD with those on other unrelated enzymes, confirming its specific action on the target [1] |
| Animal Protocol |
1. For the inflammation-induced anemia model in rats: JNJ-42041935 was formulated and administered to rats at a dose of 100 μmol/kg once a day for a continuous 14-day period via an unspecified route; a control group was set up, which received an exogenous erythropoietin receptor agonist at a dose of 50 μg/kg via intraperitoneal injection (intermittent high-dose regimen); during the experimental period, hematological parameters related to anemia (such as red blood cell count, hemoglobin concentration, hematocrit) were regularly measured to evaluate the therapeutic effect of JNJ-42041935 on inflammation-induced anemia, and the body weight and general condition of the rats were also monitored to assess the safety of the drug [1] |
| References |
[1]. Pharmacological characterization of 1-(5-chloro-6-(trifluoromethoxy)-1H-benzoimidazol-2-yl)-1H-pyrazole-4-carboxylic acid (JNJ-42041935), a potent and selective hypoxia-inducible factor prolyl hydroxylase inhibitor. Mol Pharmacol. 2011. |
| Additional Infomation |
1. Hypoxia-inducible factor (HIF) prolyl hydroxylase (PHD) enzymes are novel therapeutic targets for anemia, ulcerative colitis, ischemic diseases, metabolic diseases and other disorders [1] 2. JNJ-42041935 is a novel small-molecule PHD inhibitor identified through structure-based drug design methods [1] 3. JNJ-42041935 serves as a valuable pharmacological tool for investigating the biological effects of PHD inhibition, and the results of animal experiments demonstrate that PHD inhibitors have great potential for the treatment of inflammation-induced anemia [1] |
Solubility Data
| Solubility (In Vitro) | DMSO : ≥ 36 mg/mL (~103.85 mM) |
| Solubility (In Vivo) |
Solubility in Formulation 1: ≥ 2.5 mg/mL (7.21 mM) (saturation unknown) in 10% DMSO + 40% PEG300 + 5% Tween80 + 45% Saline (add these co-solvents sequentially from left to right, and one by one), clear solution. For example, if 1 mL of working solution is to be prepared, you can add 100 μL of 25.0 mg/mL clear DMSO stock solution to 400 μL PEG300 and mix evenly; then add 50 μL Tween-80 to the above solution and mix evenly; then add 450 μL normal saline to adjust the volume to 1 mL. Preparation of saline: Dissolve 0.9 g of sodium chloride in 100 mL ddH₂ O to obtain a clear solution. Solubility in Formulation 2: ≥ 2.5 mg/mL (7.21 mM) (saturation unknown) in 10% DMSO + 90% (20% SBE-β-CD in Saline) (add these co-solvents sequentially from left to right, and one by one), clear solution. For example, if 1 mL of working solution is to be prepared, you can add 100 μL of 25.0 mg/mL clear DMSO stock solution to 900 μL of 20% SBE-β-CD physiological saline solution and mix evenly. Preparation of 20% SBE-β-CD in Saline (4°C,1 week): Dissolve 2 g SBE-β-CD in 10 mL saline to obtain a clear solution. Solubility in Formulation 3: ≥ 2.5 mg/mL (7.21 mM) (saturation unknown) in 10% DMSO + 90% Corn Oil (add these co-solvents sequentially from left to right, and one by one), clear solution. For example, if 1 mL of working solution is to be prepared, you can add 100 μL of 25.0 mg/mL clear DMSO stock solution to 900 μL of corn oil and mix evenly. (Please use freshly prepared in vivo formulations for optimal results.) |
| Preparing Stock Solutions | 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | |
| 1 mM | 2.8848 mL | 14.4238 mL | 28.8475 mL | |
| 5 mM | 0.5770 mL | 2.8848 mL | 5.7695 mL | |
| 10 mM | 0.2885 mL | 1.4424 mL | 2.8848 mL |