Physicochemical Properties
| Molecular Formula | C26H28CLN3O7 |
| Molecular Weight | 529.96942615509 |
| Exact Mass | 529.161 |
| CAS # | 851376-05-1 |
| PubChem CID | 11249539 |
| Appearance | White to off-white solid powder |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 5 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 9 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 8 |
| Heavy Atom Count | 37 |
| Complexity | 618 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
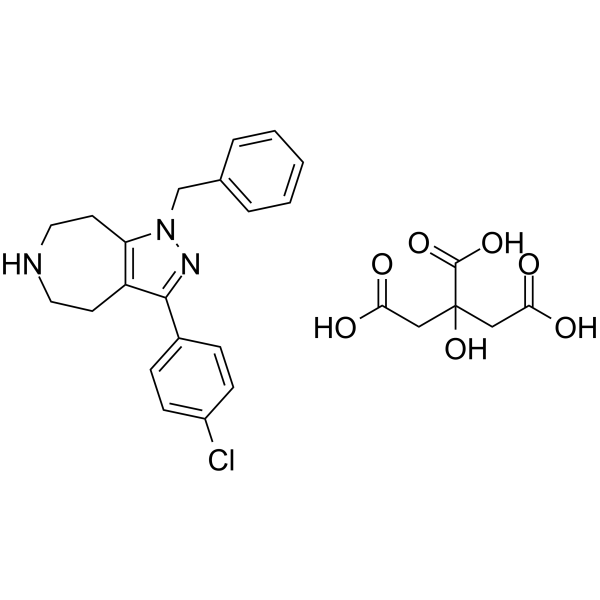
| SMILES | O=C(CC(CC(O)=O)(C(O)=O)O)O.ClC1C=CC(C2C3CCNCCC=3N(CC3C=CC=CC=3)N=2)=CC=1 |
| InChi Key | DIQZMBPDLFAJLK-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
| InChi Code | InChI=1S/C20H20ClN3.C6H8O7/c21-17-8-6-16(7-9-17)20-18-10-12-22-13-11-19(18)24(23-20)14-15-4-2-1-3-5-15;7-3(8)1-6(13,5(11)12)2-4(9)10/h1-9,22H,10-14H2;13H,1-2H2,(H,7,8)(H,9,10)(H,11,12) |
| Chemical Name | 1-benzyl-3-(4-chlorophenyl)-5,6,7,8-tetrahydro-4H-pyrazolo[3,4-d]azepine;2-hydroxypropane-1,2,3-tricarboxylic acid |
| HS Tariff Code | 2934.99.9001 |
| Storage |
Powder-20°C 3 years 4°C 2 years In solvent -80°C 6 months -20°C 1 month Note: Please store this product in a sealed and protected environment, avoid exposure to moisture. |
| Shipping Condition | Room temperature (This product is stable at ambient temperature for a few days during ordinary shipping and time spent in Customs) |
Biological Activity
| Targets | Rat 5-HT7 Receptor 8.19 (pKi, in HEK293 cells ) Human 5-HT7 Receptor 8.20 (pKi, in HEK293 cells ) |
| ln Vitro | High affinity [3H]5-CT binding sites from the rat and human 5-HT7 receptors expressed in HEK293 cells were displaced by JNJ-18038683 (pKi=8.19±0.02 and 8.20±0.01, respectively). On the natural 5-HT7 in rat thalamus membranes, comparable values (pKi=8.50±0.20) are found. The values of the hill slope are nearly equal to one, indicating one-site competitive binding. The assessment of adenylate cyclase activity in HEK293 cells expressing the human or rat 5-HT7 receptor determines the antagonist potency of JNJ-18038683. Rat and human 5-HT7/HEK293 cells exhibit enhanced adenylyl cyclase activity in response to 5-HT, with pEC50 values of 8.09 and 8.12, respectively. The concentration-dependent reduction of 5-HT (100 nM)-stimulated adenylyl cyclase is seen while using JNJ-18038683. The related Ki values from [3H]5-CT binding studies[1] and the pKB values found for JNJ-18038683 accord well. |
| ln Vivo | REM sleep is dose-dependently suppressed by JNJ-18038683, often in the first four hours following therapy. After oral delivery, the duration of REM sleep is considerably reduced during the first four hours (P<0.05) starting at a dose of 1 mg/kg. Alongside this, there is a tendency for the REM sleep latency to be prolonged in a dosage-related manner. Only at the highest tested dose (10 mg/kg; P<0.05) does there appear to be a significant increase in REM latency. These changes in REM sleep appear to be condition-specific. A further investigation is carried out to ascertain whether the repeated administration of JNJ-18038683 for a duration of seven days would lead to any modification of the EEG sleep response, specifically on REM sleep, in rats both during and following treatment. For seven days in a row, JNJ-18038683 is given subcutaneously at a dose of 1 mg/kg every day, two hours into the light phase. JNJ-18038683 causes a prolonging of the REM sleep latency and a considerable reduction in the amount of time spent in REM sleep within the first eight hours following the injection on the first day of treatment. During the seven days of repeated treatment, the REM sleep latency increases; on the first recovery day following treatment termination, it returns to normal. Throughout the seven-day repeated treatment, there is no discernible increase in the amount of time spent in REM sleep; instead, a rebound takes place on the first recovery day following treatment termination. Throughout the course of the treatment, neither the NREM sleep latency nor the total NREM sleep duration are impacted[1]. |
| References |
[1]. Translational evaluation of JNJ-18038683, a 5-hydroxytryptamine type 7 receptor antagonist, on rapid eye movement sleep and in major depressive disorder. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2012 Aug;342(2):429-40. |
Solubility Data
| Solubility (In Vitro) | DMSO: 200 mg/mL (377.38 mM) |
| Solubility (In Vivo) |
Solubility in Formulation 1: ≥ 5 mg/mL (9.43 mM) (saturation unknown) in 10% DMSO + 40% PEG300 + 5% Tween80 + 45% Saline (add these co-solvents sequentially from left to right, and one by one), clear solution. For example, if 1 mL of working solution is to be prepared, you can add 100 μL of 50.0 mg/mL clear DMSO stock solution to 400 μL PEG300 and mix evenly; then add 50 μL Tween-80 to the above solution and mix evenly; then add 450 μL normal saline to adjust the volume to 1 mL. Preparation of saline: Dissolve 0.9 g of sodium chloride in 100 mL ddH₂ O to obtain a clear solution. Solubility in Formulation 2: ≥ 5 mg/mL (9.43 mM) (saturation unknown) in 10% DMSO + 90% (20% SBE-β-CD in Saline) (add these co-solvents sequentially from left to right, and one by one), clear solution. For example, if 1 mL of working solution is to be prepared, you can add 100 μL of 50.0 mg/mL clear DMSO stock solution to 900 μL of 20% SBE-β-CD physiological saline solution and mix evenly. Preparation of 20% SBE-β-CD in Saline (4°C,1 week): Dissolve 2 g SBE-β-CD in 10 mL saline to obtain a clear solution. Solubility in Formulation 3: ≥ 5 mg/mL (9.43 mM) (saturation unknown) in 10% DMSO + 90% Corn Oil (add these co-solvents sequentially from left to right, and one by one), clear solution. For example, if 1 mL of working solution is to be prepared, you can add 100 μL of 50.0 mg/mL clear DMSO stock solution to 900 μL of corn oil and mix evenly. (Please use freshly prepared in vivo formulations for optimal results.) |
| Preparing Stock Solutions | 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | |
| 1 mM | 1.8869 mL | 9.4345 mL | 18.8690 mL | |
| 5 mM | 0.3774 mL | 1.8869 mL | 3.7738 mL | |
| 10 mM | 0.1887 mL | 0.9434 mL | 1.8869 mL |