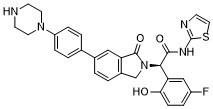
JBJ-04-125-02 R-isomer, the R-enantiomer of JBJ-04-125-02, is a novel, highly potent, mutant-specific, allosteric and orally bioavailable EGFR inhibitor with an IC50 of 0.26 nM for EGFRL858R/T790M. JBJ-04-125-02 can inhibit cancer cell proliferation and EGFRL858R/T790M/C797S signaling. JBJ-04-125-02 has anti-tumor activities.
Physicochemical Properties
| Molecular Formula | C29H26FN5O3S |
| Molecular Weight | 543.6118 |
| Exact Mass | 543.17 |
| Elemental Analysis | C, 64.07; H, 4.82; F, 3.49; N, 12.88; O, 8.83; S, 5.90 |
| CAS # | 2060610-53-7 |
| Related CAS # | (Rac)-JBJ-04-125-02;2140807-05-0 |
| PubChem CID | 124173751 |
| Appearance | Typically exists as solid at room temperature |
| LogP | 3.8 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 3 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 8 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 6 |
| Heavy Atom Count | 39 |
| Complexity | 870 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 1 |
| SMILES | C1CN(CCN1)C2=CC=C(C=C2)C3=CC4=C(CN(C4=O)[C@H](C5=C(C=CC(=C5)F)O)C(=O)NC6=NC=CS6)C=C3 |
| InChi Key | VHQVOTINPRYDAO-AREMUKBSSA-N |
| InChi Code | InChI=1S/C29H26FN5O3S/c30-21-5-8-25(36)24(16-21)26(27(37)33-29-32-11-14-39-29)35-17-20-2-1-19(15-23(20)28(35)38)18-3-6-22(7-4-18)34-12-9-31-10-13-34/h1-8,11,14-16,26,31,36H,9-10,12-13,17H2,(H,32,33,37)/t26-/m1/s1 |
| Chemical Name | (2R)-2-(5-fluoro-2-hydroxyphenyl)-2-[3-oxo-5-(4-piperazin-1-ylphenyl)-1H-isoindol-2-yl]-N-(1,3-thiazol-2-yl)acetamide |
| Synonyms | JBJ-04-125-02; 2060610-53-7; (2R)-2-(5-fluoro-2-hydroxyphenyl)-2-{1-oxo-6-[4-(piperazin-1-yl)phenyl]-1,3-dihydro-2H-isoindol-2-yl}-N-(1,3-thiazol-2-yl)acetamide; (2R)-2-(5-fluoro-2-hydroxyphenyl)-2-[3-oxo-5-(4-piperazin-1-ylphenyl)-1H-isoindol-2-yl]-N-(1,3-thiazol-2-yl)acetamide; SCHEMBL18360815; GTPL12982; BCP32863; EX-A4047 |
| HS Tariff Code | 2934.99.9001 |
| Storage |
Powder-20°C 3 years 4°C 2 years In solvent -80°C 6 months -20°C 1 month |
| Shipping Condition | Room temperature (This product is stable at ambient temperature for a few days during ordinary shipping and time spent in Customs) |
Biological Activity
| Targets | EGFR(L858R/T790M) |
| ln Vitro | H1975 cells treated with JBJ-04-125-02 (0-1000 nM; 72 hours) exhibit reduced cell growth at low nanomolar concentrations [1]. In Ba/F3 cells that have been transfected with EGFRL858R, EGFRL858R/T790M, or EGFRL858R/T790M/C797S mutations, JBJ-04-125-02 therapy also suppresses cell proliferation [1]. In Ba/F3, H1975, and NIH-3T3 cells, the inhibitory effect of JBJ-04-125-02 (0.01-10 μM) on EGFR phosphorylation was investigated. JBJ-04-125-02 inhibited downstream phosphorylation of AKT and ERK1/2 and mutant EGFR, demonstrating mutant selectivity [1]. |
| ln Vivo | Significant tumor regression was observed within 4 weeks of treatment with JBJ-04-125-02 (50 mg/kg; oral gavage; once daily; for 15 weeks; EGFRL858R/T790M/C797S genetically modified mice) [1]. After receiving a 3 mg/kg intravenous (IV) dose, JBJ-04-125-02 displays a high area under the curve (728,577 min·ng/mL) and a moderate half-life of 3 hours. The average maximum plasma concentration is 1.1 μmol/L and the oral bioavailability is 3% when JBJ-04-125-02 is administered orally at a dose of 20 mg/kg [1]. |
| Enzyme Assay | Biochemical assays with L858R/T790M EGFR were carried out using a homogeneous time-resolved fluorescence (HTRF) KinEASE-TK (Cisbio) assay as described previously at the ICCB Longwood Screening Facility at Harvard Medical School. Assays were performed with enzyme concentration of 20pM and 100µM ATP. Inhibitor compounds in DMSO were dispensed directly into 384-well plates with the D300 Digital dispenser (Hewlett Packard) followed immediately by the addition of aqueous buffered solutions using the Multidrop Combi Reagent Dispenser (Thermo Fisher). IC50 values were determined with 11- or 23-point inhibition curves in triplicate.[1] |
| Cell Assay |
Cell Proliferation Assay[1] Cell Types: H1975 Cell Tested Concentrations: 0 nM, 0.1 nM, 1 nM, 10 nM, 100 nM, 1000 nM Incubation Duration: 72 hrs (hours) Experimental Results: Low nanomolar concentrations inhibited cell proliferation of H1975 cells. |
| Animal Protocol |
Animal/Disease Models: EGFRL858R/T790M/C797S genetically engineered mice (GEM) [1] Doses: 50 mg/kg Route of Administration: po (oral gavage); one time/day; lasted for 15 weeks. Experimental Results: Tumors were Dramatically diminished within 4 weeks of treatment. |
| References | [1]. To C, et al. Single and Dual Targeting of Mutant EGFR with an Allosteric Inhibitor. Cancer Discov. 2019 Jul;9(7):926-943. |
| Additional Infomation | In summary, we identify a single agent mutant-selective allosteric EGFR inhibitor, JBJ-04-125-02. Although effective in vitro and in vivo, there are still limitations to this approach. The identification of JBJ-04-125-02 serves as an important proof of concept to demonstrate the feasibility of developing a single agent mutant selective allosteric EGFR inhibitor. Current efforts should focus on developing an allosteric inhibitor that can ideally target not only L858R but also Del_19 mutation; however, since the allosteric pocket in which JBJ-04-125-02 and previous allosteric inhibitors bind is uniquely formed in the presence of the L858R mutation, it remains a challenge to develop an allosteric inhibitor that could simultaneously inhibit both mutant forms of EGFR. Intriguingly, although osimertinib is more effective than gefitinib or erlotinib in EGFR TKI naïve patients, it is disproportionally more effective in patients with EGFR exon 19 deletions (median PFS 21.4 vs. 11.0 months) compared to those with an L858R mutation (median PFS 14.4 vs. 9.5 months), suggesting a need to continue to develop new therapeutic approaches specifically for patients with EGFR L858R mutant NSCLC. The greatest therapeutic potential of JBJ-04-125-02 is observed when it is combined with osimertinib, and as such, the two-drug combination could potentially lead to enhanced clinical benefits beyond those currently achievable with single agent osimertinib in patients with EGFR L858R mutant lung cancer.[1] |
Solubility Data
| Solubility (In Vitro) | May dissolve in DMSO (in most cases), if not, try other solvents such as H2O, Ethanol, or DMF with a minute amount of products to avoid loss of samples |
| Solubility (In Vivo) |
Note: Listed below are some common formulations that may be used to formulate products with low water solubility (e.g. < 1 mg/mL), you may test these formulations using a minute amount of products to avoid loss of samples. Injection Formulations (e.g. IP/IV/IM/SC) Injection Formulation 1: DMSO : Tween 80: Saline = 10 : 5 : 85 (i.e. 100 μL DMSO stock solution → 50 μL Tween 80 → 850 μL Saline) *Preparation of saline: Dissolve 0.9 g of sodium chloride in 100 mL ddH ₂ O to obtain a clear solution. Injection Formulation 2: DMSO : PEG300 :Tween 80 : Saline = 10 : 40 : 5 : 45 (i.e. 100 μL DMSO → 400 μLPEG300 → 50 μL Tween 80 → 450 μL Saline) Injection Formulation 3: DMSO : Corn oil = 10 : 90 (i.e. 100 μL DMSO → 900 μL Corn oil) Example: Take the Injection Formulation 3 (DMSO : Corn oil = 10 : 90) as an example, if 1 mL of 2.5 mg/mL working solution is to be prepared, you can take 100 μL 25 mg/mL DMSO stock solution and add to 900 μL corn oil, mix well to obtain a clear or suspension solution (2.5 mg/mL, ready for use in animals). Injection Formulation 4: DMSO : 20% SBE-β-CD in saline = 10 : 90 [i.e. 100 μL DMSO → 900 μL (20% SBE-β-CD in saline)] *Preparation of 20% SBE-β-CD in Saline (4°C,1 week): Dissolve 2 g SBE-β-CD in 10 mL saline to obtain a clear solution. Injection Formulation 5: 2-Hydroxypropyl-β-cyclodextrin : Saline = 50 : 50 (i.e. 500 μL 2-Hydroxypropyl-β-cyclodextrin → 500 μL Saline) Injection Formulation 6: DMSO : PEG300 : castor oil : Saline = 5 : 10 : 20 : 65 (i.e. 50 μL DMSO → 100 μLPEG300 → 200 μL castor oil → 650 μL Saline) Injection Formulation 7: Ethanol : Cremophor : Saline = 10: 10 : 80 (i.e. 100 μL Ethanol → 100 μL Cremophor → 800 μL Saline) Injection Formulation 8: Dissolve in Cremophor/Ethanol (50 : 50), then diluted by Saline Injection Formulation 9: EtOH : Corn oil = 10 : 90 (i.e. 100 μL EtOH → 900 μL Corn oil) Injection Formulation 10: EtOH : PEG300:Tween 80 : Saline = 10 : 40 : 5 : 45 (i.e. 100 μL EtOH → 400 μLPEG300 → 50 μL Tween 80 → 450 μL Saline) Oral Formulations Oral Formulation 1: Suspend in 0.5% CMC Na (carboxymethylcellulose sodium) Oral Formulation 2: Suspend in 0.5% Carboxymethyl cellulose Example: Take the Oral Formulation 1 (Suspend in 0.5% CMC Na) as an example, if 100 mL of 2.5 mg/mL working solution is to be prepared, you can first prepare 0.5% CMC Na solution by measuring 0.5 g CMC Na and dissolve it in 100 mL ddH2O to obtain a clear solution; then add 250 mg of the product to 100 mL 0.5% CMC Na solution, to make the suspension solution (2.5 mg/mL, ready for use in animals). Oral Formulation 3: Dissolved in PEG400 Oral Formulation 4: Suspend in 0.2% Carboxymethyl cellulose Oral Formulation 5: Dissolve in 0.25% Tween 80 and 0.5% Carboxymethyl cellulose Oral Formulation 6: Mixing with food powders Note: Please be aware that the above formulations are for reference only. InvivoChem strongly recommends customers to read literature methods/protocols carefully before determining which formulation you should use for in vivo studies, as different compounds have different solubility properties and have to be formulated differently. (Please use freshly prepared in vivo formulations for optimal results.) |
| Preparing Stock Solutions | 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | |
| 1 mM | 1.8396 mL | 9.1978 mL | 18.3955 mL | |
| 5 mM | 0.3679 mL | 1.8396 mL | 3.6791 mL | |
| 10 mM | 0.1840 mL | 0.9198 mL | 1.8396 mL |