Physicochemical Properties
| Molecular Formula | C23H25FN2O5 |
| Molecular Weight | 428.45 |
| Elemental Analysis | C, 64.48; H, 5.88; F, 4.43; N, 6.54; O, 18.67 |
| CAS # | 475110-48-6 |
| Appearance | Typically exists as solids at room temperature |
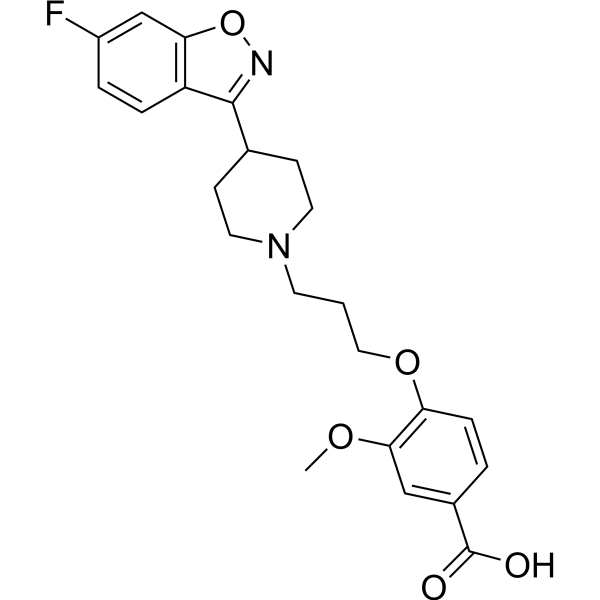
| SMILES | COC1C=C(C(=O)O)C=CC=1OCCCN1CCC(C2=NOC3C=C(C=CC2=3)F)CC1 |
| Synonyms | Iloperidone carboxylic acid; P95-12113; Iloperidone metabolite P95; Iloperidone Carboxylic Acid; 475110-48-6; DV65CD1JA2; P 95-12113; P-95-12113; Benzoic acid, 4-(3-(4-(6-fluoro-1,2-benzisoxazol-3-yl)-1-piperidinyl)propoxy)-3-methoxy-; 4-[3-[4-(6-fluoro-1,2-benzisoxazol-3-yl)-1-piperidinyl]propoxy]-3-methoxy-benzoic acid; |
| HS Tariff Code | 2934.99.9001 |
| Storage |
Powder-20°C 3 years 4°C 2 years In solvent -80°C 6 months -20°C 1 month |
| Shipping Condition | Room temperature (This product is stable at ambient temperature for a few days during ordinary shipping and time spent in Customs) |
Biological Activity
| Targets | Human 5-HT2A Receptor 8.15 (pKi); rat α1-adrenergic receptor 7.67 (pKi); human α2C-adrenoceptor 7.32 (pKi); human α2B-adrenoceptor 7.08 (pKi); human α2A-adrenoceptor 6.42 (pKi); Rat D3 Receptor 6.11 (pKi); Human D1 Receptor 5.94 (pKi); Human 5-HT6 Receptor 5.59 (pKi) |
| ln Vitro | Iloperidone is a novel atypical antipsychotic compound currently under clinical development for the treatment of psychotic disorders. In radioligand binding studies, iloperidone binds with high affinity to serotonin (5-HT) 5-HT2A and noradrenaline alpha1 and alpha2C receptors [Neuropsychopharmacology (2001) 25, 904-914]. The human metabolism of iloperidone generates two major metabolites, P88-8991 and P95-12113. The aim of this study was to compare the receptor affinity profile of P88-8991 and P95-12113 with that of the parent compound. The receptor affinity profile of P88-8991 is comparable to that of iloperidone. This metabolite binds to the following monoamine receptors (pKi values in nM): serotonin 5-HT2A receptors (9.56), adrenergic alpha1 (8.08) and alpha2C (7.79) receptors, and D2A receptors (7.80). Lower affinity is seen for other dopamine, serotonin, alpha2-adrenergic and histamine H1 receptors. In contrast, P95-12113 shows affinity for 5-HT2A receptors (pKi 8.15; which is 60-fold lower than that of iloperidone), adrenergic alpha1 (7.67), alpha2C (7.32) and alpha2B (7.08) receptors. Given this affinity profile, and the observation that P95-12113 does not readily cross the blood-brain barrier, it is unlikely that this metabolite contributes to the therapeutic effect of iloperidone in patients with schizophrenia. However, the comparable receptor binding profile of P88-8991 indicates that it is likely to contribute to the clinical profile of iloperidone [1]. |
| References |
[1]. Receptor profile of P88-8991 and P95-12113, metabolites of the novel antipsychotic iloperidone. Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry. 2002 Apr;26(3):553-60. |
Solubility Data
| Solubility (In Vitro) | May dissolve in DMSO (in most cases), if not, try other solvents such as H2O, Ethanol, or DMF with a minute amount of products to avoid loss of samples |
| Solubility (In Vivo) |
Note: Listed below are some common formulations that may be used to formulate products with low water solubility (e.g. < 1 mg/mL), you may test these formulations using a minute amount of products to avoid loss of samples. Injection Formulations (e.g. IP/IV/IM/SC) Injection Formulation 1: DMSO : Tween 80: Saline = 10 : 5 : 85 (i.e. 100 μL DMSO stock solution → 50 μL Tween 80 → 850 μL Saline) *Preparation of saline: Dissolve 0.9 g of sodium chloride in 100 mL ddH ₂ O to obtain a clear solution. Injection Formulation 2: DMSO : PEG300 :Tween 80 : Saline = 10 : 40 : 5 : 45 (i.e. 100 μL DMSO → 400 μLPEG300 → 50 μL Tween 80 → 450 μL Saline) Injection Formulation 3: DMSO : Corn oil = 10 : 90 (i.e. 100 μL DMSO → 900 μL Corn oil) Example: Take the Injection Formulation 3 (DMSO : Corn oil = 10 : 90) as an example, if 1 mL of 2.5 mg/mL working solution is to be prepared, you can take 100 μL 25 mg/mL DMSO stock solution and add to 900 μL corn oil, mix well to obtain a clear or suspension solution (2.5 mg/mL, ready for use in animals). Injection Formulation 4: DMSO : 20% SBE-β-CD in saline = 10 : 90 [i.e. 100 μL DMSO → 900 μL (20% SBE-β-CD in saline)] *Preparation of 20% SBE-β-CD in Saline (4°C,1 week): Dissolve 2 g SBE-β-CD in 10 mL saline to obtain a clear solution. Injection Formulation 5: 2-Hydroxypropyl-β-cyclodextrin : Saline = 50 : 50 (i.e. 500 μL 2-Hydroxypropyl-β-cyclodextrin → 500 μL Saline) Injection Formulation 6: DMSO : PEG300 : castor oil : Saline = 5 : 10 : 20 : 65 (i.e. 50 μL DMSO → 100 μLPEG300 → 200 μL castor oil → 650 μL Saline) Injection Formulation 7: Ethanol : Cremophor : Saline = 10: 10 : 80 (i.e. 100 μL Ethanol → 100 μL Cremophor → 800 μL Saline) Injection Formulation 8: Dissolve in Cremophor/Ethanol (50 : 50), then diluted by Saline Injection Formulation 9: EtOH : Corn oil = 10 : 90 (i.e. 100 μL EtOH → 900 μL Corn oil) Injection Formulation 10: EtOH : PEG300:Tween 80 : Saline = 10 : 40 : 5 : 45 (i.e. 100 μL EtOH → 400 μLPEG300 → 50 μL Tween 80 → 450 μL Saline) Oral Formulations Oral Formulation 1: Suspend in 0.5% CMC Na (carboxymethylcellulose sodium) Oral Formulation 2: Suspend in 0.5% Carboxymethyl cellulose Example: Take the Oral Formulation 1 (Suspend in 0.5% CMC Na) as an example, if 100 mL of 2.5 mg/mL working solution is to be prepared, you can first prepare 0.5% CMC Na solution by measuring 0.5 g CMC Na and dissolve it in 100 mL ddH2O to obtain a clear solution; then add 250 mg of the product to 100 mL 0.5% CMC Na solution, to make the suspension solution (2.5 mg/mL, ready for use in animals). Oral Formulation 3: Dissolved in PEG400 Oral Formulation 4: Suspend in 0.2% Carboxymethyl cellulose Oral Formulation 5: Dissolve in 0.25% Tween 80 and 0.5% Carboxymethyl cellulose Oral Formulation 6: Mixing with food powders Note: Please be aware that the above formulations are for reference only. InvivoChem strongly recommends customers to read literature methods/protocols carefully before determining which formulation you should use for in vivo studies, as different compounds have different solubility properties and have to be formulated differently. (Please use freshly prepared in vivo formulations for optimal results.) |
| Preparing Stock Solutions | 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | |
| 1 mM | 2.3340 mL | 11.6700 mL | 23.3399 mL | |
| 5 mM | 0.4668 mL | 2.3340 mL | 4.6680 mL | |
| 10 mM | 0.2334 mL | 1.1670 mL | 2.3340 mL |