IOX2 is a novel and potent inhibitor of hypoxia-inducible factor (HIF-1α) prolyl hydroxylase-2 (PHD2) with considerable medical uses. It inhibits PHD2 with an IC50 of 21 nM in a cell-free assay,and displays >100-fold selectivity over JMJD2A, JMJD2C, JMJD2E, JMJD3, or the 2OG oxygenase FIH.
Physicochemical Properties
| Molecular Formula | C19H16N2O5 |
| Molecular Weight | 352.3407 |
| Exact Mass | 352.105 |
| CAS # | 931398-72-0 |
| Related CAS # | IOX2 sodium;2377239-85-3 |
| PubChem CID | 54685215 |
| Appearance | White to off-white solid powder |
| Density | 1.5±0.1 g/cm3 |
| Boiling Point | 642.8±55.0 °C at 760 mmHg |
| Flash Point | 342.5±31.5 °C |
| Vapour Pressure | 0.0±2.0 mmHg at 25°C |
| Index of Refraction | 1.689 |
| LogP | 1.02 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 3 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 5 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 5 |
| Heavy Atom Count | 26 |
| Complexity | 609 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| InChi Key | CAOSCCRYLYQBES-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
| InChi Code | InChI=1S/C19H16N2O5/c22-15(23)10-20-18(25)16-17(24)13-8-4-5-9-14(13)21(19(16)26)11-12-6-2-1-3-7-12/h1-9,24H,10-11H2,(H,20,25)(H,22,23) |
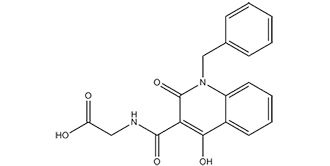
| Chemical Name | 2-[(1-benzyl-4-hydroxy-2-oxoquinoline-3-carbonyl)amino]acetic acid |
| Synonyms | IOX-2; IOX2; IOX 2 |
| HS Tariff Code | 2934.99.9001 |
| Storage |
Powder-20°C 3 years 4°C 2 years In solvent -80°C 6 months -20°C 1 month |
| Shipping Condition | Room temperature (This product is stable at ambient temperature for a few days during ordinary shipping and time spent in Customs) |
Biological Activity
| ln Vitro | Thrombin (0.03 U/mL) or collagen-related peptide (CRP; 0.25 μg/mL)-induced platelet aggregation and ATP release were dose-dependently inhibited by IOX2 (0, 10, 25, and 50 μM). IOX2 does not, however, alter the expression of P-selectin or the surface concentrations of GPVI, αIIbβ3, or glycoprotein (GP)Ibα[1]. In addition to preventing clot retraction, IOX2 also prevents platelet spreading on collagen or fibrinogen [1]. Normal human dermal fibroblasts (NHDF) and epidermal keratinocytes (NHEK) grown in normoxic and hypoxic conditions exhibit increased transcript levels of VEGF-A and BNIP3 in response to IOX2 (50 μM; 24 h) [2]. |
| ln Vivo | In mice, IOX2 (10 mg/kg; i.p.; single dose) reduces platelet hemostatic activity and causes arterial thrombosis [1]. |
| Animal Protocol |
Animal/Disease Models: Mouse[1] Doses: 10 mg/kg Route of Administration: intraperitoneal (ip)injection Experimental Results: Upregulated HIF-1α in platelets, diminished ROS generation, and downregulated NOX1 expression. Increased the phosphorylation level of VASP (Ser157/239), and inhibited the Phosphorylation of p38 (Thr180/Tyr182), ERK1/2 (Thr202/Tyr204), AKT (Thr308/Ser473), and PKCδ (Thr505) in CRP- or thrombin-stimulated platelets. |
| References |
[1]. Inhibition of Hypoxia-Inducible Factor Prolyl-Hydroxylase Modulates Platelet Function. Thromb Haemost. 2022 Oct;122(10):1693-1705. [2]. Impairment of hypoxia-induced HIF-1α signaling in keratinocytes and fibroblasts by sulfur mustard is counteracted by a selective PHD-2 inhibitor. Arch Toxicol. 2016 May;90(5):1141-50. |
| Additional Infomation | 2-[[[4-hydroxy-2-oxo-1-(phenylmethyl)-3-quinolinyl]-oxomethyl]amino]acetic acid is a member of quinolines. |
Solubility Data
| Solubility (In Vitro) | DMSO: 7 mg/mL (19.9 mM) Water:<1 mg/mL Ethanol:<1 mg/mL |
| Solubility (In Vivo) |
Solubility in Formulation 1: ≥ 2.5 mg/mL (7.10 mM) (saturation unknown) in 10% DMSO + 40% PEG300 +5% Tween-80 + 45% Saline (add these co-solvents sequentially from left to right, and one by one), clear solution. For example, if 1 mL of working solution is to be prepared, you can add 100 μL of 25.0 mg/mL clear DMSO stock solution to 400 μL PEG300 and mix evenly; then add 50 μL Tween-80 + to the above solution and mix evenly; then add 450 μL normal saline to adjust the volume to 1 mL. Preparation of saline: Dissolve 0.9 g of sodium chloride in 100 mL ddH₂ O to obtain a clear solution. (Please use freshly prepared in vivo formulations for optimal results.) |
| Preparing Stock Solutions | 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | |
| 1 mM | 2.8382 mL | 14.1908 mL | 28.3817 mL | |
| 5 mM | 0.5676 mL | 2.8382 mL | 5.6763 mL | |
| 10 mM | 0.2838 mL | 1.4191 mL | 2.8382 mL |