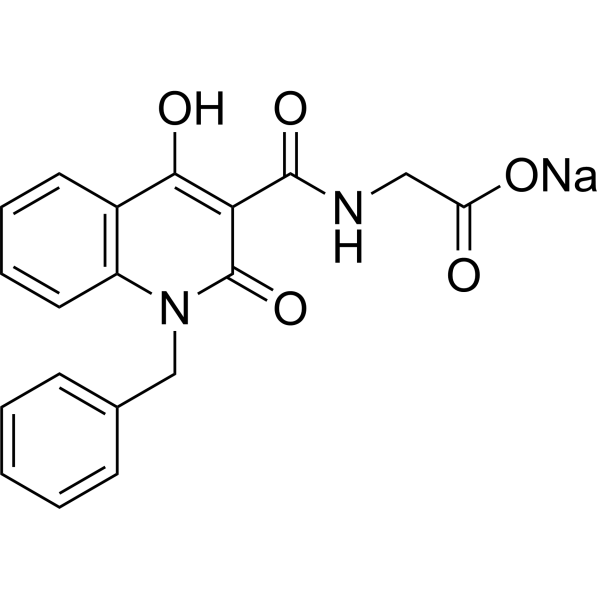
Physicochemical Properties
| CAS # | 2377239-85-3 |
| Related CAS # | IOX2;931398-72-0 |
| PubChem CID | 139036077 |
| Appearance | Typically exists as solid at room temperature |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 2 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 5 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 5 |
| Heavy Atom Count | 27 |
| Complexity | 615 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| HS Tariff Code | 2934.99.9001 |
| Storage |
Powder-20°C 3 years 4°C 2 years In solvent -80°C 6 months -20°C 1 month |
| Shipping Condition | Room temperature (This product is stable at ambient temperature for a few days during ordinary shipping and time spent in Customs) |
Biological Activity
| ln Vitro | When IOX2 sodium (0, 10, 25, and 50 μM) is combined with either cutase (0.03 U/mL) or factor-activated protein-related peptide (CRP; 0.25 μg/mL), RNA polymerization and ATP release are induced. Nonetheless, P-selected expression and surface levels of glycoproteins (GP)Ibα, GPVI, or αIIbβ3 remain unaffected by IOX2 [1]. Moreover, IOX2 natriuretics prevent clot retraction and spreading on collagen or fibrinogen [1]. In normal human epidermal cells (NHEK) and normal human dermal fibroblasts (NHDF) cultured under normoxic and hypoxic conditions, 50 μM; 24 h) enhances the modulated levels of VEGF-A and BNIP3 [2]. |
| ln Vivo | IOX2odium (10 mg/kg; intraperitoneal injection; single dosage) affects hemostasis and arterial thrombosis in mice [1]. |
| Animal Protocol |
Animal/Disease Models: Mice [1] Doses: 10 mg/kg Route of Administration: intraperitoneal (ip) injection Experimental Results: Up-regulate HIF-1α in platelets, reduce ROS production, and down-regulate NOX1 expression. Increases the phosphorylation level of VASP (Ser157/239) in CRP or thrombin and inhibits the phosphorylation of p38 (Thr180/Tyr182), ERK1/2 (Thr202/Tyr204), AKT (Thr308/Ser473) and PKCδ (Thr505) - Stimulate platelets. |
| References |
[1]. Inhibition of Hypoxia-Inducible Factor Prolyl-Hydroxylase Modulates Platelet Function. Thromb Haemost. 2022 Oct;122(10):1693-1705. [2]. Impairment of hypoxia-induced HIF-1α signaling in keratinocytes and fibroblasts by sulfur mustard is counteracted by a selective PHD-2 inhibitor. Arch Toxicol. 2016 May;90(5):1141-50. |
Solubility Data
| Solubility (In Vitro) | May dissolve in DMSO (in most cases), if not, try other solvents such as H2O, Ethanol, or DMF with a minute amount of products to avoid loss of samples |
| Solubility (In Vivo) |
Note: Listed below are some common formulations that may be used to formulate products with low water solubility (e.g. < 1 mg/mL), you may test these formulations using a minute amount of products to avoid loss of samples. Injection Formulations (e.g. IP/IV/IM/SC) Injection Formulation 1: DMSO : Tween 80: Saline = 10 : 5 : 85 (i.e. 100 μL DMSO stock solution → 50 μL Tween 80 → 850 μL Saline) *Preparation of saline: Dissolve 0.9 g of sodium chloride in 100 mL ddH ₂ O to obtain a clear solution. Injection Formulation 2: DMSO : PEG300 :Tween 80 : Saline = 10 : 40 : 5 : 45 (i.e. 100 μL DMSO → 400 μLPEG300 → 50 μL Tween 80 → 450 μL Saline) Injection Formulation 3: DMSO : Corn oil = 10 : 90 (i.e. 100 μL DMSO → 900 μL Corn oil) Example: Take the Injection Formulation 3 (DMSO : Corn oil = 10 : 90) as an example, if 1 mL of 2.5 mg/mL working solution is to be prepared, you can take 100 μL 25 mg/mL DMSO stock solution and add to 900 μL corn oil, mix well to obtain a clear or suspension solution (2.5 mg/mL, ready for use in animals). Injection Formulation 4: DMSO : 20% SBE-β-CD in saline = 10 : 90 [i.e. 100 μL DMSO → 900 μL (20% SBE-β-CD in saline)] *Preparation of 20% SBE-β-CD in Saline (4°C,1 week): Dissolve 2 g SBE-β-CD in 10 mL saline to obtain a clear solution. Injection Formulation 5: 2-Hydroxypropyl-β-cyclodextrin : Saline = 50 : 50 (i.e. 500 μL 2-Hydroxypropyl-β-cyclodextrin → 500 μL Saline) Injection Formulation 6: DMSO : PEG300 : castor oil : Saline = 5 : 10 : 20 : 65 (i.e. 50 μL DMSO → 100 μLPEG300 → 200 μL castor oil → 650 μL Saline) Injection Formulation 7: Ethanol : Cremophor : Saline = 10: 10 : 80 (i.e. 100 μL Ethanol → 100 μL Cremophor → 800 μL Saline) Injection Formulation 8: Dissolve in Cremophor/Ethanol (50 : 50), then diluted by Saline Injection Formulation 9: EtOH : Corn oil = 10 : 90 (i.e. 100 μL EtOH → 900 μL Corn oil) Injection Formulation 10: EtOH : PEG300:Tween 80 : Saline = 10 : 40 : 5 : 45 (i.e. 100 μL EtOH → 400 μLPEG300 → 50 μL Tween 80 → 450 μL Saline) Oral Formulations Oral Formulation 1: Suspend in 0.5% CMC Na (carboxymethylcellulose sodium) Oral Formulation 2: Suspend in 0.5% Carboxymethyl cellulose Example: Take the Oral Formulation 1 (Suspend in 0.5% CMC Na) as an example, if 100 mL of 2.5 mg/mL working solution is to be prepared, you can first prepare 0.5% CMC Na solution by measuring 0.5 g CMC Na and dissolve it in 100 mL ddH2O to obtain a clear solution; then add 250 mg of the product to 100 mL 0.5% CMC Na solution, to make the suspension solution (2.5 mg/mL, ready for use in animals). Oral Formulation 3: Dissolved in PEG400 Oral Formulation 4: Suspend in 0.2% Carboxymethyl cellulose Oral Formulation 5: Dissolve in 0.25% Tween 80 and 0.5% Carboxymethyl cellulose Oral Formulation 6: Mixing with food powders Note: Please be aware that the above formulations are for reference only. InvivoChem strongly recommends customers to read literature methods/protocols carefully before determining which formulation you should use for in vivo studies, as different compounds have different solubility properties and have to be formulated differently. (Please use freshly prepared in vivo formulations for optimal results.) |