Physicochemical Properties
| Molecular Formula | C14H18N2O2 |
| Molecular Weight | 246.3049 |
| Exact Mass | 246.136 |
| Elemental Analysis | C, 68.27; H, 7.37; N, 11.37; O, 12.99 |
| CAS # | 487-58-1 |
| Related CAS # | 487-58-1 |
| PubChem CID | 442106 |
| Appearance | White to off-white solid powder |
| Melting Point | 255℃ |
| LogP | -2.12 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 1 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 2 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 3 |
| Heavy Atom Count | 18 |
| Complexity | 306 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 1 |
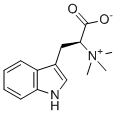
| SMILES | [O-]C(C([H])(C([H])([H])C1=C([H])N([H])C2=C([H])C([H])=C([H])C([H])=C12)[N+](C([H])([H])[H])(C([H])([H])[H])C([H])([H])[H])=O |
| InChi Key | AOHCBEAZXHZMOR-ZDUSSCGKSA-N |
| InChi Code | InChI=1S/C14H18N2O2/c1-16(2,3)13(14(17)18)8-10-9-15-12-7-5-4-6-11(10)12/h4-7,9,13,15H,8H2,1-3H3/t13-/m0/s1 |
| Chemical Name | (2S)-3-(1H-indol-3-yl)-2-(trimethylazaniumyl)propanoate |
| Synonyms | Hypaphorine; Hypaforin; Tryptophan betaine; L-Hypaphorine |
| HS Tariff Code | 2934.99.03.00 |
| Storage |
Powder-20°C 3 years 4°C 2 years In solvent -80°C 6 months -20°C 1 month Note: Please store this product in a sealed and protected environment (e.g. under nitrogen), avoid exposure to moisture and light. |
| Shipping Condition | Room temperature (This product is stable at ambient temperature for a few days during ordinary shipping and time spent in Customs) |
Biological Activity
| ln Vitro | Hypaphorine inhibits LPS-induced phosphorylation of ERK, nuclear factor kappa beta ((NFκB), NFκB inhibitor IκBα, and IKKβ, as well as cyclooxygenase-2 (COX-2) and inducible nitric oxide synthase (iNOS) expression. It also prevents NFκB from translocating into the nucleus in LPS-treated RAW 264.7 cells.[1] |
| ln Vivo | A potential therapeutic agent for treating osteoclast-based bone loss is hypaphorine, which inhibits RANKL-induced osteoclastogenesis through a decrease in the phosphorylation of NF-κB p65, ERK, p38, and c-Jun N-terminal kinase (JNK), and ERK, p38, and p38 kinases.[2] |
| Cell Assay | Incubating the cells in 2% serum medium for 24 hours prior to treatment stopped the cell growth. The indicated cells were then plated in 96-well culture plates at a density of 5×103 cells/well, stimulated with varying concentrations of vaccaria hypaphorine (6.25, 12.5, 25, 50, 100, 200 μM), and incubated for 24 hours at 37°C in a 5% COsub>2/sub> saturated humidity condition. Finally, at 540 nm, the optical density (OD) was determined. |
| Animal Protocol | C57BL/6J mice induced by LPS 10 and 30 mg/kg p.o. |
| References |
[1]. BMC Complement Altern Med . 2017 Feb 20;17(1):120. [2]. Biomed Pharmacother . 2018 Jan:97:1155-1163. |
| Additional Infomation |
Hypaphorine is an amino acid betaine obtaine by exhaustive methylation of the alpha-amino group of L-tryptophan with concomitant deprotonation of the carboxy group. It has a role as a plant metabolite, a xenobiotic and a fungal metabolite. It is an amino-acid betaine, a L-tryptophan derivative and an indole alkaloid. Hypaphorine has been reported in Pisolithus tinctorius, Caragana sinica, and other organisms with data available. |
Solubility Data
| Solubility (In Vitro) |
H2O: ~100 mg/mL (~406.0 mM) DMSO: < 1 mg/mL |
| Solubility (In Vivo) |
Solubility in Formulation 1: 100 mg/mL (406.01 mM) in PBS (add these co-solvents sequentially from left to right, and one by one), clear solution; with sonication. (Please use freshly prepared in vivo formulations for optimal results.) |
| Preparing Stock Solutions | 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | |
| 1 mM | 4.0601 mL | 20.3004 mL | 40.6009 mL | |
| 5 mM | 0.8120 mL | 4.0601 mL | 8.1202 mL | |
| 10 mM | 0.4060 mL | 2.0300 mL | 4.0601 mL |