Physicochemical Properties
| Molecular Formula | C18H23N5O2 |
| Molecular Weight | 341.407523393631 |
| Exact Mass | 341.185 |
| CAS # | 1782531-99-0 |
| Related CAS # | 1782531-99-0(HCl);502137-98-6; |
| PubChem CID | 135403620 |
| Appearance | Light yellow to yellow solid powder |
| LogP | 1.3 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 1 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 5 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 4 |
| Heavy Atom Count | 25 |
| Complexity | 625 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
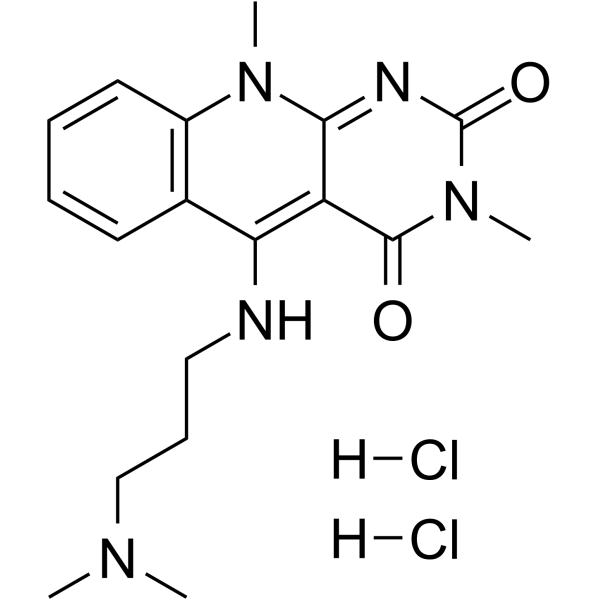
| SMILES | O=C1C2/C(/C3C=CC=CC=3N(C)C=2NC(N1C)=O)=N/CCCN(C)C |
| InChi Key | ACSJNMXHJOVJON-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
| InChi Code | InChI=1S/C18H23N5O2/c1-21(2)11-7-10-19-15-12-8-5-6-9-13(12)22(3)16-14(15)17(24)23(4)18(25)20-16/h5-6,8-9H,7,10-11H2,1-4H3,(H,20,25) |
| Chemical Name | 5-[3-(dimethylamino)propylimino]-3,10-dimethyl-1H-pyrimido[4,5-b]quinoline-2,4-dione |
| HS Tariff Code | 2934.99.9001 |
| Storage |
Powder-20°C 3 years 4°C 2 years In solvent -80°C 6 months -20°C 1 month Note: Please store this product in a sealed and protected environment, avoid exposure to moisture. |
| Shipping Condition | Room temperature (This product is stable at ambient temperature for a few days during ordinary shipping and time spent in Customs) |
Biological Activity
| Targets | Hdm2[1]; Apoptosis[1]; Antimalarial[2] |
| ln Vitro | Tumor cells expressing wild-type p53 are specifically eliminated by HLI373 (3-15 μM; 15 hours)[1]. Cellular Hdm2 is stabilized by HLI373 (10–50 μM) in a dose-dependent way. HLI373 (3 μM) stimulates transcription of p53[1].HLI373 inhibits Hdm2's auto-ubiquitylation with selectivity[1]. P53 is degraded by co-transfection with plasmids encoding Hdm2 and p53. Degradation of p53 is prevented by incubating with HLI373 (5–10 μM) for 8 hours. In cells, HLI373 raises the levels of the proteins p53 and Hdm2[1]. HLI 373 demonstrates early growth inhibition and reduced IC50 values (below 6 μM) against the chloroquine-sensitive P. falciparum D6 strain (PfD6) as well as the chloroquine-resistant P. falciparum W2 strain (PfW2)[2]. The MDM2 inhibitor HLI-373 can stop the activity of its substrate protein p53 being ubiquitinated by blocking the activity of ubiquitin E3 ligase. As an E3 ubiquitin ligase, HLI-373 targets the C-terminus[3]. |
| Cell Assay |
Cell Viability Assay[1] Cell Types: Wild type p53 mouse embryo fibroblasts (MEFs), and p53-deficient MEFs Tested Concentrations: 3, 10, 15 μM Incubation Duration: 15 hrs (hours) Experimental Results: Increased cell death in wild type p53 MEFs in a dose-dependent manner, p53-deficient MEFs were relatively resistant. Western Blot Analysis[1] Cell Types: U2OS cells Tested Concentrations: 5, 10 μM Incubation Duration: 8 hrs (hours) Experimental Results: Blocked p53 degradation caused by co-transfection with plasmids encoding p53 and Hdm2. |
| References |
[1]. Targeting Tumor Cells Expressing p53 With a Water-Soluble Inhibitor of Hdm2. Mol Cancer Ther. 2008 Aug;7(8):2445-54. [2]. Inhibitors of Ubiquitin E3 Ligase as Potential New Antimalarial Drug Leads. BMC Pharmacol Toxicol. 2017 Jun 2;18(1):40. [3]. MDM2 Promotes Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transition and Metastasis of Ovarian Cancer SKOV3 Cells. Br J Cancer. 2017 Oct 10;117(8):1192-1201. |
| Additional Infomation | 5-[3-(dimethylamino)propylamino]-3,10-dimethylpyrimido[4,5-b]quinoline-2,4-dione is an aminoquinoline. |
Solubility Data
| Solubility (In Vitro) |
H2O : ~38 mg/mL (~91.71 mM) DMSO : ~4 mg/mL (~9.65 mM) |
| Solubility (In Vivo) |
Note: Listed below are some common formulations that may be used to formulate products with low water solubility (e.g. < 1 mg/mL), you may test these formulations using a minute amount of products to avoid loss of samples. Injection Formulations (e.g. IP/IV/IM/SC) Injection Formulation 1: DMSO : Tween 80: Saline = 10 : 5 : 85 (i.e. 100 μL DMSO stock solution → 50 μL Tween 80 → 850 μL Saline) *Preparation of saline: Dissolve 0.9 g of sodium chloride in 100 mL ddH ₂ O to obtain a clear solution. Injection Formulation 2: DMSO : PEG300 :Tween 80 : Saline = 10 : 40 : 5 : 45 (i.e. 100 μL DMSO → 400 μLPEG300 → 50 μL Tween 80 → 450 μL Saline) Injection Formulation 3: DMSO : Corn oil = 10 : 90 (i.e. 100 μL DMSO → 900 μL Corn oil) Example: Take the Injection Formulation 3 (DMSO : Corn oil = 10 : 90) as an example, if 1 mL of 2.5 mg/mL working solution is to be prepared, you can take 100 μL 25 mg/mL DMSO stock solution and add to 900 μL corn oil, mix well to obtain a clear or suspension solution (2.5 mg/mL, ready for use in animals). Injection Formulation 4: DMSO : 20% SBE-β-CD in saline = 10 : 90 [i.e. 100 μL DMSO → 900 μL (20% SBE-β-CD in saline)] *Preparation of 20% SBE-β-CD in Saline (4°C,1 week): Dissolve 2 g SBE-β-CD in 10 mL saline to obtain a clear solution. Injection Formulation 5: 2-Hydroxypropyl-β-cyclodextrin : Saline = 50 : 50 (i.e. 500 μL 2-Hydroxypropyl-β-cyclodextrin → 500 μL Saline) Injection Formulation 6: DMSO : PEG300 : castor oil : Saline = 5 : 10 : 20 : 65 (i.e. 50 μL DMSO → 100 μLPEG300 → 200 μL castor oil → 650 μL Saline) Injection Formulation 7: Ethanol : Cremophor : Saline = 10: 10 : 80 (i.e. 100 μL Ethanol → 100 μL Cremophor → 800 μL Saline) Injection Formulation 8: Dissolve in Cremophor/Ethanol (50 : 50), then diluted by Saline Injection Formulation 9: EtOH : Corn oil = 10 : 90 (i.e. 100 μL EtOH → 900 μL Corn oil) Injection Formulation 10: EtOH : PEG300:Tween 80 : Saline = 10 : 40 : 5 : 45 (i.e. 100 μL EtOH → 400 μLPEG300 → 50 μL Tween 80 → 450 μL Saline) Oral Formulations Oral Formulation 1: Suspend in 0.5% CMC Na (carboxymethylcellulose sodium) Oral Formulation 2: Suspend in 0.5% Carboxymethyl cellulose Example: Take the Oral Formulation 1 (Suspend in 0.5% CMC Na) as an example, if 100 mL of 2.5 mg/mL working solution is to be prepared, you can first prepare 0.5% CMC Na solution by measuring 0.5 g CMC Na and dissolve it in 100 mL ddH2O to obtain a clear solution; then add 250 mg of the product to 100 mL 0.5% CMC Na solution, to make the suspension solution (2.5 mg/mL, ready for use in animals). Oral Formulation 3: Dissolved in PEG400 Oral Formulation 4: Suspend in 0.2% Carboxymethyl cellulose Oral Formulation 5: Dissolve in 0.25% Tween 80 and 0.5% Carboxymethyl cellulose Oral Formulation 6: Mixing with food powders Note: Please be aware that the above formulations are for reference only. InvivoChem strongly recommends customers to read literature methods/protocols carefully before determining which formulation you should use for in vivo studies, as different compounds have different solubility properties and have to be formulated differently. (Please use freshly prepared in vivo formulations for optimal results.) |
| Preparing Stock Solutions | 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | |
| 1 mM | 2.9290 mL | 14.6451 mL | 29.2903 mL | |
| 5 mM | 0.5858 mL | 2.9290 mL | 5.8581 mL | |
| 10 mM | 0.2929 mL | 1.4645 mL | 2.9290 mL |