Physicochemical Properties
| Molecular Formula | C18H18CL2N2O4S |
| Molecular Weight | 429.32 |
| Exact Mass | 428.036 |
| CAS # | 2415263-08-8 |
| PubChem CID | 146018923 |
| Appearance | White to off-white solid powder |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 3 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 5 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 6 |
| Heavy Atom Count | 27 |
| Complexity | 634 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| InChi Key | YWFDTXJORDWLGD-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
| InChi Code | InChI=1S/C18H17ClN2O4S.ClH/c19-13-3-5-16(25-8-1-7-20)15(10-13)18(22)21-14-4-2-12-6-9-26(23,24)17(12)11-14;/h2-6,9-11H,1,7-8,20H2,(H,21,22);1H |
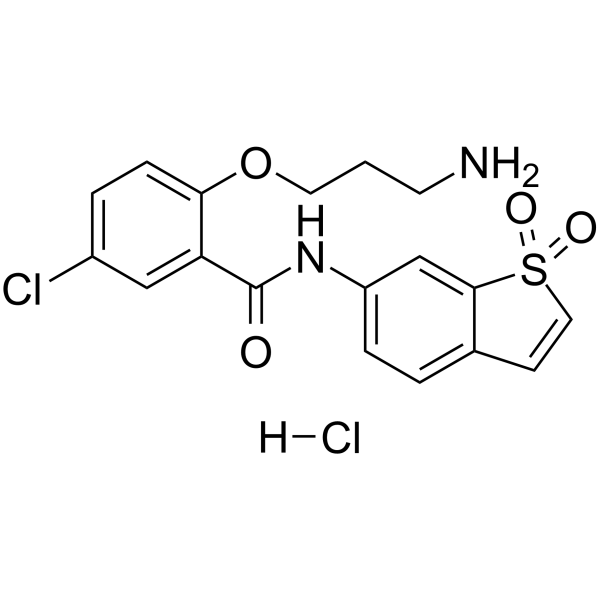
| Chemical Name | 2-(3-aminopropoxy)-5-chloro-N-(1,1-dioxo-1-benzothiophen-6-yl)benzamide;hydrochloride |
| HS Tariff Code | 2934.99.9001 |
| Storage |
Powder-20°C 3 years 4°C 2 years In solvent -80°C 6 months -20°C 1 month |
| Shipping Condition | Room temperature (This product is stable at ambient temperature for a few days during ordinary shipping and time spent in Customs) |
Biological Activity
| Targets | STAT3 |
| ln Vitro | HJC0416 hydrochloride, with IC50 values of 1.76 µM and 1.97 µM, respectively, inhibits the proliferation of both ER-positive and ER-negative (triple negative) breast cancer cells. AsPC1 and Panc-1, two pancreatic cancer cell lines, exhibit a strong antiproliferative impact against it, with IC50 values of 40 nM and 1.88 µM, respectively[1]. HJC0416 hydrochloride (1–10 µM; 48 hours) causes apoptosis and suppresses cell proliferation in MDA-MB-231 breast cancer cells, along with alterations in cellular morphology[1].The STAT3 promoter activity is reduced by about 51% in MDA-MB-231 cells transiently transfecting with the pSTAT3-Luc vector, but stattic (HY-13818) only reduces the STAT3 promoter activity by 39%[1]. Comparing HJC0416 hydrochloride (1–10 µM; 12 hours) to Stattic (HY-13818), it is equally effective in inhibiting the synthesis of STAT3 proteins and phosphorylation at the Tyr-705 site. In MDA-MB-231 cells, it also causes cleaved caspase-3 and downregulates cyclin D1 levels[1]. |
| ln Vivo | In comparison to the control mice, the intraperitoneal injection of HJC0416 hydrochloride (10 mg/kg) results in a 67% reduction in tumor volume after 7 days. Likewise, at a dose of 100 mg/kg, HJC0416 hydrochloride (oral administration; 100 mg/kg; 14 days) likewise significantly lowers tumor volume by 46%. Tumor volume decrease seemed to be superior with the ip approach. It is particularly remarkable that, at a dose of 100 mg/kg, HJC0416 does not exhibit any discernible toxicity[1]. |
| Cell Assay |
Cell Cycle Analysis[1] Cell Types: MDA- MB-231 breast cancer cells Tested Concentrations: 1-10 µM Incubation Duration: 48 hrs (hours) Experimental Results: Induced cell apoptosis in cancer cells. Apoptosis Analysis[1] Cell Types: MDA-MB-231 breast cancer cells Tested Concentrations: 1 µM; 5 µM; 10 µM Incubation Duration: 12 hrs (hours) Experimental Results: diminished p-STAT3 phosphorylation expression and cyclin D1 level. |
| Animal Protocol |
Animal/Disease Models: Mice with MDA-MB-231 cells[1] Doses: 10 mg/kg (ip); 100 mg/kg (oral) Route of Administration: intraperitoneal (ip)injection, 7 days; oral administration, 14 days Experimental Results: demonstrated antitumor effects in the MDA-MB-231 triple-negative breast cancer murine xenograft model. |
| References |
[1]. Discovery of Potent Anticancer Agent HJC0416, an Orally Bioavailable Small Molecule Inhibitor of Signal Transducer and Activator of Transcription 3 (STAT3). Eur J Med Chem. 2014 Jul 23;82:195-203. |
Solubility Data
| Solubility (In Vitro) | May dissolve in DMSO (in most cases), if not, try other solvents such as H2O, Ethanol, or DMF with a minute amount of products to avoid loss of samples |
| Solubility (In Vivo) |
Note: Listed below are some common formulations that may be used to formulate products with low water solubility (e.g. < 1 mg/mL), you may test these formulations using a minute amount of products to avoid loss of samples. Injection Formulations (e.g. IP/IV/IM/SC) Injection Formulation 1: DMSO : Tween 80: Saline = 10 : 5 : 85 (i.e. 100 μL DMSO stock solution → 50 μL Tween 80 → 850 μL Saline) *Preparation of saline: Dissolve 0.9 g of sodium chloride in 100 mL ddH ₂ O to obtain a clear solution. Injection Formulation 2: DMSO : PEG300 :Tween 80 : Saline = 10 : 40 : 5 : 45 (i.e. 100 μL DMSO → 400 μLPEG300 → 50 μL Tween 80 → 450 μL Saline) Injection Formulation 3: DMSO : Corn oil = 10 : 90 (i.e. 100 μL DMSO → 900 μL Corn oil) Example: Take the Injection Formulation 3 (DMSO : Corn oil = 10 : 90) as an example, if 1 mL of 2.5 mg/mL working solution is to be prepared, you can take 100 μL 25 mg/mL DMSO stock solution and add to 900 μL corn oil, mix well to obtain a clear or suspension solution (2.5 mg/mL, ready for use in animals). Injection Formulation 4: DMSO : 20% SBE-β-CD in saline = 10 : 90 [i.e. 100 μL DMSO → 900 μL (20% SBE-β-CD in saline)] *Preparation of 20% SBE-β-CD in Saline (4°C,1 week): Dissolve 2 g SBE-β-CD in 10 mL saline to obtain a clear solution. Injection Formulation 5: 2-Hydroxypropyl-β-cyclodextrin : Saline = 50 : 50 (i.e. 500 μL 2-Hydroxypropyl-β-cyclodextrin → 500 μL Saline) Injection Formulation 6: DMSO : PEG300 : castor oil : Saline = 5 : 10 : 20 : 65 (i.e. 50 μL DMSO → 100 μLPEG300 → 200 μL castor oil → 650 μL Saline) Injection Formulation 7: Ethanol : Cremophor : Saline = 10: 10 : 80 (i.e. 100 μL Ethanol → 100 μL Cremophor → 800 μL Saline) Injection Formulation 8: Dissolve in Cremophor/Ethanol (50 : 50), then diluted by Saline Injection Formulation 9: EtOH : Corn oil = 10 : 90 (i.e. 100 μL EtOH → 900 μL Corn oil) Injection Formulation 10: EtOH : PEG300:Tween 80 : Saline = 10 : 40 : 5 : 45 (i.e. 100 μL EtOH → 400 μLPEG300 → 50 μL Tween 80 → 450 μL Saline) Oral Formulations Oral Formulation 1: Suspend in 0.5% CMC Na (carboxymethylcellulose sodium) Oral Formulation 2: Suspend in 0.5% Carboxymethyl cellulose Example: Take the Oral Formulation 1 (Suspend in 0.5% CMC Na) as an example, if 100 mL of 2.5 mg/mL working solution is to be prepared, you can first prepare 0.5% CMC Na solution by measuring 0.5 g CMC Na and dissolve it in 100 mL ddH2O to obtain a clear solution; then add 250 mg of the product to 100 mL 0.5% CMC Na solution, to make the suspension solution (2.5 mg/mL, ready for use in animals). Oral Formulation 3: Dissolved in PEG400 Oral Formulation 4: Suspend in 0.2% Carboxymethyl cellulose Oral Formulation 5: Dissolve in 0.25% Tween 80 and 0.5% Carboxymethyl cellulose Oral Formulation 6: Mixing with food powders Note: Please be aware that the above formulations are for reference only. InvivoChem strongly recommends customers to read literature methods/protocols carefully before determining which formulation you should use for in vivo studies, as different compounds have different solubility properties and have to be formulated differently. (Please use freshly prepared in vivo formulations for optimal results.) |
| Preparing Stock Solutions | 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | |
| 1 mM | 2.3293 mL | 11.6463 mL | 23.2926 mL | |
| 5 mM | 0.4659 mL | 2.3293 mL | 4.6585 mL | |
| 10 mM | 0.2329 mL | 1.1646 mL | 2.3293 mL |