Physicochemical Properties
| Molecular Formula | C15H10O5 |
| Molecular Weight | 270.24 |
| Exact Mass | 270.052 |
| CAS # | 548-83-4 |
| Related CAS # | Galangin-13C3 |
| PubChem CID | 5281616 |
| Appearance | Light yellow to yellow solid powder |
| Density | 1.6±0.1 g/cm3 |
| Boiling Point | 518.6±50.0 °C at 760 mmHg |
| Melting Point | 214-215 °C(lit.) |
| Flash Point | 202.0±23.6 °C |
| Vapour Pressure | 0.0±1.4 mmHg at 25°C |
| Index of Refraction | 1.748 |
| LogP | 2.83 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 3 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 5 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 1 |
| Heavy Atom Count | 20 |
| Complexity | 424 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| InChi Key | VCCRNZQBSJXYJD-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
| InChi Code | InChI=1S/C15H10O5/c16-9-6-10(17)12-11(7-9)20-15(14(19)13(12)18)8-4-2-1-3-5-8/h1-7,16-17,19H |
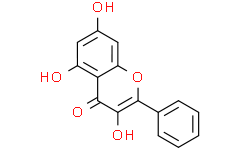
| Chemical Name | 3,5,7-trihydroxy-2-phenylchromen-4-one |
| Synonyms | Norizalpinin Galangin |
| HS Tariff Code | 2934.99.9001 |
| Storage |
Powder-20°C 3 years 4°C 2 years In solvent -80°C 6 months -20°C 1 month |
| Shipping Condition | Room temperature (This product is stable at ambient temperature for a few days during ordinary shipping and time spent in Customs) |
Biological Activity
| ln Vitro | Thin layer chromatography was used to measure how dose-dependently galangin (Norizalpinin) blocks the downstream activation of DMBA. Moreover, galangin prevents DMBA-DNA adducts and DMBA-induced cell proliferation. As shown by O-determinase activity in intact cells and by isolated microsomes from DMBA-treated cells, galangal produced a strong dose-dependent suppression of CYP1A1 activity. The results of the double reciprocal plot analysis of inhibition kinetics indicate that galangal, as opposed to non-galangin, increased the levels of CYP1A1 mRNA, indicating that it may be an agonist of the aryl hydrocarbon receptor. However, it inhibits the induction of CYP1A1 mRNA by -p-dioxin (TCDD) or DMBA. Moreover, galangin prevents the control of reporter vectors carrying the CYP1A1 promoter by TCDD or DMBA [1]. Cells are treated with galangin to induce autophagy (at 130 μM) and labeling (at 370 μM). Specifically, treatment of HepG2 cells with galangin results in a rise in microtubule-associated protein light chain 3 levels, an accumulation of autophagosomes, and an increase in the percentage of cells within the vacuole. Additionally, p53 expression is elevated. While overexpressing p53 in Hep3B cells returns the majority of galangin-induced vacuolated cells to normal levels, p53 inhibition in HepG2 cells alleviates galangin-induced autophagy [2]. |
| ADME/Pharmacokinetics |
Metabolism / Metabolites Galangin has known human metabolites that include (2S,3S,4S,5R)-6-(5,7-dihydroxy-4-oxo-2-phenylchromen-3-yl)oxy-3,4,5-trihydroxyoxane-2-carboxylic acid, Kaempferol, and (2S,3S,4S,5R)-6-(3,5-dihydroxy-4-oxo-2-phenylchromen-7-yl)oxy-3,4,5-trihydroxyoxane-2-carboxylic acid. |
| References |
[1]. The flavonoid galangin is an inhibitor of CYP1A1 activity and an agonist/antagonist of the aryl hydrocarbon receptor. Br J Cancer. 1999 Mar;79(9-10):1340-6. [2]. Galangin induces autophagy through upregulation of p53 in HepG2 cells. Pharmacology. 2012;89(5-6):247-55. |
| Additional Infomation |
Galangin is a 7-hydroxyflavonol with additional hydroxy groups at positions 3 and 5 respectively; a growth inhibitor of breast tumor cells. It has a role as an antimicrobial agent, an EC 3.1.1.3 (triacylglycerol lipase) inhibitor and a plant metabolite. It is a trihydroxyflavone and a 7-hydroxyflavonol. Galangin has been reported in Camellia sinensis, Apis, and other organisms with data available. |
Solubility Data
| Solubility (In Vitro) | DMSO : ~125 mg/mL (~462.55 mM) |
| Solubility (In Vivo) |
Solubility in Formulation 1: ≥ 2.08 mg/mL (7.70 mM) (saturation unknown) in 10% DMSO + 40% PEG300 +5% Tween-80 + 45% Saline (add these co-solvents sequentially from left to right, and one by one), clear solution. For example, if 1 mL of working solution is to be prepared, you can add 100 μL of 20.8 mg/mL clear DMSO stock solution to 400 μL PEG300 and mix evenly; then add 50 μL Tween-80 + to the above solution and mix evenly; then add 450 μL normal saline to adjust the volume to 1 mL. Preparation of saline: Dissolve 0.9 g of sodium chloride in 100 mL ddH₂ O to obtain a clear solution. (Please use freshly prepared in vivo formulations for optimal results.) |
| Preparing Stock Solutions | 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | |
| 1 mM | 3.7004 mL | 18.5021 mL | 37.0041 mL | |
| 5 mM | 0.7401 mL | 3.7004 mL | 7.4008 mL | |
| 10 mM | 0.3700 mL | 1.8502 mL | 3.7004 mL |