Physicochemical Properties
| Molecular Formula | C22H20FN5O2 |
| Molecular Weight | 405.4249 |
| Exact Mass | 405.16 |
| Elemental Analysis | C, 65.18; H, 4.97; F, 4.69; N, 17.27; O, 7.89 |
| CAS # | 1449277-10-4 |
| Related CAS # | 1449277-10-4 |
| PubChem CID | 89730041 |
| Appearance | Yellow solid powder |
| Density | 1.5±0.1 g/cm3 |
| Boiling Point | 734.5±60.0 °C at 760 mmHg |
| Flash Point | 398.0±32.9 °C |
| Vapour Pressure | 0.0±2.4 mmHg at 25°C |
| Index of Refraction | 1.712 |
| LogP | 2.54 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 2 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 6 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 4 |
| Heavy Atom Count | 30 |
| Complexity | 668 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| SMILES | FC1=C([H])C([H])=C([H])C(=C1[H])C1C([H])=C([H])C2=C(C(N([H])[H])=NC([H])=C2C(N([H])C2([H])C([H])([H])N(C2([H])[H])C(C2([H])C([H])([H])C2([H])[H])=O)=O)N=1 |
| InChi Key | FYXCIBJXJYBWPX-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
| InChi Code | InChI=1S/C22H20FN5O2/c23-14-3-1-2-13(8-14)18-7-6-16-17(9-25-20(24)19(16)27-18)21(29)26-15-10-28(11-15)22(30)12-4-5-12/h1-3,6-9,12,15H,4-5,10-11H2,(H2,24,25)(H,26,29) |
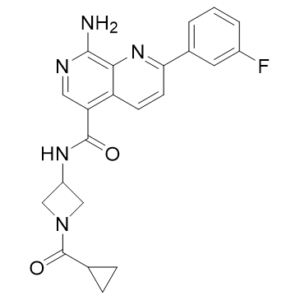
| Chemical Name | 8-amino-N-[1-(cyclopropanecarbonyl)azetidin-3-yl]-2-(3-fluorophenyl)-1,7-naphthyridine-5-carboxamide |
| Synonyms | GNE 495; GNE495; GNE-495 |
| HS Tariff Code | 2934.99.9001 |
| Storage |
Powder-20°C 3 years 4°C 2 years In solvent -80°C 6 months -20°C 1 month |
| Shipping Condition | Room temperature (This product is stable at ambient temperature for a few days during ordinary shipping and time spent in Customs) |
Biological Activity
| Targets | MAP4K4 (IC50 = 3.7 nM) |
| ln Vitro | GNE-495 is a strong MAP4K4 inhibitor that works well to promote angiogenesis. GNE-495 exhibits minimum body stability, permeability, efficient ideal cellular equilibrium, and MAP4K4 adsorption [1]. |
| ln Vivo | High doses of GNE-495—25 and 50 mg/kg—were given intraperitoneally to newborn mouse pups. In every species examined, GNE-495 demonstrates favorable internal characteristics, including low clearance, moderate terminal half-phase decay, and appropriate leverage levels (F=37–47%) [1]. |
| Animal Protocol |
Rats, Mice and Pups For the brain cassette study, three male Sprague-Dawley (SD) rats receive an intravenous (IV) bolus dose of six test substances (for example, GNE-495; 0.5 mg/kg). GNE-495 is injected intravenously in bolus doses of 1 mg/kg in female CD-1 mice for the mouse PK study. GNE-495 (5 mg/kg) is additionally injected intravenously (PO) into female CD-1 mice. The rat brain cassette PK is dosed at 2 mL/kg, and all other doses are administered at 5 mL/kg. Water and food are available to animals at all times, and they are not fasted before receiving a dose. Three blood samples (~60 μL) are taken from each mouse up to either 9 or 24 hours after the compound of interest is given. This is done using a serial sampling method, and it involves taking three blood samples from each mouse. After being mixed with K2EDTA and placed on ice or in a cold Kryorack immediately after collection, the blood is then centrifuged to separate the plasma. Blood samples are centrifuged for 10–15 minutes at 4°C while being spun at a speed of 1000-2000× g within an hour of being drawn. This process yields the plasma. The plasma samples are stored at -70 to -80°C until analysis. For neonate PK, 3-day-old CD1 pups are injected with 25 mg/kg and 50 mg/kg GNE-495. Blood samples are taken intraperitoneally at the times specified, retinas are taken one hour after the dose, snap frozen in liquid nitrogen, and kept at -80°C until analysis. The concentrations of plasma and retinal lysate are assessed using LC/MS/MS. |
| References |
[1]. Structure-Based Design of GNE-495, a Potent and Selective MAP4K4 Inhibitor with Efficacy in Retinal Angiogenesis. ACS Med Chem Lett. 2015 Jun 29;6(8):913-8. |
Solubility Data
| Solubility (In Vitro) | DMSO: ~2.2 mg/mL (~5.4 mM) |
| Solubility (In Vivo) |
Solubility in Formulation 1: ≥ 0.22 mg/mL (0.54 mM) (saturation unknown) in 10% DMSO + 40% PEG300 + 5% Tween80 + 45% Saline (add these co-solvents sequentially from left to right, and one by one), clear solution. For example, if 1 mL of working solution is to be prepared, you can add 100 μL of 2.2 mg/mL clear DMSO stock solution to 400 μL PEG300 and mix evenly; then add 50 μL Tween-80 to the above solution and mix evenly; then add 450 μL normal saline to adjust the volume to 1 mL. Preparation of saline: Dissolve 0.9 g of sodium chloride in 100 mL ddH₂ O to obtain a clear solution. Solubility in Formulation 2: ≥ 0.22 mg/mL (0.54 mM) (saturation unknown) in 10% DMSO + 90% (20% SBE-β-CD in Saline) (add these co-solvents sequentially from left to right, and one by one), clear solution. For example, if 1 mL of working solution is to be prepared, you can add 100 μL of 2.2 mg/mL clear DMSO stock solution to 900 μL of 20% SBE-β-CD physiological saline solution and mix evenly. Preparation of 20% SBE-β-CD in Saline (4°C,1 week): Dissolve 2 g SBE-β-CD in 10 mL saline to obtain a clear solution. Solubility in Formulation 3: ≥ 0.22 mg/mL (0.54 mM) (saturation unknown) in 10% DMSO + 90% Corn Oil (add these co-solvents sequentially from left to right, and one by one), clear solution. For example, if 1 mL of working solution is to be prepared, you can add 100 μL of 2.2 mg/mL clear DMSO stock solution to 900 μL of corn oil and mix evenly. (Please use freshly prepared in vivo formulations for optimal results.) |
| Preparing Stock Solutions | 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | |
| 1 mM | 2.4666 mL | 12.3329 mL | 24.6658 mL | |
| 5 mM | 0.4933 mL | 2.4666 mL | 4.9332 mL | |
| 10 mM | 0.2467 mL | 1.2333 mL | 2.4666 mL |