Physicochemical Properties
| Molecular Formula | C18H14F3N5O2 |
| Molecular Weight | 389.33 |
| Elemental Analysis | C, 55.53; H, 3.62; F, 14.64; N, 17.99; O, 8.22 |
| CAS # | 1590403-33-0 |
| Appearance | White to off-white solid powder |
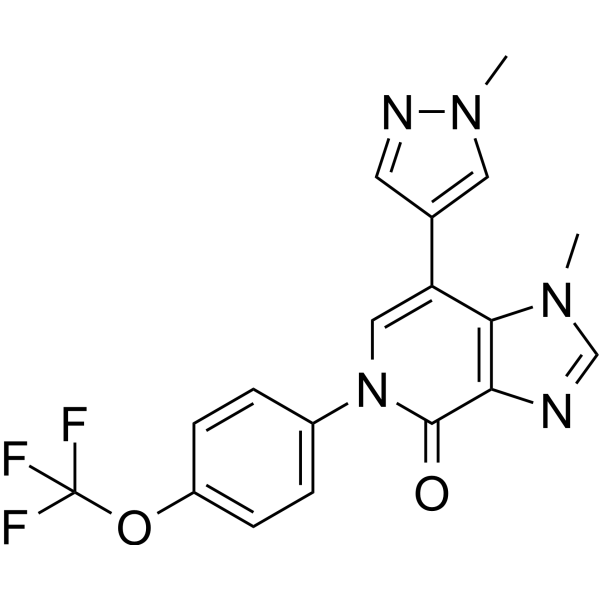
| SMILES | CN1C=C(C=N1)C2=CN(C(=O)C3=C2N(C=N3)C)C4=CC=C(C=C4)OC(F)(F)F |
| Synonyms | AK3287; AK3 287; SEA5EKP5LY; GDC-3280; AKEX 0011; SCHEMBL16474443; AKEX-0011; GDC3280; BDBM168497; ...; 1590403-33-0; AKEX0011 |
| HS Tariff Code | 2934.99.9001 |
| Storage |
Powder-20°C 3 years 4°C 2 years In solvent -80°C 6 months -20°C 1 month |
| Shipping Condition | Room temperature (This product is stable at ambient temperature for a few days during ordinary shipping and time spent in Customs) |
Biological Activity
| Targets | ASK1 - p38 MAPK signaling pathway |
| ln Vitro |
AKEX0011 inhibits the secretion of inflammatory cytokines in silica-stimulated macrophage cell lines by blocking the ASK1-p38 pathway. It reduces the levels of TNF-α, IL-1β, IL-6, TGF-β, IL-4, and IL-10, as detected by ELISA [1] - AKEX0011 suppresses macrophage apoptosis in both pre-treatment and post-treatment models, which is associated with the inhibition of the ASK1-p38 pathway. Apoptosis is measured by flow cytometry using Annexin V/PI staining [1] - AKEX0011 regulates macrophage polarization by inhibiting M1 polarization, as shown by decreased expression of M1 markers (iNOS, CD86) and altered expression of M2 markers (CD206, Arg-1) detected via qPCR and western blot [1] |
| ln Vivo |
- In a murine silicosis model, AKEX0011 alleviates silica-induced lung damage (assessed by histopathology) and improves respiratory dysfunction. It reduces the secretion of inflammatory and fibrotic factors (TNF-α, IL-1β, IL-6, TGF-β, IL-4, IL-10) in lung tissues, measured by ELISA [1] - AKEX0011 decreases the deposition of fibrosis-related proteins (collagen I, fibronectin, α-SMA) in lung tissues of silicosis mice, detected by immunohistochemistry and western blot. This effect is observed in both early and advanced treatment stages [1] - AKEX0011 attenuates silicosis by inhibiting apoptosis (TUNEL assay) and regulating macrophage polarization in vivo, with reduced ASK1 and p38 phosphorylation in lung tissues (western blot) [1] |
| Cell Assay |
- For cytokine secretion: Macrophage cell lines are stimulated with silica and treated with AKEX0011 at various concentrations. After 24-48 hours, supernatants are collected, and cytokine levels (TNF-α, IL-1β, etc.) are measured by ELISA [1] - For apoptosis detection: Macrophages are treated with AKEX0011 before or after silica stimulation. Cells are stained with Annexin V/PI and analyzed by flow cytometry to quantify apoptotic cells [1] - For macrophage polarization: Silica-stimulated macrophages are treated with AKEX0011. qPCR is used to detect mRNA levels of iNOS, CD86, CD206, and Arg-1; western blot is used to measure protein expression of these markers [1] |
| Animal Protocol |
- Mice are induced to develop silicosis by intratracheal instillation of silica. AKEX0011 is administered via intraperitoneal injection at different time points (early treatment: starting 1 day post-induction; advanced treatment: starting 14 days post-induction). The treatment is continued for a specified period, and mice are sacrificed to collect lung tissues for histopathological and molecular analysis [1] |
| References |
[1]. A Novel N-Arylpyridone Compound Alleviates the Inflammatory and Fibrotic Reaction of Silicosis by Inhibiting the ASK1-p38 Pathway and Regulating Macrophage Polarization. Front Pharmacol. 2022 Mar 23;13:848435. |
| Additional Infomation |
- AKEX0011 is a novel N-arylpyridone compound that exerts protective effects against silica-induced pulmonary inflammation and fibrosis in vitro and in vivo, making it a potential candidate for silicosis treatment [1] - Its mechanism of action primarily involves inhibiting the ASK1-p38 MAPK signaling pathway, thereby regulating macrophage polarization, suppressing macrophage apoptosis, and reducing inflammatory and fibrotic responses [1] |
Solubility Data
| Solubility (In Vitro) | DMSO : ~31.25 mg/mL (~80.27 mM; with ultrasonication (<60°C)) |
| Solubility (In Vivo) |
Note: Listed below are some common formulations that may be used to formulate products with low water solubility (e.g. < 1 mg/mL), you may test these formulations using a minute amount of products to avoid loss of samples. Injection Formulations (e.g. IP/IV/IM/SC) Injection Formulation 1: DMSO : Tween 80: Saline = 10 : 5 : 85 (i.e. 100 μL DMSO stock solution → 50 μL Tween 80 → 850 μL Saline) *Preparation of saline: Dissolve 0.9 g of sodium chloride in 100 mL ddH ₂ O to obtain a clear solution. Injection Formulation 2: DMSO : PEG300 :Tween 80 : Saline = 10 : 40 : 5 : 45 (i.e. 100 μL DMSO → 400 μLPEG300 → 50 μL Tween 80 → 450 μL Saline) Injection Formulation 3: DMSO : Corn oil = 10 : 90 (i.e. 100 μL DMSO → 900 μL Corn oil) Example: Take the Injection Formulation 3 (DMSO : Corn oil = 10 : 90) as an example, if 1 mL of 2.5 mg/mL working solution is to be prepared, you can take 100 μL 25 mg/mL DMSO stock solution and add to 900 μL corn oil, mix well to obtain a clear or suspension solution (2.5 mg/mL, ready for use in animals). Injection Formulation 4: DMSO : 20% SBE-β-CD in saline = 10 : 90 [i.e. 100 μL DMSO → 900 μL (20% SBE-β-CD in saline)] *Preparation of 20% SBE-β-CD in Saline (4°C,1 week): Dissolve 2 g SBE-β-CD in 10 mL saline to obtain a clear solution. Injection Formulation 5: 2-Hydroxypropyl-β-cyclodextrin : Saline = 50 : 50 (i.e. 500 μL 2-Hydroxypropyl-β-cyclodextrin → 500 μL Saline) Injection Formulation 6: DMSO : PEG300 : castor oil : Saline = 5 : 10 : 20 : 65 (i.e. 50 μL DMSO → 100 μLPEG300 → 200 μL castor oil → 650 μL Saline) Injection Formulation 7: Ethanol : Cremophor : Saline = 10: 10 : 80 (i.e. 100 μL Ethanol → 100 μL Cremophor → 800 μL Saline) Injection Formulation 8: Dissolve in Cremophor/Ethanol (50 : 50), then diluted by Saline Injection Formulation 9: EtOH : Corn oil = 10 : 90 (i.e. 100 μL EtOH → 900 μL Corn oil) Injection Formulation 10: EtOH : PEG300:Tween 80 : Saline = 10 : 40 : 5 : 45 (i.e. 100 μL EtOH → 400 μLPEG300 → 50 μL Tween 80 → 450 μL Saline) Oral Formulations Oral Formulation 1: Suspend in 0.5% CMC Na (carboxymethylcellulose sodium) Oral Formulation 2: Suspend in 0.5% Carboxymethyl cellulose Example: Take the Oral Formulation 1 (Suspend in 0.5% CMC Na) as an example, if 100 mL of 2.5 mg/mL working solution is to be prepared, you can first prepare 0.5% CMC Na solution by measuring 0.5 g CMC Na and dissolve it in 100 mL ddH2O to obtain a clear solution; then add 250 mg of the product to 100 mL 0.5% CMC Na solution, to make the suspension solution (2.5 mg/mL, ready for use in animals). Oral Formulation 3: Dissolved in PEG400 Oral Formulation 4: Suspend in 0.2% Carboxymethyl cellulose Oral Formulation 5: Dissolve in 0.25% Tween 80 and 0.5% Carboxymethyl cellulose Oral Formulation 6: Mixing with food powders Note: Please be aware that the above formulations are for reference only. InvivoChem strongly recommends customers to read literature methods/protocols carefully before determining which formulation you should use for in vivo studies, as different compounds have different solubility properties and have to be formulated differently. (Please use freshly prepared in vivo formulations for optimal results.) |
| Preparing Stock Solutions | 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | |
| 1 mM | 2.5685 mL | 12.8426 mL | 25.6852 mL | |
| 5 mM | 0.5137 mL | 2.5685 mL | 5.1370 mL | |
| 10 mM | 0.2569 mL | 1.2843 mL | 2.5685 mL |