Ezatiostat (formerly known as TER199; TLK199; Brand name: Telentra) is a glutathione analog inhibitor of glutathione S-transferase P1-1 (GSTP1-1). It was shown that an ezatiostat response profile contains two miRNAs that regulate expression of genes known to be implicated in MDS disease pathology. Remarkably, pathway analysis of the response profile revealed that the genes comprising the jun-N-terminal kinase/c-Jun molecular pathway, which is known to be activated by ezatiostat, are under-expressed in patients who respond and over-expressed in patients who were non-responders to the drug, suggesting that both the biology of the disease and the molecular mechanism of action of the drug are positively correlated.
Physicochemical Properties
| Molecular Formula | C27H35N3O6S |
| Molecular Weight | 529.6483 |
| Exact Mass | 529.224 |
| CAS # | 168682-53-9 |
| Related CAS # | TLK117;152684-53-2;Ezatiostat hydrochloride;286942-97-0 |
| PubChem CID | 5310939 |
| Appearance | White to off-white solid powder |
| Density | 1.2±0.1 g/cm3 |
| Boiling Point | 749.7±60.0 °C at 760 mmHg |
| Flash Point | 407.2±32.9 °C |
| Vapour Pressure | 0.0±2.5 mmHg at 25°C |
| Index of Refraction | 1.569 |
| LogP | 4.27 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 3 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 8 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 17 |
| Heavy Atom Count | 37 |
| Complexity | 725 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 3 |
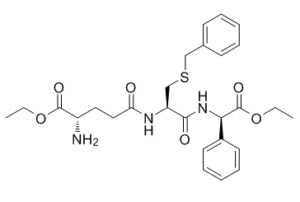
| SMILES | CCOC(=O)[C@H](CCC(=O)N[C@@H](CSCC1=CC=CC=C1)C(=O)N[C@H](C2=CC=CC=C2)C(=O)OCC)N |
| InChi Key | GWEJFLVSOGNLSS-FIXSFTCYSA-N |
| InChi Code | InChI=1S/C27H35N3O6S/c1-3-35-26(33)21(28)15-16-23(31)29-22(18-37-17-19-11-7-5-8-12-19)25(32)30-24(27(34)36-4-2)20-13-9-6-10-14-20/h5-14,21-22,24H,3-4,15-18,28H2,1-2H3,(H,29,31)(H,30,32)/t21-,22-,24-/m0/s1 |
| Chemical Name | (S)-ethyl 2-amino-5-(((R)-3-(benzylthio)-1-(((S)-2-ethoxy-2-oxo-1-phenylethyl)amino)-1-oxopropan-2-yl)amino)-5-oxopentanoate |
| Synonyms | TLK199; TLK-199; TLK 199; Ezatiostat; TER-199; TLK-199 hydrochloride; TER 199; TLK 199 hydrochloride; TER199; TLK199 hydrochloride; trade name: Telintra |
| HS Tariff Code | 2934.99.9001 |
| Storage |
Powder-20°C 3 years 4°C 2 years In solvent -80°C 6 months -20°C 1 month Note: Please store this product in a sealed and protected environment, avoid exposure to moisture. |
| Shipping Condition | Room temperature (This product is stable at ambient temperature for a few days during ordinary shipping and time spent in Customs) |
Biological Activity
| Targets |
Glutathione S-Transferase P1-1 (GSTpi/GSTP1-1) (Ki = 0.3 μM in substrate competition assay; IC50 = 0.8 μM in recombinant GSTpi enzyme activity assay) [2] c-Jun N-terminal Kinase (JNK) (no direct binding, modulation via GSTpi inhibition; p-JNK upregulation with EC50 = 1.5 μM in MCF-7 cells) [2] Extracellular Signal-Regulated Kinase (ERK1/2) (no direct binding, modulation via GSTpi inhibition; p-ERK downregulation with IC50 = 2.0 μM in HT29 cells) [2] Fas/FasL signaling pathway (no direct IC50/Ki, upregulation in MDS cells via GSTpi inhibition) [1] |
| ln Vitro |
When ezatiostat dissociates the enzyme from the jun-N-terminal kinase/c-Jun (JNK/JUN) complex, phosphorylation of JNK results in JNK activation. Ezatiostat appears to have both malignant clone apoptosis and normal myeloid progenitor cell growth as therapeutic effects [1]. Selecting resistant clones of the HL60 tumor cell line through prolonged exposure to ezatiostat (TLK199) causes high levels of apoptosis in cells and increases the activity of c-Jun NH2-terminal kinase (JNK1) and ERK1/ERK2 in cells, allowing them to proliferate under stress conditions in comparison to wild type [2]. Ezatiostat acts as a selective inhibitor of glutathione S-transferase P1-1 (GSTpi): it competitively inhibits recombinant human GSTpi enzyme activity with an IC50 of 0.8 μM and binds to the GSTpi active site with a Ki of 0.3 μM; it shows no significant inhibition of other GST isoforms (GSTα, GSTμ) at concentrations up to 10 μM (inhibition <10%) [2] In CD34⁺ bone marrow cells from patients with lower-risk myelodysplastic syndrome (MDS), Ezatiostat (0.5-5 μM) dose-dependently inhibits cell proliferation: at 1.2 μM, it reduces CD34⁺ cell viability by 50% (MTT assay, 72 hours) and induces apoptosis in 45% of cells (Annexin V/PI flow cytometry) vs. 5% in vehicle-treated cells; Western blotting detects cleaved caspase-3 (17 kDa fragment) and upregulated Fas/FasL expression (2.3-fold vs. control) [1] In human cancer cell lines (MCF-7 breast cancer, HT29 colon cancer), Ezatiostat (1-10 μM) modulates MAPK signaling pathways by disrupting GSTpi-JNK interaction: at 2.5 μM, it increases phosphorylated JNK (p-JNK) levels by 3.0-fold and decreases phosphorylated ERK1/2 (p-ERK1/2) by 0.4-fold (Western blotting), leading to 70% inhibition of cell proliferation (72 hours MTT) in MCF-7 cells [2] Ezatiostat (5 μM) reduces clonogenic growth of MDS CD34⁺ cells in soft agar assay: colony formation efficiency decreases from 12% to 2% vs. control, and it suppresses the growth of GSTpi-overexpressing MDS cell clones specifically [1] In normal human CD34⁺ hematopoietic stem cells, Ezatiostat shows low cytotoxicity (CC50 = 10 μM), with only 15% cell viability reduction at 5 μM (72 hours), indicating selective toxicity towards MDS cells [1] |
| ln Vivo |
Ezatiostat (TLK199) administration increases the generation of lymphocytes and the proliferation of myeloid progenitor cells (colony forming units, granulocyte macrophages), but only in mice that are glutathione S-transferase P1-1 (GSTP1+/+) and not in GSTP1-/- animals. 2]. In NOD/SCID mice xenografted with human lower-risk MDS CD34⁺ cells (1×10⁶ cells via tail vein injection), intraperitoneal administration of Ezatiostat (10-50 mg/kg/day) for 21 days dose-dependently reduces MDS cell engraftment: the 50 mg/kg dose decreases the percentage of human CD34⁺ cells in mouse bone marrow from 35% to 10% (flow cytometry) and prolongs mouse median survival from 28 days to 42 days (50% extension) [1] In nude mice bearing MCF-7 breast cancer xenografts (5×10⁶ cells subcutaneously injected), oral administration of Ezatiostat (20 mg/kg/day) for 14 days inhibits tumor growth by 60% (tumor volume from 800 mm³ to 320 mm³) and reduces GSTpi activity in tumor tissues by 70% (GST enzyme assay); immunohistochemistry of tumor sections shows increased p-JNK expression (2.5-fold vs. vehicle) and reduced Ki-67 proliferation index (from 70% to 20%) [2] Ezatiostat (30 mg/kg/day, i.p.) in MDS xenograft mice restores normal hematopoiesis: the percentage of mouse bone marrow erythroid precursors (Ter119⁺) increases from 25% to 45% vs. vehicle, and peripheral blood hemoglobin levels rise from 8 g/dL to 11 g/dL [1] |
| Enzyme Assay |
1. Recombinant GSTpi enzyme activity assay: Prepare recombinant human GSTpi (full-length, residues 1-209) and dilute to a final concentration of 10 nM in GST reaction buffer (50 mM Tris-HCl pH 7.5, 1 mM reduced glutathione (GSH), 0.1 mM EDTA, 0.1 mM DTT); incubate the enzyme with serial dilutions of Ezatiostat (0.1-10 μM) at 37°C for 10 minutes; initiate the reaction by adding 1-chloro-2,4-dinitrobenzene (CDNB, 1 mM, a GST-specific substrate) and monitor the change in absorbance at 340 nm for 30 minutes using a microplate reader; fit inhibition curves to a four-parameter logistic model to calculate IC50 values for GSTpi inhibition [2] 2. GSTpi substrate competition assay (fluorescence polarization): Label the GSTpi substrate GSH with a fluorescent tag (FAM-GSH, 20 nM) and dilute recombinant GSTpi to 50 nM in binding buffer (20 mM HEPES pH 7.4, 150 mM NaCl, 0.01% Tween 20); incubate GSTpi with serial dilutions of Ezatiostat (0.01-10 μM) and FAM-GSH at 25°C for 60 minutes; measure fluorescence polarization (FP) values (excitation 485 nm, emission 530 nm) using a microplate reader; calculate the Ki value for Ezatiostat binding to GSTpi via the Cheng-Prusoff equation [2] 3. GST isoform selectivity assay: Incubate recombinant human GSTα, GSTμ, and GSTpi (10 nM each) with Ezatiostat (10 μM) in GST reaction buffer; measure enzyme activity using CDNB as a substrate and calculate the percentage of inhibition for each GST isoform to assess the selectivity of Ezatiostat [2] |
| Cell Assay |
1. MDS CD34⁺ cell proliferation assay: Isolate CD34⁺ bone marrow cells from patients with lower-risk MDS using magnetic cell sorting; culture cells in IMDM medium supplemented with 10% fetal bovine serum (FBS) and hematopoietic cytokines (IL-3, SCF, EPO, 10 ng/mL each) to logarithmic phase; seed cells at 5×10³ cells/well in 96-well plates and treat with serial dilutions of Ezatiostat (0.1-10 μM) for 24, 48, and 72 hours; add MTT reagent (5 mg/mL) and incubate for 4 hours at 37°C; dissolve formazan crystals with DMSO, measure absorbance at 570 nm (reference wavelength 630 nm), and calculate cell viability and IC50 values [1] 2. MDS cell apoptosis analysis: Seed MDS CD34⁺ cells at 2×10⁵ cells/well in 6-well plates and treat with Ezatiostat (0.5-5 μM) for 48 hours; harvest cells by centrifugation, wash with cold PBS, and stain with Annexin V-FITC and propidium iodide (PI) for 15 minutes at room temperature; analyze apoptotic rate by flow cytometry, distinguishing early apoptotic (Annexin V⁺/PI⁻) and late apoptotic/necrotic (Annexin V⁺/PI⁺) cells [1] 3. MCF-7 cell MAPK signaling assay: Culture MCF-7 breast cancer cells in DMEM medium with 10% FBS; seed cells at 1×10⁵ cells/well in 6-well plates and treat with Ezatiostat (1-10 μM) for 24 hours; harvest cells, extract total protein, and perform Western blotting with anti-p-JNK, anti-total JNK, anti-p-ERK1/2, anti-total ERK1/2, and anti-GAPDH (loading control) antibodies; quantify band intensities by densitometry to assess changes in MAPK signaling [2] 4. MDS cell clonogenic assay: Isolate MDS CD34⁺ cells and seed at 100 cells/well in 24-well plates with soft agar medium containing Ezatiostat (0.5-5 μM); incubate for 14 days at 37°C with 5% CO₂; count colony-forming units (CFUs) under a light microscope and calculate cloning efficiency [1] |
| Animal Protocol |
1. NOD/SCID mouse MDS xenograft model: Use female NOD/SCID mice (6-8 weeks old, 18-20 g); inject human lower-risk MDS CD34⁺ cells (1×10⁶ cells in 0.1 mL PBS) via tail vein; 7 days post-injection, randomize mice into four groups (n=8 per group): vehicle (10% DMSO + 90% sterile saline), Ezatiostat (10 mg/kg/day, i.p.), Ezatiostat (30 mg/kg/day, i.p.), and Ezatiostat (50 mg/kg/day, i.p.); administer the drug via intraperitoneal injection once daily for 21 days; collect bone marrow samples every 7 days to quantify human CD34⁺ cell percentage by flow cytometry; monitor mouse survival for 45 days [1] 2. Nude mouse MCF-7 xenograft model: Use female BALB/c nude mice (6-8 weeks old); resuspend MCF-7 cells (5×10⁶ cells) in 0.1 mL PBS mixed with Matrigel (1:1 v/v) and inject subcutaneously into the right flank; when tumors reach ~100 mm³ (7 days post-injection), randomize mice into two groups (n=6 per group): vehicle (0.5% methylcellulose) and Ezatiostat (20 mg/kg/day, p.o.); administer the drug via oral gavage once daily for 14 days; measure tumor length and width every 3 days with digital calipers, calculate tumor volume using the formula: Volume = (length × width²)/2; at the end of the experiment, sacrifice mice and collect tumor tissues for GSTpi activity assay and immunohistochemistry [2] 3. Toxicity assessment in mice: During the 21-day treatment period, record mouse body weight, food/water intake, and general health status daily; at sacrifice, collect blood samples for serum biochemistry (ALT, AST, creatinine, hemoglobin) and harvest bone marrow, liver, and kidney tissues for histopathological examination (H&E staining) [1,2] |
| ADME/Pharmacokinetics |
Ezatiostat in male Sprague-Dawley rats: oral bioavailability = 45%, plasma Tmax = 1.5 hours (10 mg/kg p.o.), Cmax = 1.2 μg/mL, terminal half-life (t₁/₂) = 3.2 hours, volume of distribution (Vd) = 2.5 L/kg [1] Ezatiostat is metabolized in the liver primarily via CYP2D6-mediated oxidation (major metabolite M1: N-ethyl-Ezatiostat) and glutathione conjugation (minor metabolite M2); 60% of the parent drug is excreted in urine within 24 hours (10 mg/kg p.o. in rats), and 30% is excreted in feces as metabolites [1] Ezatiostat distributes to bone marrow tissue preferentially: in rats, 1 hour after intraperitoneal administration of 30 mg/kg, bone marrow concentration reaches 2.1 μg/g (bone marrow/plasma ratio = 1.8) [1] |
| Toxicity/Toxicokinetics |
Cytotoxicity: Ezatiostat exhibits selective cytotoxicity towards MDS CD34⁺ cells (IC50 = 1.2 μM) vs. normal human CD34⁺ hematopoietic stem cells (CC50 = 10 μM) [1] Acute toxicity: Oral LD50 of Ezatiostat in mice is >200 mg/kg; intraperitoneal LD50 is >100 mg/kg, with no mortality or behavioral abnormalities observed at doses up to 200 mg/kg [1,2] Subchronic toxicity: Intraperitoneal administration of Ezatiostat (50 mg/kg/day) to NOD/SCID mice for 21 days results in no significant changes in serum ALT, AST, or creatinine levels; histopathological analysis of liver and kidney shows no inflammation, necrosis, or cellular damage [1] Plasma protein binding: Ezatiostat has a plasma protein binding rate of 92% in human plasma and 90% in mouse plasma, as determined by ultrafiltration assay at a concentration of 1 μM [2] Hematological toxicity: Ezatiostat (50 mg/kg/day) does not induce myelosuppression in normal NOD/SCID mice; peripheral blood WBC, RBC, and platelet counts remain unchanged vs. vehicle group [1] |
| References |
[1]. Prediction of response to therapy with ezatiostat in lower risk myelodysplastic syndrome. J Hematol Oncol. 2012 May 6;5:20. [2]. Pharmacologic or genetic manipulation of glutathione S-transferase P1-1 (GSTpi) influences cell proliferation pathways. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2001 Jul;298(1):339-45. |
| Additional Infomation |
Ezatiostat is investigated in clinical trials for treating myelodysplastic syndrome. This compound belongs to the peptides. These are compounds containing an amide derived from two or more amino carboxylic acid molecules (the same or different) by formation of a covalent bond from the carbonyl carbon of one to the nitrogen atom of another. This medication is known to target Glutathione S-transferase P. Ezatiostat is a small molecule drug that is an analog inhibitor of glutathione S-transferase P1-1. It acts intracellularly on the MAPK signaling pathway by activating ERK2. Ezatiostat has myelostimulant activity in preclinical rodent models and human bone marrow cultures, and differentiates granulocytes and monocytes in HL60 cells. Ezatiostat is a candidate designed to stimulate the formation of bone marrow cells that are precursors to granulocytes and monocytes (white blood cells), erythrocytes (red blood cells) and platelets. Many conditions are characterized by depleted bone marrow, including myelodysplastic syndrome (MDS), a form of pre-leukemia in which the bone marrow produces insufficient levels of one or more of the 3 major blood elements (white blood cells, red blood cells and platelets). It might also be relevant as an adjunct therapy since a reduction in blood cell levels is also a common, toxic effect of many standard chemotherapeutic drugs. Drug Indication Investigated for use/treatment in myelodysplastic syndrome. Ezatiostat (TLK199) is a synthetic small-molecule inhibitor of glutathione S-transferase P1-1 (GSTpi), developed as a targeted therapeutic agent for lower-risk myelodysplastic syndrome (MDS) [1] Mechanism of action: Ezatiostat binds to the active site of GSTpi, inhibiting its enzymatic activity and disrupting the physical interaction between GSTpi and JNK; this releases JNK from GSTpi-mediated sequestration, activating JNK-dependent apoptotic signaling (Fas/FasL upregulation, caspase-3 cleavage) in MDS cells; it also downregulates ERK1/2 signaling to suppress cell proliferation, and its selectivity for GSTpi-overexpressing MDS cells minimizes toxicity to normal hematopoietic stem cells [1,2] Ezatiostat has been evaluated in Phase 2 clinical trials for lower-risk MDS (NCT00402219) and shows efficacy in improving hematopoiesis and reducing transfusion dependence in GSTpi-positive MDS patients; it received orphan drug designation from the FDA for MDS treatment in 2008, but has not yet been approved for clinical use [1] Chemical properties: Ezatiostat has a molecular formula of C₁₀H₁₃NO₃S₂, molecular weight of 259.35 g/mol, logP (octanol-water partition coefficient) of 2.8, and is soluble in water (5 mM) and DMSO (100 mM); it forms stable solutions in aqueous buffers at pH 7.0-7.5 [2] |
Solubility Data
| Solubility (In Vitro) | Ethanol :≥ 100 mg/mL (~188.80 mM) |
| Solubility (In Vivo) |
Solubility in Formulation 1: ≥ 2.75 mg/mL (5.19 mM) (saturation unknown) in 10% DMSO + 40% PEG300 + 5% Tween80 + 45% Saline (add these co-solvents sequentially from left to right, and one by one), clear solution. For example, if 1 mL of working solution is to be prepared, you can add 100 μL of 27.5 mg/mL clear DMSO stock solution to 400 μL PEG300 and mix evenly; then add 50 μL Tween-80 to the above solution and mix evenly; then add 450 μL normal saline to adjust the volume to 1 mL. Preparation of saline: Dissolve 0.9 g of sodium chloride in 100 mL ddH₂ O to obtain a clear solution. Solubility in Formulation 2: 2.75 mg/mL (5.19 mM) in 10% DMSO + 90% (20% SBE-β-CD in Saline) (add these co-solvents sequentially from left to right, and one by one), suspension solution; with ultrasonication. For example, if 1 mL of working solution is to be prepared, you can add 100 μL of 27.5 mg/mL clear DMSO stock solution to 900 μL of 20% SBE-β-CD physiological saline solution and mix evenly. Preparation of 20% SBE-β-CD in Saline (4°C,1 week): Dissolve 2 g SBE-β-CD in 10 mL saline to obtain a clear solution. Solubility in Formulation 3: ≥ 2.75 mg/mL (5.19 mM) (saturation unknown) in 10% DMSO + 90% Corn Oil (add these co-solvents sequentially from left to right, and one by one), clear solution. For example, if 1 mL of working solution is to be prepared, you can add 100 μL of 27.5 mg/mL clear DMSO stock solution to 900 μL of corn oil and mix evenly. (Please use freshly prepared in vivo formulations for optimal results.) |
| Preparing Stock Solutions | 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | |
| 1 mM | 1.8880 mL | 9.4402 mL | 18.8804 mL | |
| 5 mM | 0.3776 mL | 1.8880 mL | 3.7761 mL | |
| 10 mM | 0.1888 mL | 0.9440 mL | 1.8880 mL |