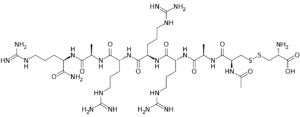
Etelcalcetide (formerly known as AMG-416, KAI-4169; ONO5163; velcalcetide, trade name Parsabiv) is an FDA approved calcimimetic drug for the treatment of secondary hyperparathyroidism in chronic kidney disease (CKD) patients undergoing hemodialysis. At the conclusion of each dialysis session, it is injected. The way etelcalcetide works is by attaching itself to the parathyroid gland's calcium-sensing receptor and turning it on. Currently, Amgen and Ono Pharmaceuticals in Japan are the owners of Parsabiv. A peptide called etelcalcetide primarily consists of D-amino acids as opposed to the more common L-amino acids. To be more precise, it is the disulfide of L-cysteine with N-acetyl-D-cysteinyl-D-alanyl-D-arginyl-D-arginyl-D-alanyl-D-argininamide.
Physicochemical Properties
| Molecular Formula | C38H73N21O10S2 |
| Molecular Weight | 1048.26 |
| Exact Mass | 1047.53 |
| Elemental Analysis | C, 43.54; H, 7.02; N, 28.06; O, 15.26; S, 6.12 |
| CAS # | 1262780-97-1 |
| Related CAS # | Etelcalcetide hydrochloride; 1334237-71-6 |
| PubChem CID | 71511839 |
| Appearance | Solid powder |
| LogP | 1.672 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 18 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 17 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 36 |
| Heavy Atom Count | 71 |
| Complexity | 1910 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 8 |
| SMILES | N=C(N)NCCC[C@H](C(=O)N)NC(=O)[C@@H](C)NC(=O)[C@@H](CCCNC(=N)N)NC(=O)[C@@H](CCCNC(=N)N)NC(=O)[C@@H](CCCNC(=N)N)NC(=O)[C@@H](C)NC(=O)[C@H](NC(=O)C)CSSC[C@H](N)C(O)=O |
| InChi Key | ANIAZGVDEUQPRI-ZJQCGQFWSA-N |
| InChi Code | InChI=1S/C38H73N21O10S2/c1-18(28(62)56-22(27(40)61)8-4-12-49-35(41)42)53-30(64)23(9-5-13-50-36(43)44)58-32(66)25(11-7-15-52-38(47)48)59-31(65)24(10-6-14-51-37(45)46)57-29(63)19(2)54-33(67)26(55-20(3)60)17-71-70-16-21(39)34(68)69/h18-19,21-26H,4-17,39H2,1-3H3,(H2,40,61)(H,53,64)(H,54,67)(H,55,60)(H,56,62)(H,57,63)(H,58,66)(H,59,65)(H,68,69)(H4,41,42,49)(H4,43,44,50)(H4,45,46,51)(H4,47,48,52)/t18-,19-,21+,22-,23-,24-,25-,26-/m1/s1 |
| Chemical Name | (2R)-3-[[(2S)-2-acetamido-3-[[(2R)-1-[[(2R)-1-[[(2R)-1-[[(2R)-1-[[(2R)-1-[[(2R)-1-amino-5-(diaminomethylideneamino)-1-oxopentan-2-yl]amino]-1-oxopropan-2-yl]amino]-5-(diaminomethylideneamino)-1-oxopentan-2-yl]amino]-5-(diaminomethylideneamino)-1-oxopentan-2-yl]amino]-5-(diaminomethylideneamino)-1-oxopentan-2-yl]amino]-1-oxopropan-2-yl]amino]-3-oxopropyl]disulfanyl]-2-aminopropanoic acid |
| Synonyms | KAI-4169; KAI4169; KAI 4169; AMG-416; AMG 416; AMG416; ONO5163; ONO 5163; ONO-5163; Etelcalcetide; Velcalcetide; Telcalcetide. Ac-D-Cys-D-Ala-D-Arg-D-Arg-D-Arg-D-Ala-D-Arg-NH2. |
| HS Tariff Code | 2934.99.9001 |
| Storage |
Powder-20°C 3 years 4°C 2 years In solvent -80°C 6 months -20°C 1 month |
| Shipping Condition | Room temperature (This product is stable at ambient temperature for a few days during ordinary shipping and time spent in Customs) |
Biological Activity
| ADME/Pharmacokinetics |
Absorption, Distribution and Excretion The pharmacokinetics of etelcalcetide is linear and does not change over time following single (5 to 60 mg) and multiple intravenous doses (2.5 to 20 mg) in chronic kidney disease patients with secondary hyperparathyroidism requiring hemodialysis. Etelcalcetide exhibited tri-exponential decay following intravenous administration. Based on population pharmacokinetic analysis, following three times a week intravenous dosing at the end of each 3- to 6-hour hemodialysis session in chronic kidney disease patients, etelcalcetide plasma levels reached steady state in 7-8 weeks after dosing with a predicted accumulation ratio of 3- to 4-fold Etelcalcetide is cleared by renal excretion 796 L 7.66 L/hr Metabolism / Metabolites Etelcalcetide is not metabolized by CYP450 enzymes. Etelcalcetide is biotransformed in blood by reversible disulfide exchange with endogenous thiols to predominantly form conjugates with serum albumin. Following a single radiolabeled dose of etelcalcetide in chronic kidney disease patients with secondary hyperparathyroidism requiring hemodialysis, the plasma exposure of biotransformation products is approximately 5-fold higher than that of etelcalcetide and their concentration-time course parallels that of etelcalcetide. Biological Half-Life 3 to 4 days |
| Toxicity/Toxicokinetics |
Effects During Pregnancy and Lactation ◉ Summary of Use during Lactation No information is available on etelcalcetide during breastfeeding. Because etelcalcetide is a large molecule with a molecular weight of 1047.5 Da, the amount in milk is likely to be low. The manufacturer recommends that breastfeeding be avoided during use. An alternate drug may be preferred, especially while nursing a newborn or preterm infant. ◉ Effects in Breastfed Infants Relevant published information was not found as of the revision date. ◉ Effects on Lactation and Breastmilk Relevant published information was not found as of the revision date. Protein Binding Etelcalcetide is predominately bound to plasma albumin by reversible covalent binding. Non-covalent binding of etelcalcetide to plasma proteins is low with a fraction unbound ratio of 0.53. The ratio of blood-to-plasma [14C]-etelcalcetide concentrations is approximately 0.6. |
| References |
[1]. Activation of dopamine D4 receptors by ABT-724 induces penile erection in rats. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2004 Apr 27;101(17):6758-63. |
| Additional Infomation |
Etelcalcetide is an oligopeptide. Etelcalcetide is a calcimimetic drug for the treatment of secondary hyperparathyroidism in patients undergoing hemodialysis. Etelcalcetide was approved (trade name Parsabiv) for the treatment of secondary hyperparathyroidism (HPT) in adult patients with chronic kidney disease (CKD) on hemodialysis in February, 2017. Etelcalcetide is a Calcium-sensing Receptor Agonist. The mechanism of action of etelcalcetide is as an Increased Calcium-sensing Receptor Sensitivity. Etelcalcetide is a calcimimetic and calcium-sensing receptor (CaSR) agonist composed of a synthetic peptide comprised of seven D-amino acids that can be used to treat secondary hyperparathyroidism (sHPT) in hemodialysis patients with chronic kidney disease (CKD). Upon intravenous administration, etelcalcetide mimics calcium and allosterically binds to and activates the CaSR expressed by the parathyroid gland. This suppresses the synthesis and secretion of parathyroid hormone (PTH), thereby reducing PTH levels and lowering serum calcium and phosphorus levels. Elevated PTH is often observed in patients with CKD and is associated with dysregulated calcium-phosphate homeostasis. See also: Etelcalcetide Hydrochloride (active moiety of). Drug Indication Etelcalcetide is a calcium-sensing receptor agonist indicated for: Secondary hyperparathyroidism (HPT) in adult patients with chronic kidney disease (CKD) on hemodialysis. Parsabiv is indicated for the treatment of secondary hyperparathyroidism (SHPT) in adult patients with chronic kidney disease (CKD) on haemodialysis therapy. Treatment of hyperparathyroidism Mechanism of Action Etelcalcetide is a calcimimetic agent that allosterically modulates the calcium-sensing receptor (CaSR). Etelcalcetide binds to the CaSR and enhances activation of the receptor by extracellular calcium. Activation of the CaSR on parathyroid chief cells decreases PTH secretion. Pharmacodynamics Following a single intravenous bolus administration of etelcalcetide, PTH levels decreased within 30 minutes post dose. In the single-dose study, the extent and duration of the reduction in PTH increased with increasing dose. Reduction in PTH levels correlated with plasma etelcalcetide concentrations in hemodialysis patients. The reduction in PTH resulted in reductions in calcium and attenuation of post-dialytic phosphate elevation. The effect of reducing PTH levels was maintained throughout the 6-month dosing period when etelcalcetide was administered by intravenous bolus three times a week. |
Solubility Data
| Solubility (In Vitro) |
|
|||
| Solubility (In Vivo) |
Note: Listed below are some common formulations that may be used to formulate products with low water solubility (e.g. < 1 mg/mL), you may test these formulations using a minute amount of products to avoid loss of samples. Injection Formulations (e.g. IP/IV/IM/SC) Injection Formulation 1: DMSO : Tween 80: Saline = 10 : 5 : 85 (i.e. 100 μL DMSO stock solution → 50 μL Tween 80 → 850 μL Saline) *Preparation of saline: Dissolve 0.9 g of sodium chloride in 100 mL ddH ₂ O to obtain a clear solution. Injection Formulation 2: DMSO : PEG300 :Tween 80 : Saline = 10 : 40 : 5 : 45 (i.e. 100 μL DMSO → 400 μLPEG300 → 50 μL Tween 80 → 450 μL Saline) Injection Formulation 3: DMSO : Corn oil = 10 : 90 (i.e. 100 μL DMSO → 900 μL Corn oil) Example: Take the Injection Formulation 3 (DMSO : Corn oil = 10 : 90) as an example, if 1 mL of 2.5 mg/mL working solution is to be prepared, you can take 100 μL 25 mg/mL DMSO stock solution and add to 900 μL corn oil, mix well to obtain a clear or suspension solution (2.5 mg/mL, ready for use in animals). Injection Formulation 4: DMSO : 20% SBE-β-CD in saline = 10 : 90 [i.e. 100 μL DMSO → 900 μL (20% SBE-β-CD in saline)] *Preparation of 20% SBE-β-CD in Saline (4°C,1 week): Dissolve 2 g SBE-β-CD in 10 mL saline to obtain a clear solution. Injection Formulation 5: 2-Hydroxypropyl-β-cyclodextrin : Saline = 50 : 50 (i.e. 500 μL 2-Hydroxypropyl-β-cyclodextrin → 500 μL Saline) Injection Formulation 6: DMSO : PEG300 : castor oil : Saline = 5 : 10 : 20 : 65 (i.e. 50 μL DMSO → 100 μLPEG300 → 200 μL castor oil → 650 μL Saline) Injection Formulation 7: Ethanol : Cremophor : Saline = 10: 10 : 80 (i.e. 100 μL Ethanol → 100 μL Cremophor → 800 μL Saline) Injection Formulation 8: Dissolve in Cremophor/Ethanol (50 : 50), then diluted by Saline Injection Formulation 9: EtOH : Corn oil = 10 : 90 (i.e. 100 μL EtOH → 900 μL Corn oil) Injection Formulation 10: EtOH : PEG300:Tween 80 : Saline = 10 : 40 : 5 : 45 (i.e. 100 μL EtOH → 400 μLPEG300 → 50 μL Tween 80 → 450 μL Saline) Oral Formulations Oral Formulation 1: Suspend in 0.5% CMC Na (carboxymethylcellulose sodium) Oral Formulation 2: Suspend in 0.5% Carboxymethyl cellulose Example: Take the Oral Formulation 1 (Suspend in 0.5% CMC Na) as an example, if 100 mL of 2.5 mg/mL working solution is to be prepared, you can first prepare 0.5% CMC Na solution by measuring 0.5 g CMC Na and dissolve it in 100 mL ddH2O to obtain a clear solution; then add 250 mg of the product to 100 mL 0.5% CMC Na solution, to make the suspension solution (2.5 mg/mL, ready for use in animals). Oral Formulation 3: Dissolved in PEG400 Oral Formulation 4: Suspend in 0.2% Carboxymethyl cellulose Oral Formulation 5: Dissolve in 0.25% Tween 80 and 0.5% Carboxymethyl cellulose Oral Formulation 6: Mixing with food powders Note: Please be aware that the above formulations are for reference only. InvivoChem strongly recommends customers to read literature methods/protocols carefully before determining which formulation you should use for in vivo studies, as different compounds have different solubility properties and have to be formulated differently. (Please use freshly prepared in vivo formulations for optimal results.) |
| Preparing Stock Solutions | 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | |
| 1 mM | 0.9540 mL | 4.7698 mL | 9.5396 mL | |
| 5 mM | 0.1908 mL | 0.9540 mL | 1.9079 mL | |
| 10 mM | 0.0954 mL | 0.4770 mL | 0.9540 mL |