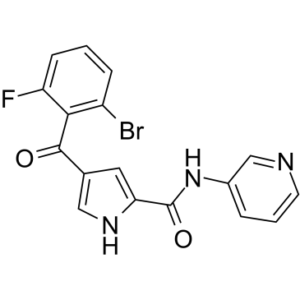
ERK5-IN-2 is a novel, potent, orally bioavailable, sub-micromolar, and selective ERK5 inhibitor with selectivity over p38α and BRD4. For ERK5 and ERK5 MEF2D, it has IC50 values of 0.82 μM, 3 μM, respectively. Both the growth of tumor xenografts and the angiogenesis induced by basic fibroblast growth factor (bFGF) in Matrigel plugs are inhibited by ERK5-IN-2. Endothelial cell angiogenesis and tumor cell motility are two cellular phenotypes that have been linked to extracellular regulated kinase 5 (ERK5) signaling. A series of pyrrole-2-carboxamides substituted at the 4-position with an aroyl group were found to exhibit IC50 values in the micromolar range, but had no selectivity against p38 MAP kinase. These novel ERK5 inhibitors, such as ERK5-IN-2, were discovered using high throughput screening. Truncation of the N-substituent attenuated the inhibition of p38α, which was important because it only slightly increased potency (∼3-fold) against ERK5. The selective inhibitor 4-(2-bromo-6-fluorobenzoyl)-N-(pyridin-3-yl)-1H-pyrrole-2-carboxamide (IC50 0.82 μM for ERK5; IC50 > 120 μM for p38α). This compound's complex crystal structure with ERK5 has been determined (PDB 5O7I). This substance was orally bioavailable and prevented tumor xenograft growth and bFGF-driven angiogenesis in Matrigel plugs. The selective ERK5 inhibitor that is described in this article offers a lead for further development into a tool compound for more in-depth studies looking to understand how ERK5 signaling affects cancer and other diseases.
Physicochemical Properties
| Molecular Formula | C17H11BRFN3O2 |
| Molecular Weight | 388.190546274185 |
| Exact Mass | 387.001 |
| CAS # | 1888305-96-1 |
| Related CAS # | 1888305-96-1 |
| PubChem CID | 118959080 |
| Appearance | White to off-white solid |
| LogP | 2.9 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 2 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 4 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 4 |
| Heavy Atom Count | 24 |
| Complexity | 479 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| InChi Key | ATKCERYALDNMPL-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
| InChi Code | InChI=1S/C17H11BrFN3O2/c18-12-4-1-5-13(19)15(12)16(23)10-7-14(21-8-10)17(24)22-11-3-2-6-20-9-11/h1-9,21H,(H,22,24) |
| Chemical Name | 4-(2-bromo-6-fluorobenzoyl)-N-pyridin-3-yl-1H-pyrrole-2-carboxamide |
| Synonyms | ERK5-IN 2; ERK5 IN-2; ERK5-IN-2 |
| HS Tariff Code | 2934.99.9001 |
| Storage |
Powder-20°C 3 years 4°C 2 years In solvent -80°C 6 months -20°C 1 month Note: This product requires protection from light (avoid light exposure) during transportation and storage. |
| Shipping Condition | Room temperature (This product is stable at ambient temperature for a few days during ordinary shipping and time spent in Customs) |
Biological Activity
| Targets | ERK5 (IC50 = 0.82 μM); ERK5 MEF2D (IC50 = 3 μM) |
| ln Vivo | ERK5-IN-2 (Compound 46) (cartilage; 100 mg/kg; 7 days in CD1 mice and 10 days in CD1 nude (nu/nu) mice) possesses low hemoglobin concentrations and anti-angiogenic properties [1]. In caco-2 cell permeability tests in humans and animals, ERK5-IN-2 (iv or intravenous 10 mg/kg for 0.083-24 hours) shows low internal clearance, high flux, and low efflux ratio (ER) |
| Animal Protocol |
Animal/Disease Models: Matrigel-vaccinated female CD1 mice (8-10 weeks old) and female CD1 nude (nu/nu) mice (8-10 weeks old) bearing A2780 human ovarian cancer xenografts [1] Doses: 100 mg/1]. kg Route of Administration: Po; twice (two times) daily; 7 days for CD1 mice, 10 days for CD1 nude mice (nu/nu) Experimental Results: Significant reduction in tumor volume. Animal/Disease Models: 8-10 weeks old female CD1 mice [1] Doses: 10 mg/kg Route of Administration: intravenous (iv) (iv)injection or oral administration; 0.083-24 hrs (hrs (hours)) Experimental Results: The terminal plasma half-life is 38 minutes, and the plasma clearance rate is 27mL/ min/kg, oral bioavailability is 68%. |
| References |
[1]. Identification of a novel orally bioavailable ERK5 inhibitor with selectivity over p38α and BRD4. Eur J Med Chem. 2019 May 25;178:530-543. |
Solubility Data
| Solubility (In Vitro) |
DMSO: 78~250 mg/mL (200.9~644.0 mM) Ethanol: ~3 mg/mL (~7.7 mM) |
| Solubility (In Vivo) |
Solubility in Formulation 1: ≥ 2.08 mg/mL (5.36 mM) (saturation unknown) in 10% DMSO + 40% PEG300 + 5% Tween80 + 45% Saline (add these co-solvents sequentially from left to right, and one by one), clear solution. For example, if 1 mL of working solution is to be prepared, you can add 100 μL of 20.8 mg/mL clear DMSO stock solution to 400 μL PEG300 and mix evenly; then add 50 μL Tween-80 to the above solution and mix evenly; then add 450 μL normal saline to adjust the volume to 1 mL. Preparation of saline: Dissolve 0.9 g of sodium chloride in 100 mL ddH₂ O to obtain a clear solution. Solubility in Formulation 2: ≥ 2.08 mg/mL (5.36 mM) (saturation unknown) in 10% DMSO + 90% (20% SBE-β-CD in Saline) (add these co-solvents sequentially from left to right, and one by one), clear solution. For example, if 1 mL of working solution is to be prepared, you can add 100 μL of 20.8 mg/mL clear DMSO stock solution to 900 μL of 20% SBE-β-CD physiological saline solution and mix evenly. Preparation of 20% SBE-β-CD in Saline (4°C,1 week): Dissolve 2 g SBE-β-CD in 10 mL saline to obtain a clear solution. Solubility in Formulation 3: ≥ 2.08 mg/mL (5.36 mM) (saturation unknown) in 10% DMSO + 90% Corn Oil (add these co-solvents sequentially from left to right, and one by one), clear solution. For example, if 1 mL of working solution is to be prepared, you can add 100 μL of 20.8 mg/mL clear DMSO stock solution to 900 μL of corn oil and mix evenly. (Please use freshly prepared in vivo formulations for optimal results.) |
| Preparing Stock Solutions | 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | |
| 1 mM | 2.5761 mL | 12.8803 mL | 25.7606 mL | |
| 5 mM | 0.5152 mL | 2.5761 mL | 5.1521 mL | |
| 10 mM | 0.2576 mL | 1.2880 mL | 2.5761 mL |