Physicochemical Properties
| Molecular Formula | C27H33CLO12 |
| Molecular Weight | 584.996728658676 |
| CAS # | 1351438-75-9 |
| Appearance | Typically exists as solids at room temperature |
| Density | 1.6±0.1 g/cm3 |
| Boiling Point | 857.0±65.0 °C at 760 mmHg |
| Flash Point | 472.1±34.3 °C |
| Vapour Pressure | 0.0±0.3 mmHg at 25°C |
| Index of Refraction | 1.666 |
| LogP | 1.55 |
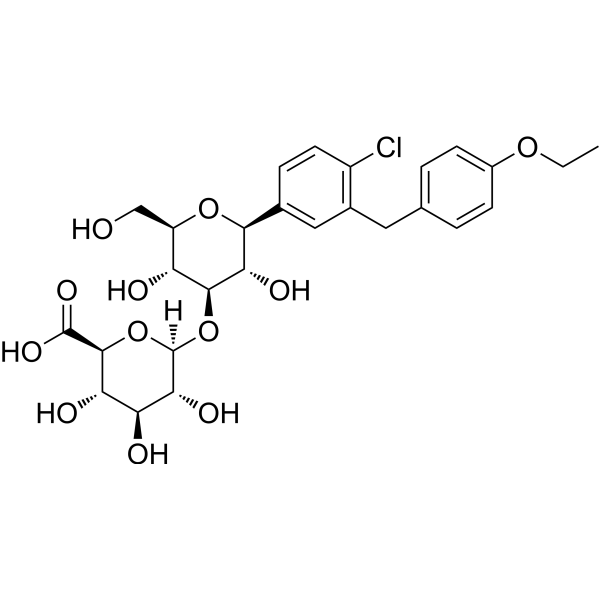
| SMILES | ClC1C=CC(=CC=1CC1C=CC(=CC=1)OCC)[C@H]1[C@@H]([C@H]([C@@H]([C@@H](CO)O1)O)O[C@H]1[C@@H]([C@H]([C@@H]([C@@H](C(=O)O)O1)O)O)O)O |
| Synonyms | BMS-801576; Dapagliflozin 3-o-glucuronide; 1351438-75-9; Dapagliflozin M-15 metabolite; UNII-X42P3B148J; BMS-801576; X42P3B148J; Dapagliflozin3-O-beta-D-Glucuronide; Dapagliflozin 3-O-beta-D-Glucuronide; |
| HS Tariff Code | 2934.99.9001 |
| Storage |
Powder-20°C 3 years 4°C 2 years In solvent -80°C 6 months -20°C 1 month Note: (1). This product requires protection from light (avoid light exposure) during transportation and storage.(2). Please store this product in a sealed and protected environment (e.g. under nitrogen), avoid exposure to moisture. |
| Shipping Condition | Room temperature (This product is stable at ambient temperature for a few days during ordinary shipping and time spent in Customs) |
Biological Activity
| Targets | Phase II metabolite of Dapagliflozin |
| ln Vivo | Sodium-glucose co-transporter 2 (SGLT2) is predominantly expressed in the S1 segment of the proximal tubule of the kidney and is the major transporter responsible for mediating renal glucose reabsorption. Dapagliflozin is an orally active, highly selective SGLT2 inhibitor that improves glycemic control in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) by reducing renal glucose reabsorption leading to urinary glucose excretion (glucuresis). Orally administered dapagliflozin is rapidly absorbed generally achieving peak plasma concentrations within 2 h. Dose-proportional systemic exposure to dapagliflozin has been observed over a wide dose range (0.1-500 mg) with an oral bioavailability of 78 %. Dapagliflozin has extensive extravascular distribution (mean volume of distribution of 118 L). Dapagliflozin metabolism occurs predominantly in the liver and kidneys by uridine diphosphate-glucuronosyltransferase-1A9 to the major metabolite dapagliflozin 3-O-glucuronide (this metabolite is not an SGLT2 inhibitor at clinically relevant exposures). Dapagliflozin is not appreciably cleared by renal excretion (<2 % of dose is recovered in urine as parent). Dapagliflozin 3-O-glucuronide elimination occurs mainly via renal excretion, with 61 % of a dapagliflozin dose being recovered as this metabolite in urine. The half-life for orally administered dapagliflozin 10 mg was 12.9 h. Maximal increases in urinary glucose excretion were seen at doses ≥20 mg/day in patients with T2DM. No clinically relevant differences were observed in dapagliflozin exposure with respect to age, race, sex, body weight, food, or presence of T2DM. Pharmacodynamic changes are dependent on plasma glucose and renal function, and decreases in urinary glucose excretion were observed due to the lower filtered load (plasma glucose × glomerular filtration rate) in healthy volunteers compared to subjects with T2DM. After multiple doses of dapagliflozin, urinary glucose excretion was associated with dose-related decreases in plasma glucose parameters in subjects with T2DM. Patients with severe renal or hepatic impairment show higher systemic exposure to dapagliflozin. No clinically relevant drug interactions were observed that would necessitate dose adjustment of dapagliflozin when administered with other antidiabetic or cardiovascular medications, as well as drugs that could potentially influence dapagliflozin metabolism [1]. |
| References |
[1]. Kasichayanula S, et al., Clinical pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of dapagliflozin, a selective inhibitor of sodium-glucose co-transporter type 2. Clin Pharmacokinet. 2014 Jan;53(1):17-27. |
Solubility Data
| Solubility (In Vitro) | DMSO : ~1 mg/mL (~1.71 mM; with heating and sonication) |
| Solubility (In Vivo) |
Note: Listed below are some common formulations that may be used to formulate products with low water solubility (e.g. < 1 mg/mL), you may test these formulations using a minute amount of products to avoid loss of samples. Injection Formulations (e.g. IP/IV/IM/SC) Injection Formulation 1: DMSO : Tween 80: Saline = 10 : 5 : 85 (i.e. 100 μL DMSO stock solution → 50 μL Tween 80 → 850 μL Saline) *Preparation of saline: Dissolve 0.9 g of sodium chloride in 100 mL ddH ₂ O to obtain a clear solution. Injection Formulation 2: DMSO : PEG300 :Tween 80 : Saline = 10 : 40 : 5 : 45 (i.e. 100 μL DMSO → 400 μLPEG300 → 50 μL Tween 80 → 450 μL Saline) Injection Formulation 3: DMSO : Corn oil = 10 : 90 (i.e. 100 μL DMSO → 900 μL Corn oil) Example: Take the Injection Formulation 3 (DMSO : Corn oil = 10 : 90) as an example, if 1 mL of 2.5 mg/mL working solution is to be prepared, you can take 100 μL 25 mg/mL DMSO stock solution and add to 900 μL corn oil, mix well to obtain a clear or suspension solution (2.5 mg/mL, ready for use in animals). Injection Formulation 4: DMSO : 20% SBE-β-CD in saline = 10 : 90 [i.e. 100 μL DMSO → 900 μL (20% SBE-β-CD in saline)] *Preparation of 20% SBE-β-CD in Saline (4°C,1 week): Dissolve 2 g SBE-β-CD in 10 mL saline to obtain a clear solution. Injection Formulation 5: 2-Hydroxypropyl-β-cyclodextrin : Saline = 50 : 50 (i.e. 500 μL 2-Hydroxypropyl-β-cyclodextrin → 500 μL Saline) Injection Formulation 6: DMSO : PEG300 : castor oil : Saline = 5 : 10 : 20 : 65 (i.e. 50 μL DMSO → 100 μLPEG300 → 200 μL castor oil → 650 μL Saline) Injection Formulation 7: Ethanol : Cremophor : Saline = 10: 10 : 80 (i.e. 100 μL Ethanol → 100 μL Cremophor → 800 μL Saline) Injection Formulation 8: Dissolve in Cremophor/Ethanol (50 : 50), then diluted by Saline Injection Formulation 9: EtOH : Corn oil = 10 : 90 (i.e. 100 μL EtOH → 900 μL Corn oil) Injection Formulation 10: EtOH : PEG300:Tween 80 : Saline = 10 : 40 : 5 : 45 (i.e. 100 μL EtOH → 400 μLPEG300 → 50 μL Tween 80 → 450 μL Saline) Oral Formulations Oral Formulation 1: Suspend in 0.5% CMC Na (carboxymethylcellulose sodium) Oral Formulation 2: Suspend in 0.5% Carboxymethyl cellulose Example: Take the Oral Formulation 1 (Suspend in 0.5% CMC Na) as an example, if 100 mL of 2.5 mg/mL working solution is to be prepared, you can first prepare 0.5% CMC Na solution by measuring 0.5 g CMC Na and dissolve it in 100 mL ddH2O to obtain a clear solution; then add 250 mg of the product to 100 mL 0.5% CMC Na solution, to make the suspension solution (2.5 mg/mL, ready for use in animals). Oral Formulation 3: Dissolved in PEG400 Oral Formulation 4: Suspend in 0.2% Carboxymethyl cellulose Oral Formulation 5: Dissolve in 0.25% Tween 80 and 0.5% Carboxymethyl cellulose Oral Formulation 6: Mixing with food powders Note: Please be aware that the above formulations are for reference only. InvivoChem strongly recommends customers to read literature methods/protocols carefully before determining which formulation you should use for in vivo studies, as different compounds have different solubility properties and have to be formulated differently. (Please use freshly prepared in vivo formulations for optimal results.) |
| Preparing Stock Solutions | 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | |
| 1 mM | 1.7094 mL | 8.5470 mL | 17.0940 mL | |
| 5 mM | 0.3419 mL | 1.7094 mL | 3.4188 mL | |
| 10 mM | 0.1709 mL | 0.8547 mL | 1.7094 mL |