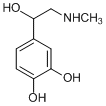
DL-Adrenaline [(±)-Epinephrine; Racepinefrine; Racepinephrine; DL-Epinephrine], an adrenoceptor agonist, is a hormone and a neurotransmitter secreted by the medulla of the adrenal glands. Adrenaline in its L-form acts directly on alpha and beta adrenergic receptors, making it a strong sympathomimetic.
Physicochemical Properties
| Molecular Formula | C9H13NO3 | |
| Molecular Weight | 183.2 | |
| Exact Mass | 183.089 | |
| Elemental Analysis | C, 59.00; H, 7.15; N, 7.65; O, 26.20 | |
| CAS # | 329-65-7 | |
| Related CAS # | 329-65-7; 329-63-5 (HCl) | |
| PubChem CID | 838 | |
| Appearance | Solid powder | |
| Density | 1.3±0.1 g/cm3 | |
| Boiling Point | 413.1±40.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |
| Melting Point | 197 °C (dec.)(lit.) | |
| Flash Point | 207.9±17.9 °C | |
| Vapour Pressure | 0.0±1.0 mmHg at 25°C | |
| Index of Refraction | 1.608 | |
| LogP | -0.63 | |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 4 | |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 4 | |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 3 | |
| Heavy Atom Count | 13 | |
| Complexity | 154 | |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 | |
| SMILES | OC(C1=CC(O)=C(O)C=C1)CNC |
|
| InChi Key | UCTWMZQNUQWSLP-UHFFFAOYSA-N | |
| InChi Code | InChI=1S/C9H13NO3/c1-10-5-9(13)6-2-3-7(11)8(12)4-6/h2-4,9-13H,5H2,1H3 | |
| Chemical Name | 4-[1-hydroxy-2-(methylamino)ethyl]benzene-1,2-diol | |
| Synonyms |
|
|
| HS Tariff Code | 2934.99.9001 | |
| Storage |
Powder-20°C 3 years 4°C 2 years In solvent -80°C 6 months -20°C 1 month |
|
| Shipping Condition | Room temperature (This product is stable at ambient temperature for a few days during ordinary shipping and time spent in Customs) |
Biological Activity
| Targets | Adrenergic Receptor | ||
| ln Vitro |
|
||
| ln Vivo |
|
||
| Animal Protocol |
|
||
| ADME/Pharmacokinetics |
Absorption, Distribution and Excretion To refer to the pharmacokinetic data of L-epinephrine, refer to the drug entry for [DB00668]. To refer to the pharmacokinetic data of L-epinephrine, refer to the drug entry for [DB00668]. To refer to the pharmacokinetic data of L-epinephrine, refer to the drug entry for [DB00668]. To refer to the pharmacokinetic data of L-epinephrine, refer to the drug entry for [DB00668]. Metabolism / Metabolites To refer to the pharmacokinetic data of L-epinephrine, refer to the drug entry for [DB00668]. Biological Half-Life To refer to the pharmacokinetic data of L-epinephrine, refer to the drug entry for [DB00668]. |
||
| Toxicity/Toxicokinetics |
Effects During Pregnancy and Lactation ◉ Summary of Use during Lactation No information is available on the use of epinephrine during breastfeeding. Because of its poor oral bioavailability and short half-life, any epinephrine in milk is unlikely to affect the infant. High intravenous doses of epinephrine might reduce milk production or milk letdown. Low-dose intramuscular (such as Epi-Pen), epidural, topical, inhaled or ophthalmic epinephrine are unlikely to interfere with breastfeeding. To substantially diminish the effect of the drug after using eye drops, place pressure over the tear duct by the corner of the eye for 1 minute or more, then remove the excess solution with an absorbent tissue. Epinephrine is the first line-medication of choice for treatment of anaphylaxis; it should be used in the same manner in breastfeeding and non-breastfeeding patients. ◉ Effects in Breastfed Infants Relevant published information was not found as of the revision date. ◉ Effects on Lactation and Breastmilk Relevant published information in nursing mothers was not found as of the revision date. Intravenous epinephrine infusion in nonnursing subjects and in women with hyperprolactinemia decreases serum prolactin concentrations. Animal data indicate that intraarterial epinephrine can decrease serum oxytocin and inhibit milk ejection. However, low-dose infusion of epinephrine as part of epidural analgesia does not impair breastfeeding in nursing mothers. The prolactin level in a mother with established lactation may not affect her ability to breastfeed. An Egyptian study compared lidocaine 2% (n = 75) to lidocaine 2% plus epinephrine 1:200,000 (n = 70) as a wound infiltration following cesarean section. Patients who received epinephrine in combination with lidocaine began breastfeeding at 89 minutes following surgery compared to 132 minutes for those receiving lidocaine alone. The difference was statistically significant. Protein Binding To refer to the pharmacokinetic data of L-epinephrine, refer to the drug entry for [DB00668]. |
||
| References |
[1]. Am J Physiol . 1982 Apr;242(4):H593-601. [2]. Br J Dis Chest . 1986 Jan;80(1):1-6. |
||
| Additional Infomation |
3,4-dihydroxyl-alpha-[methylamino]methylbenzyl alcohol appears as odorless light brown or nearly white crystals. (NTP, 1992) Adrenaline is a racemate comprising equimolar amounts of (R)-adrenaline and (S)-adrenaline. It has a role as a human metabolite. It contains a (R)-adrenaline and a (S)-adrenaline. Racepinephrine is a racemic mixture consisting of d-[DB00668] and l-[DB00668] enantiomers. Epinephrine is a non-selective α- and β-adrenergic receptor agonist. It is a bronchodilator used in the temporary relief of mild symptoms of intermittent asthma including wheezing, tightness of chest and shortness of breath. It is an active ingredient in oral inhalation over-the-counter products as racepinephrine hydrochloride. DL-Adrenaline has been reported in Homo sapiens with data available. A racemic mixture of d-epinephrine and l-epinephrine. See also: Racepinephrine Hydrochloride (has salt form); Epinephrine (annotation moved to). Drug Indication Indicated for temporary relief of mild symptoms of intermittent asthma. FDA Label Mechanism of Action Epinephrine is a non-selective agonist at α- and β-adrenergic receptors, which are all G-protein-coupled receptors. The main therapeutic effect of epinephrine arises from its agonist action on β2-adrenergic receptors, which activate adenylyl cyclase and increase intracellular cyclic AMP production. Epinephrine causes smooth muscle relaxation on various tissues, including bronchial smooth muscles. As a result, epinephrine serves to alleviate bronchospasm, wheezing and tightness of chest that may occur during asthmatic attacks. Via its relaxer effects on the smooth muscle of the stomach, intestine, uterus and urinary bladder, epinephrine may also alleviate pruritus, urticaria, and angioedema and may relieve gastrointestinal and genitourinary symptoms associated with anaphylaxis. Epinephrine also acts on the α-adrenergic receptors on vascular smooth muscles, particularly in the skin and splanchnic vascular beds, to cause constriction. Epinephrine is thought to reduce capillary leakage by constricting precapillary arterioles, reducing hydrostatic pressure and consequently bronchial mucosal edema. |
Solubility Data
| Solubility (In Vitro) |
|
|||
| Solubility (In Vivo) |
|
| Preparing Stock Solutions | 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | |
| 1 mM | 5.4585 mL | 27.2926 mL | 54.5852 mL | |
| 5 mM | 1.0917 mL | 5.4585 mL | 10.9170 mL | |
| 10 mM | 0.5459 mL | 2.7293 mL | 5.4585 mL |