Physicochemical Properties
| Molecular Formula | C3H6O4 |
| Molecular Weight | 106.08 |
| Exact Mass | 106.026 |
| CAS # | 6000-40-4 |
| PubChem CID | 439194 |
| Appearance | Typically exists as solid at room temperature |
| Density | 1.6±0.1 g/cm3 |
| Boiling Point | 412.0±30.0 °C at 760 mmHg |
| Flash Point | 217.1±21.1 °C |
| Vapour Pressure | 0.0±2.2 mmHg at 25°C |
| Index of Refraction | 1.515 |
| LogP | -1.92 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 3 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 4 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 2 |
| Heavy Atom Count | 7 |
| Complexity | 69.3 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 1 |
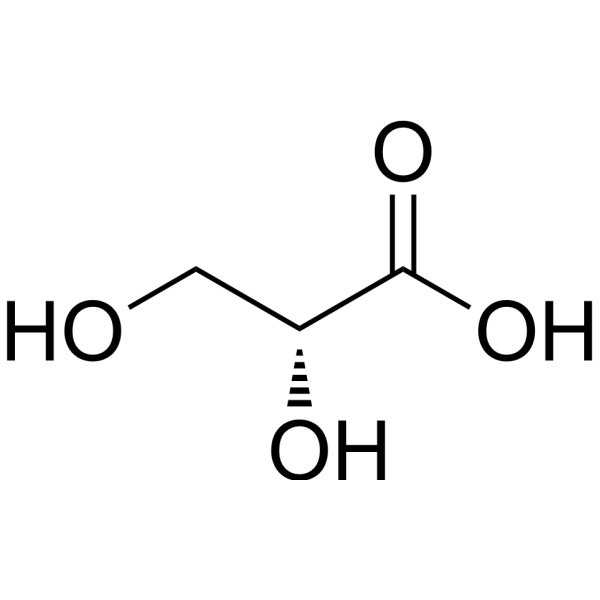
| SMILES | C([C@H](C(=O)O)O)O |
| InChi Key | RBNPOMFGQQGHHO-UWTATZPHSA-N |
| InChi Code | InChI=1S/C3H6O4/c4-1-2(5)3(6)7/h2,4-5H,1H2,(H,6,7)/t2-/m1/s1 |
| Chemical Name | (2R)-2,3-dihydroxypropanoic acid |
| HS Tariff Code | 2934.99.9001 |
| Storage |
Powder-20°C 3 years 4°C 2 years In solvent -80°C 6 months -20°C 1 month |
| Shipping Condition | Room temperature (This product is stable at ambient temperature for a few days during ordinary shipping and time spent in Customs) |
Biological Activity
| ln Vitro | Endogenous metabolites are those that the Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes has identified as products or substrates of the approximately 1900 metabolic enzymes that are encoded in human genome. Numerous of these metabolites have been shown to have harmful effects, as evidenced by the body of literature [1]. |
| References |
[1]. Endogenous toxic metabolites and implications in cancer therapy. Oncogene. 2020 Aug;39(35):5709-5720. [2]. Extraction of glyceric and glycolic acids from urine with tetrahydrofuran: utility in detection of primary hyperoxaluria. Clin Chem. 1997 Aug;43(8 Pt 1):1315-20. [3]. Long-term prognosis in primary hyperoxaluria type II (L-glyceric aciduria). Am J Kidney Dis. 1994 Feb;23(2):255-9. |
| Additional Infomation |
D-glyceric acid is the D-enantiomer of glyceric acid. It is a conjugate acid of a D-glycerate. It is an enantiomer of a L-glyceric acid. (2R)-2,3-Dihydroxypropanoic acid has been reported in Solanum tuberosum, Glycine max, and other organisms with data available. Glyceric acid is a colorless syrupy acid, obtained from oxidation of glycerol. It is a compound that is secreted excessively in the urine by patients suffering from D-glyceric aciduria and D-glycerate anemia. Deficiency of human glycerate kinase leads to D-glycerate acidemia/D-glyceric aciduria. Symptoms of the disease include progressive neurological impairment, hypotonia, seizures, failure to thrive and metabolic acidosis. Glyceric acid is a metabolite found in or produced by Saccharomyces cerevisiae. See also: D-Glycerate (annotation moved to); Glycerate (annotation moved to). |
Solubility Data
| Solubility (In Vivo) |
Note: Listed below are some common formulations that may be used to formulate products with low water solubility (e.g. < 1 mg/mL), you may test these formulations using a minute amount of products to avoid loss of samples. Injection Formulations (e.g. IP/IV/IM/SC) Injection Formulation 1: DMSO : Tween 80: Saline = 10 : 5 : 85 (i.e. 100 μL DMSO stock solution → 50 μL Tween 80 → 850 μL Saline) *Preparation of saline: Dissolve 0.9 g of sodium chloride in 100 mL ddH ₂ O to obtain a clear solution. Injection Formulation 2: DMSO : PEG300 :Tween 80 : Saline = 10 : 40 : 5 : 45 (i.e. 100 μL DMSO → 400 μLPEG300 → 50 μL Tween 80 → 450 μL Saline) Injection Formulation 3: DMSO : Corn oil = 10 : 90 (i.e. 100 μL DMSO → 900 μL Corn oil) Example: Take the Injection Formulation 3 (DMSO : Corn oil = 10 : 90) as an example, if 1 mL of 2.5 mg/mL working solution is to be prepared, you can take 100 μL 25 mg/mL DMSO stock solution and add to 900 μL corn oil, mix well to obtain a clear or suspension solution (2.5 mg/mL, ready for use in animals). Injection Formulation 4: DMSO : 20% SBE-β-CD in saline = 10 : 90 [i.e. 100 μL DMSO → 900 μL (20% SBE-β-CD in saline)] *Preparation of 20% SBE-β-CD in Saline (4°C,1 week): Dissolve 2 g SBE-β-CD in 10 mL saline to obtain a clear solution. Injection Formulation 5: 2-Hydroxypropyl-β-cyclodextrin : Saline = 50 : 50 (i.e. 500 μL 2-Hydroxypropyl-β-cyclodextrin → 500 μL Saline) Injection Formulation 6: DMSO : PEG300 : castor oil : Saline = 5 : 10 : 20 : 65 (i.e. 50 μL DMSO → 100 μLPEG300 → 200 μL castor oil → 650 μL Saline) Injection Formulation 7: Ethanol : Cremophor : Saline = 10: 10 : 80 (i.e. 100 μL Ethanol → 100 μL Cremophor → 800 μL Saline) Injection Formulation 8: Dissolve in Cremophor/Ethanol (50 : 50), then diluted by Saline Injection Formulation 9: EtOH : Corn oil = 10 : 90 (i.e. 100 μL EtOH → 900 μL Corn oil) Injection Formulation 10: EtOH : PEG300:Tween 80 : Saline = 10 : 40 : 5 : 45 (i.e. 100 μL EtOH → 400 μLPEG300 → 50 μL Tween 80 → 450 μL Saline) Oral Formulations Oral Formulation 1: Suspend in 0.5% CMC Na (carboxymethylcellulose sodium) Oral Formulation 2: Suspend in 0.5% Carboxymethyl cellulose Example: Take the Oral Formulation 1 (Suspend in 0.5% CMC Na) as an example, if 100 mL of 2.5 mg/mL working solution is to be prepared, you can first prepare 0.5% CMC Na solution by measuring 0.5 g CMC Na and dissolve it in 100 mL ddH2O to obtain a clear solution; then add 250 mg of the product to 100 mL 0.5% CMC Na solution, to make the suspension solution (2.5 mg/mL, ready for use in animals). Oral Formulation 3: Dissolved in PEG400 Oral Formulation 4: Suspend in 0.2% Carboxymethyl cellulose Oral Formulation 5: Dissolve in 0.25% Tween 80 and 0.5% Carboxymethyl cellulose Oral Formulation 6: Mixing with food powders Note: Please be aware that the above formulations are for reference only. InvivoChem strongly recommends customers to read literature methods/protocols carefully before determining which formulation you should use for in vivo studies, as different compounds have different solubility properties and have to be formulated differently. (Please use freshly prepared in vivo formulations for optimal results.) |
| Preparing Stock Solutions | 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | |
| 1 mM | 9.4268 mL | 47.1342 mL | 94.2685 mL | |
| 5 mM | 1.8854 mL | 9.4268 mL | 18.8537 mL | |
| 10 mM | 0.9427 mL | 4.7134 mL | 9.4268 mL |