Physicochemical Properties
| Molecular Formula | C6H10O7 |
| Molecular Weight | 194.14 |
| CAS # | 685-73-4 |
| Related CAS # | 685-73-4; 14984-39-5; 91510-62-2 |
| Appearance | Typically exists as solids at room temperature |
| Density | 2.0±0.1 g/cm3 |
| Boiling Point | 495.2±45.0 °C at 760 mmHg |
| Melting Point | 166°C |
| Flash Point | 211.1±22.2 °C |
| Vapour Pressure | 0.0±2.9 mmHg at 25°C |
| Index of Refraction | 1.685 |
| LogP | -2.88 |
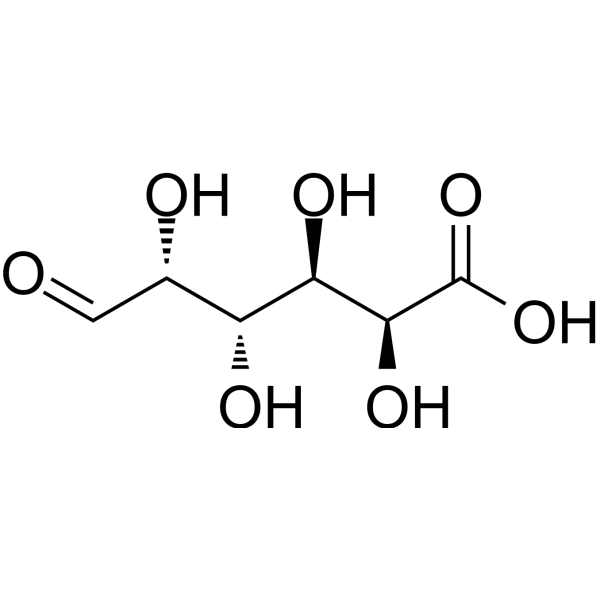
| SMILES | C(=O)[C@@H]([C@H]([C@H]([C@@H](C(=O)O)O)O)O)O |
| Synonyms | D-galUA; 685-73-4; DL-Galacturonic acid; 14982-50-4; (2S,3R,4S,5R)-2,3,4,5-tetrahydroxy-6-oxohexanoic acid; 2ENU0N1DRP; 4JK6RN80GF; Galacturonic acid, D-; Polygalacturonic Acid (Technical Grade); |
| HS Tariff Code | 2934.99.9001 |
| Storage |
Powder-20°C 3 years 4°C 2 years In solvent -80°C 6 months -20°C 1 month |
| Shipping Condition | Room temperature (This product is stable at ambient temperature for a few days during ordinary shipping and time spent in Customs) |
Biological Activity
| Targets | Endogenous Metabolite; Microbial Metabolite |
| ln Vitro | Pectin-rich biomasses, such as citrus peel and sugar beet pulp, hold promise as inexpensive feedstocks for microbial fermentations as enzymatic hydrolysis of their component polysaccharides can be accomplished inexpensively to yield high concentrations of fermentable sugars and D-galacturonic acid (D-galUA). In this study, we tackle a number of challenges associated with engineering a microbial strain to convert pectin-rich hydrolysates into commodity and specialty chemicals. First, we engineer D-galUA utilization into yeast, Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Second, we identify that the mechanism of D-galUA uptake into yeast is mediated by hexose transporters and that consumption of D-galUA is inhibited by D-glucose. Third, we enable co-utilization of D-galUA and D-glucose by identifying and expressing a heterologous transporter, GatA, from Aspergillus niger. Last, we demonstrate the use of this transporter for production of the platform chemical, meso-galactaric acid, directly from industrial Navel orange peel waste. [1] |
| References |
[1]. Engineering Saccharomyces cerevisiae for co-utilization of D-galacturonic acid and D-glucose from citrus peel waste. Nat Commun. 2018 Nov 29;9(1):5059. |
| Additional Infomation |
Aldehydo-D-galacturonic acid is a D-galacturonic acid. It is a conjugate acid of an aldehydo-D-galacturonate.
(2S,3R,4S,5R)-2,3,4,5-tetrahydroxy-6-oxohexanoic acid has been reported in Angelica gigas, Codonopsis pilosula, and other organisms with data available. aldehydo-D-galacturonate is a metabolite found in or produced by Saccharomyces cerevisiae. |
Solubility Data
| Solubility (In Vitro) |
H2O: >120 mg/mL (~580 mM)
DMSO: >120 mg/mL (~580 mM) |
| Solubility (In Vivo) |
Note: Listed below are some common formulations that may be used to formulate products with low water solubility (e.g. < 1 mg/mL), you may test these formulations using a minute amount of products to avoid loss of samples. Injection Formulations (e.g. IP/IV/IM/SC) Injection Formulation 1: DMSO : Tween 80: Saline = 10 : 5 : 85 (i.e. 100 μL DMSO stock solution → 50 μL Tween 80 → 850 μL Saline) *Preparation of saline: Dissolve 0.9 g of sodium chloride in 100 mL ddH ₂ O to obtain a clear solution. Injection Formulation 2: DMSO : PEG300 :Tween 80 : Saline = 10 : 40 : 5 : 45 (i.e. 100 μL DMSO → 400 μLPEG300 → 50 μL Tween 80 → 450 μL Saline) Injection Formulation 3: DMSO : Corn oil = 10 : 90 (i.e. 100 μL DMSO → 900 μL Corn oil) Example: Take the Injection Formulation 3 (DMSO : Corn oil = 10 : 90) as an example, if 1 mL of 2.5 mg/mL working solution is to be prepared, you can take 100 μL 25 mg/mL DMSO stock solution and add to 900 μL corn oil, mix well to obtain a clear or suspension solution (2.5 mg/mL, ready for use in animals). Injection Formulation 4: DMSO : 20% SBE-β-CD in saline = 10 : 90 [i.e. 100 μL DMSO → 900 μL (20% SBE-β-CD in saline)] *Preparation of 20% SBE-β-CD in Saline (4°C,1 week): Dissolve 2 g SBE-β-CD in 10 mL saline to obtain a clear solution. Injection Formulation 5: 2-Hydroxypropyl-β-cyclodextrin : Saline = 50 : 50 (i.e. 500 μL 2-Hydroxypropyl-β-cyclodextrin → 500 μL Saline) Injection Formulation 6: DMSO : PEG300 : castor oil : Saline = 5 : 10 : 20 : 65 (i.e. 50 μL DMSO → 100 μLPEG300 → 200 μL castor oil → 650 μL Saline) Injection Formulation 7: Ethanol : Cremophor : Saline = 10: 10 : 80 (i.e. 100 μL Ethanol → 100 μL Cremophor → 800 μL Saline) Injection Formulation 8: Dissolve in Cremophor/Ethanol (50 : 50), then diluted by Saline Injection Formulation 9: EtOH : Corn oil = 10 : 90 (i.e. 100 μL EtOH → 900 μL Corn oil) Injection Formulation 10: EtOH : PEG300:Tween 80 : Saline = 10 : 40 : 5 : 45 (i.e. 100 μL EtOH → 400 μLPEG300 → 50 μL Tween 80 → 450 μL Saline) Oral Formulations Oral Formulation 1: Suspend in 0.5% CMC Na (carboxymethylcellulose sodium) Oral Formulation 2: Suspend in 0.5% Carboxymethyl cellulose Example: Take the Oral Formulation 1 (Suspend in 0.5% CMC Na) as an example, if 100 mL of 2.5 mg/mL working solution is to be prepared, you can first prepare 0.5% CMC Na solution by measuring 0.5 g CMC Na and dissolve it in 100 mL ddH2O to obtain a clear solution; then add 250 mg of the product to 100 mL 0.5% CMC Na solution, to make the suspension solution (2.5 mg/mL, ready for use in animals). Oral Formulation 3: Dissolved in PEG400 Oral Formulation 4: Suspend in 0.2% Carboxymethyl cellulose Oral Formulation 5: Dissolve in 0.25% Tween 80 and 0.5% Carboxymethyl cellulose Oral Formulation 6: Mixing with food powders Note: Please be aware that the above formulations are for reference only. InvivoChem strongly recommends customers to read literature methods/protocols carefully before determining which formulation you should use for in vivo studies, as different compounds have different solubility properties and have to be formulated differently. (Please use freshly prepared in vivo formulations for optimal results.) |
| Preparing Stock Solutions | 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | |
| 1 mM | 5.1509 mL | 25.7546 mL | 51.5092 mL | |
| 5 mM | 1.0302 mL | 5.1509 mL | 10.3018 mL | |
| 10 mM | 0.5151 mL | 2.5755 mL | 5.1509 mL |