Physicochemical Properties
| Molecular Formula | C6CL4O2 |
| Molecular Weight | 245.88 |
| Exact Mass | 204.13 |
| CAS # | 118-75-2 |
| PubChem CID | 8371 |
| Appearance |
GOLDEN-YELLOW PLATELETS FROM ACETIC ACID OR ACETONE; MONOCLINIC PRISMS FROM BENZENE OR TOLUENE OR BY SUBLIMATION IN VACUO YELLOW LEAFLETS OR PRISMS |
| Density | 1.8±0.1 g/cm3 |
| Boiling Point | 269.5±40.0 °C at 760 mmHg |
| Melting Point | 295-296 °C (dec.) |
| Flash Point | 111.7±27.9 °C |
| Vapour Pressure | 0.0±0.6 mmHg at 25°C |
| Index of Refraction | 1.595 |
| LogP | 1.39 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 0 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 2 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 0 |
| Heavy Atom Count | 12 |
| Complexity | 278 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
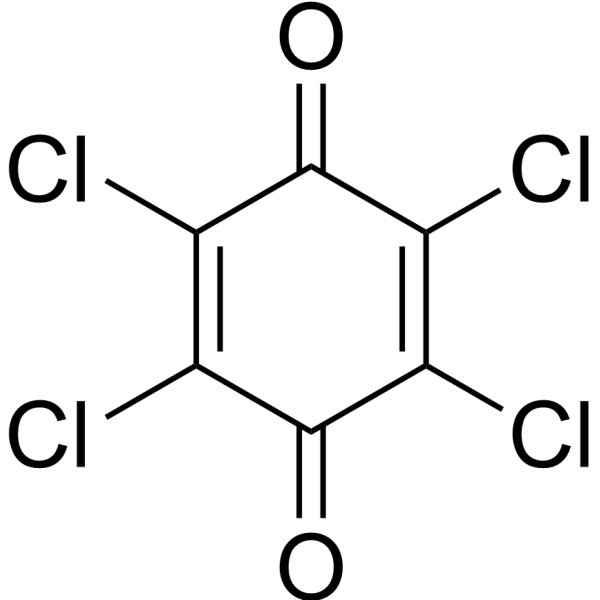
| SMILES | ClC1C(C(=C(C(C=1Cl)=O)Cl)Cl)=O |
| InChi Key | UGNWTBMOAKPKBL-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
| InChi Code | InChI=1S/C6Cl4O2/c7-1-2(8)6(12)4(10)3(9)5(1)11 |
| Chemical Name | 2,3,5,6-tetrachlorocyclohexa-2,5-diene-1,4-dione |
| Synonyms | Tetrachloro-p-benzoquinone |
| HS Tariff Code | 2934.99.9001 |
| Storage |
Powder-20°C 3 years 4°C 2 years In solvent -80°C 6 months -20°C 1 month |
| Shipping Condition | Room temperature (This product is stable at ambient temperature for a few days during ordinary shipping and time spent in Customs) |
Biological Activity
| Targets | TLR4 |
| ADME/Pharmacokinetics |
Absorption, Distribution and Excretion POORLY ABSORBED /WHEN ADMIN ORALLY IN RATS/. ...NOT ABSORBED PERCUTANEOUSLY. Metabolism / Metabolites MICROBIAL DEGRADATION OF SODIUM PENTACHLOROPHENATE WAS STUDIED IN MIXED MICROBIAL COMMUNTIES & IN AXENIC BACTERIAL CULTURE. EVIDENCE WAS OBTAINED FOR THE PROBABLE PARTICIPATION OF 2,6-DICHLOROHYDROQUINONE & TETRACHLOROHYDROQUINONE OR TETRACHLOROBENZOQUINONE AS INTERMEDIATES IN CATABOLISM OF SODIUM PENTACHLORPHENATE. A SMALL AMT OF CHLORANIL WAS FOUND IN THE URINE OF ANIMALS ADMIN SODIUM PENTACHLOROPHENOL. CHLORANIL WAS ALSO DETECTED IN INTESTINAL TISSUES & LIVERS OF MICE. WHEN CHLORANIL WAS ADDED TO CULTURES OF ASPERGILLUS NIGER, NEUROSPORA CRASSA, OR MUCOR SP, RAPID BUILDUP OF FREE RADICALS...OBSERVED BY ELECTRON SPIN RESONANCE SPECTROSCOPY. YEAST SUSPENSIONS & EXTRACTS ALSO EXHIBIT RAPID BUILDUP & DECAY OF FREE RADICAL. THIS CORRESPONDS TO SEMIQUINONE. YIELDS TETRACHLOROBENZOSEMIQUINONE IN ESCHERICHIA). /FROM TABLE/ Cultures of the basidiomycete Mycena avenacea TA8480 were shown to metabolize pentachlorophenol, tetrachloro-p-hydroquinone and 2,3,5,6-tetrachloro-p-benzoquinone. The first metabolite of the pentachlorophenol degradation pathway was identified as 2,3,5,6-tetrachloro-p-hydroquinone. ... Dechlorination of 2,3,5,6-tetrachloro-p-hydroquinone yielded 3,5,6-trichloro-2-hydroxy-p-benzoquinone. ... |
| Toxicity/Toxicokinetics |
Toxicity Data LC50 (rat) = 2,485 mg/m3/4h Non-Human Toxicity Values ORAL LD50 OF TECHNICAL CHLORANIL FREE OF TETRACHLORODIBENZO-P-DIOXINS WAS 6951 MG/KG IN FEMALE RATS. |
| References |
[1]. The acute exposure of tetrachloro-p-benzoquinone (a.k.a. chloranil) triggers inflammation and neurological dysfunction via Toll-like receptor 4 signaling: The protective role of melatonin preconditioning. Toxicology. 2017 Apr 15;381:39-50. |
| Additional Infomation |
Chloranil is a yellow powder with a slight odor. (NTP, 1992) Tetrachloro-1,4-benzoquinone is a member of the class of 1,4-benzoquiones that is 1,4-benzoquinone in which all four hydrogens are substituted by chlorines. It has a role as a metabolite and an EC 2.7.1.33 (pantothenate kinase) inhibitor. It is an organochlorine compound and a member of 1,4-benzoquinones. A quinone fungicide used for treatment of seeds and foliage. Mechanism of Action FUNGICIDAL PROPERTIES... ACTIVITY ATTRIBUTED TO ROLE IN OXIDATION-REDUCTION PROCESSES AND TO INHIBITION OF CARBOXYLASES. ... Tetrachloro-1,4-benzoquinone, a cmpd previously shown to inactivate glutathione S-transferases very efficiently by covalent binding in or close to the active site, completely prevented the alkylation of the enzyme by iodoacetamide, indicating that the reaction had taken place with the cysteine residues. ... Evidence was obtained for the covalent binding of three benzoquinone molecules per subunit, ie equivalent to the number of cysteine residues present. This threefold binding /resulted/ with a fourfold molar excess of the benzoquinone, illustrating high reactivity of this cmpd. Comparison of the number of amino acid residues modified by tetrachloro-1,4-benzoquinone with the decr of catalytic activity revealed an almost complete inhibition after modification of one cysteine residue. |
Solubility Data
| Solubility (In Vitro) | May dissolve in DMSO (in most cases), if not, try other solvents such as H2O, Ethanol, or DMF with a minute amount of products to avoid loss of samples |
| Solubility (In Vivo) |
Note: Listed below are some common formulations that may be used to formulate products with low water solubility (e.g. < 1 mg/mL), you may test these formulations using a minute amount of products to avoid loss of samples. Injection Formulations (e.g. IP/IV/IM/SC) Injection Formulation 1: DMSO : Tween 80: Saline = 10 : 5 : 85 (i.e. 100 μL DMSO stock solution → 50 μL Tween 80 → 850 μL Saline) *Preparation of saline: Dissolve 0.9 g of sodium chloride in 100 mL ddH ₂ O to obtain a clear solution. Injection Formulation 2: DMSO : PEG300 :Tween 80 : Saline = 10 : 40 : 5 : 45 (i.e. 100 μL DMSO → 400 μLPEG300 → 50 μL Tween 80 → 450 μL Saline) Injection Formulation 3: DMSO : Corn oil = 10 : 90 (i.e. 100 μL DMSO → 900 μL Corn oil) Example: Take the Injection Formulation 3 (DMSO : Corn oil = 10 : 90) as an example, if 1 mL of 2.5 mg/mL working solution is to be prepared, you can take 100 μL 25 mg/mL DMSO stock solution and add to 900 μL corn oil, mix well to obtain a clear or suspension solution (2.5 mg/mL, ready for use in animals). Injection Formulation 4: DMSO : 20% SBE-β-CD in saline = 10 : 90 [i.e. 100 μL DMSO → 900 μL (20% SBE-β-CD in saline)] *Preparation of 20% SBE-β-CD in Saline (4°C,1 week): Dissolve 2 g SBE-β-CD in 10 mL saline to obtain a clear solution. Injection Formulation 5: 2-Hydroxypropyl-β-cyclodextrin : Saline = 50 : 50 (i.e. 500 μL 2-Hydroxypropyl-β-cyclodextrin → 500 μL Saline) Injection Formulation 6: DMSO : PEG300 : castor oil : Saline = 5 : 10 : 20 : 65 (i.e. 50 μL DMSO → 100 μLPEG300 → 200 μL castor oil → 650 μL Saline) Injection Formulation 7: Ethanol : Cremophor : Saline = 10: 10 : 80 (i.e. 100 μL Ethanol → 100 μL Cremophor → 800 μL Saline) Injection Formulation 8: Dissolve in Cremophor/Ethanol (50 : 50), then diluted by Saline Injection Formulation 9: EtOH : Corn oil = 10 : 90 (i.e. 100 μL EtOH → 900 μL Corn oil) Injection Formulation 10: EtOH : PEG300:Tween 80 : Saline = 10 : 40 : 5 : 45 (i.e. 100 μL EtOH → 400 μLPEG300 → 50 μL Tween 80 → 450 μL Saline) Oral Formulations Oral Formulation 1: Suspend in 0.5% CMC Na (carboxymethylcellulose sodium) Oral Formulation 2: Suspend in 0.5% Carboxymethyl cellulose Example: Take the Oral Formulation 1 (Suspend in 0.5% CMC Na) as an example, if 100 mL of 2.5 mg/mL working solution is to be prepared, you can first prepare 0.5% CMC Na solution by measuring 0.5 g CMC Na and dissolve it in 100 mL ddH2O to obtain a clear solution; then add 250 mg of the product to 100 mL 0.5% CMC Na solution, to make the suspension solution (2.5 mg/mL, ready for use in animals). Oral Formulation 3: Dissolved in PEG400 Oral Formulation 4: Suspend in 0.2% Carboxymethyl cellulose Oral Formulation 5: Dissolve in 0.25% Tween 80 and 0.5% Carboxymethyl cellulose Oral Formulation 6: Mixing with food powders Note: Please be aware that the above formulations are for reference only. InvivoChem strongly recommends customers to read literature methods/protocols carefully before determining which formulation you should use for in vivo studies, as different compounds have different solubility properties and have to be formulated differently. (Please use freshly prepared in vivo formulations for optimal results.) |
| Preparing Stock Solutions | 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | |
| 1 mM | 4.0670 mL | 20.3351 mL | 40.6702 mL | |
| 5 mM | 0.8134 mL | 4.0670 mL | 8.1340 mL | |
| 10 mM | 0.4067 mL | 2.0335 mL | 4.0670 mL |