Physicochemical Properties
| Molecular Formula | C14H20N2O4 |
| Molecular Weight | 280.3196 |
| Exact Mass | 277.119 |
| CAS # | 145757-47-7 |
| Related CAS # | Carboxy-PTIO potassium;148819-94-7 |
| PubChem CID | 2733503 |
| Appearance | Typically exists as solid at room temperature |
| LogP | 1.756 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 1 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 3 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 2 |
| Heavy Atom Count | 20 |
| Complexity | 423 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
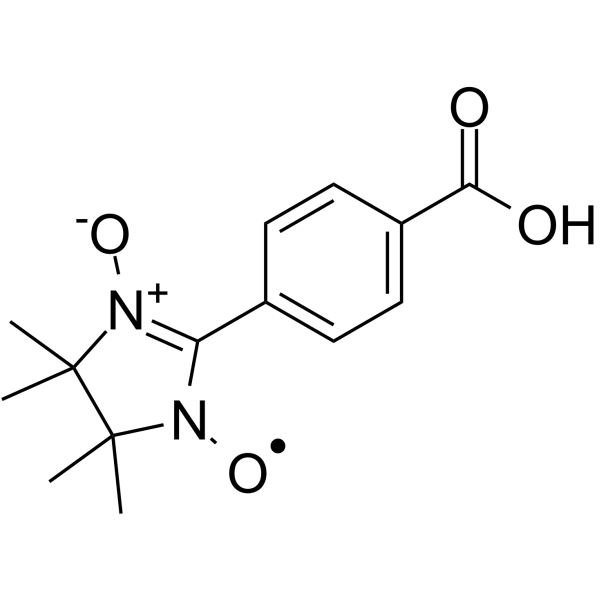
| SMILES | OC(C1C=CC(C2N(O)C(C)(C)C(C)(C)N2O)=CC=1)=O |
| InChi Key | KWNDLWPKCDMGTN-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
| InChi Code | InChI=1S/C14H17N2O4/c1-13(2)14(3,4)16(20)11(15(13)19)9-5-7-10(8-6-9)12(17)18/h5-8H,1-4H3,(H,17,18) |
| HS Tariff Code | 2934.99.9001 |
| Storage |
Powder-20°C 3 years 4°C 2 years In solvent -80°C 6 months -20°C 1 month |
| Shipping Condition | Room temperature (This product is stable at ambient temperature for a few days during ordinary shipping and time spent in Customs) |
Biological Activity
| ln Vitro | The increase of NO expression generated by physalin A treatment is greatly suppressed by Carboxy-PTIO (200 μM; 1 h prior to physalin A; 24 hours), whereas Carboxy-PTIO treatment alone shows no change[1]. Physalin A-induced cleavage of procaspase-3 and PARP is lessened by carboxy-PTIO (200 μM; 1 h before; 24 hours), which also downregulates ICAD expression and lessens DNA fragmentation in nuclei[1]. On iNOS expression, carboxy-PTIO (200 μM; 1 h before physalin A; 24 hours) has no effect. Carboxy-PTIO, on the other hand, reverses the lowered mTOR and p-mTOR levels caused by physalin A while also suppressing the conversion of LC3 I to LC3 II in A375-S2 cells[1]. |
| ln Vivo | In rats treated with lipopolysaccharide (LPS), carboxy-PTIO (intravenous injection; 0.056-1.70 mg/kg/min; infused for 1 hr beginning 90 min after the LPS injection 90 min) improves survival rates and hypotension. However, in normal rats, it does not impact every parameter[3]. |
| Cell Assay |
Cell Viability Assay[1] Cell Types: A375-S2 cells Tested Concentrations: 200 μM Incubation Duration: 1 h prior to physalin A; 24 hrs (hours) Experimental Results: diminished physalin A-induced procaspase-3 and PARP cleavage. |
| Animal Protocol |
Animal/Disease Models: SD rats[3] Doses: 0.056-1.70 mg/kg/min Route of Administration: intravenous (iv) injection; 0.056-1.70 mg/kg/min; infused for 1 hr beginning 90 min after the LPS injection 90 min Experimental Results: demonstrated a therapeutic potent value in endotoxin shock through the direct scavenging action against NO. |
| References |
[1]. Nitric oxide induces apoptosis and autophagy; autophagy down-regulates NO synthesis in physalin A-treated A375-S2 human melanoma cells.Food Chem Toxicol. 2014 Sep;71:128-35. [2]. Antagonistic action of imidazolineoxyl N-oxides against endothelium-derived relaxing factor/.NO through a radical reaction. Biochemistry. 1993 Jan 26;32(3):827-32. [3]. Therapeutic effects of imidazolineoxyl N-oxide against endotoxin shock through its direct nitric oxide-scavenging activity. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1994 Jul 29;202(2):923-30. |
| Additional Infomation | Carboxy-PTIO is a mmeber of the class of imidazolines and organic radical that is 4,4,5,5-tetramethyl-3-oxo-4,5-dihydro-1H-3lambda(5)-imidazol-1-yl]oxidanyl substituted at position 2 by a 4-carboxyphenyl group. It has a role as a radical scavenger and an apoptosis inhibitor. It is an organic radical, a benzoic acid and a member of imidazolines. It is a conjugate base of a carboxylato-PTIO. |
Solubility Data
| Solubility (In Vitro) | May dissolve in DMSO (in most cases), if not, try other solvents such as H2O, Ethanol, or DMF with a minute amount of products to avoid loss of samples |
| Solubility (In Vivo) |
Note: Listed below are some common formulations that may be used to formulate products with low water solubility (e.g. < 1 mg/mL), you may test these formulations using a minute amount of products to avoid loss of samples. Injection Formulations (e.g. IP/IV/IM/SC) Injection Formulation 1: DMSO : Tween 80: Saline = 10 : 5 : 85 (i.e. 100 μL DMSO stock solution → 50 μL Tween 80 → 850 μL Saline) *Preparation of saline: Dissolve 0.9 g of sodium chloride in 100 mL ddH ₂ O to obtain a clear solution. Injection Formulation 2: DMSO : PEG300 :Tween 80 : Saline = 10 : 40 : 5 : 45 (i.e. 100 μL DMSO → 400 μLPEG300 → 50 μL Tween 80 → 450 μL Saline) Injection Formulation 3: DMSO : Corn oil = 10 : 90 (i.e. 100 μL DMSO → 900 μL Corn oil) Example: Take the Injection Formulation 3 (DMSO : Corn oil = 10 : 90) as an example, if 1 mL of 2.5 mg/mL working solution is to be prepared, you can take 100 μL 25 mg/mL DMSO stock solution and add to 900 μL corn oil, mix well to obtain a clear or suspension solution (2.5 mg/mL, ready for use in animals). Injection Formulation 4: DMSO : 20% SBE-β-CD in saline = 10 : 90 [i.e. 100 μL DMSO → 900 μL (20% SBE-β-CD in saline)] *Preparation of 20% SBE-β-CD in Saline (4°C,1 week): Dissolve 2 g SBE-β-CD in 10 mL saline to obtain a clear solution. Injection Formulation 5: 2-Hydroxypropyl-β-cyclodextrin : Saline = 50 : 50 (i.e. 500 μL 2-Hydroxypropyl-β-cyclodextrin → 500 μL Saline) Injection Formulation 6: DMSO : PEG300 : castor oil : Saline = 5 : 10 : 20 : 65 (i.e. 50 μL DMSO → 100 μLPEG300 → 200 μL castor oil → 650 μL Saline) Injection Formulation 7: Ethanol : Cremophor : Saline = 10: 10 : 80 (i.e. 100 μL Ethanol → 100 μL Cremophor → 800 μL Saline) Injection Formulation 8: Dissolve in Cremophor/Ethanol (50 : 50), then diluted by Saline Injection Formulation 9: EtOH : Corn oil = 10 : 90 (i.e. 100 μL EtOH → 900 μL Corn oil) Injection Formulation 10: EtOH : PEG300:Tween 80 : Saline = 10 : 40 : 5 : 45 (i.e. 100 μL EtOH → 400 μLPEG300 → 50 μL Tween 80 → 450 μL Saline) Oral Formulations Oral Formulation 1: Suspend in 0.5% CMC Na (carboxymethylcellulose sodium) Oral Formulation 2: Suspend in 0.5% Carboxymethyl cellulose Example: Take the Oral Formulation 1 (Suspend in 0.5% CMC Na) as an example, if 100 mL of 2.5 mg/mL working solution is to be prepared, you can first prepare 0.5% CMC Na solution by measuring 0.5 g CMC Na and dissolve it in 100 mL ddH2O to obtain a clear solution; then add 250 mg of the product to 100 mL 0.5% CMC Na solution, to make the suspension solution (2.5 mg/mL, ready for use in animals). Oral Formulation 3: Dissolved in PEG400 Oral Formulation 4: Suspend in 0.2% Carboxymethyl cellulose Oral Formulation 5: Dissolve in 0.25% Tween 80 and 0.5% Carboxymethyl cellulose Oral Formulation 6: Mixing with food powders Note: Please be aware that the above formulations are for reference only. InvivoChem strongly recommends customers to read literature methods/protocols carefully before determining which formulation you should use for in vivo studies, as different compounds have different solubility properties and have to be formulated differently. (Please use freshly prepared in vivo formulations for optimal results.) |
| Preparing Stock Solutions | 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | |
| 1 mM | 3.5674 mL | 17.8368 mL | 35.6735 mL | |
| 5 mM | 0.7135 mL | 3.5674 mL | 7.1347 mL | |
| 10 mM | 0.3567 mL | 1.7837 mL | 3.5674 mL |