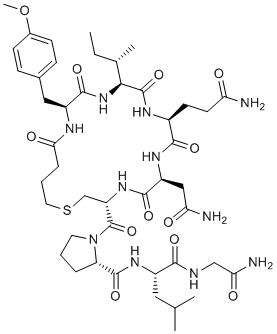
Carbetocin is a novel and potent obstetric drug acting as an agonist of the oxytocin receptor (Ki of 7.1 nM) with improved in vivo stability over oxytocin. Carbetocin exhibits a high affinity (Ki=1.17 μM) for the chimeric N-terminus (E1) of the oxytocin receptor. There is potential for using carbetocin in studies on postpartum hemorrhage. Carbetocin can pass through the blood-brain barrier and activates the central nervous system's oxytocin receptors, which has antidepressant-like effects.
Physicochemical Properties
| Molecular Formula | C45H69N11O12S |
| Molecular Weight | 988.170 |
| Exact Mass | 987.484 |
| Elemental Analysis | C, 54.70; H, 7.04; N, 15.59; O, 19.43; S, 3.24 |
| CAS # | 37025-55-1 |
| Related CAS # | Carbetocin acetate; 1631754-28-3 |
| PubChem CID | 16681432 |
| Appearance | White to off-white solid powder |
| Density | 1.2±0.1 g/cm3 |
| Boiling Point | 1477.9±65.0 °C at 760 mmHg |
| Flash Point | 847.6±34.3 °C |
| Vapour Pressure | 0.0±0.3 mmHg at 25°C |
| Index of Refraction | 1.533 |
| LogP | -3.59 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 10 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 13 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 18 |
| Heavy Atom Count | 69 |
| Complexity | 1850 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 8 |
| SMILES | O=C([C@H](CSCCCC(N[C@H](C1=O)CC2=CC=C(OC)C=C2)=O)NC([C@@H](NC([C@](NC([C@](N1)([H])[C@@H](C)CC)=O)([H])CCC(N)=O)=O)CC(N)=O)=O)N(CCC3)[C@@H]3C(N[C@@H](CC(C)C)C(NCC(N)=O)=O)=O |
| InChi Key | NSTRIRCPWQHTIA-DTRKZRJBSA-N |
| InChi Code | InChI=1S/C45H69N11O12S/c1-6-25(4)38-44(66)51-28(15-16-34(46)57)40(62)52-31(21-35(47)58)41(63)54-32(23-69-18-8-10-37(60)50-30(42(64)55-38)20-26-11-13-27(68-5)14-12-26)45(67)56-17-7-9-33(56)43(65)53-29(19-24(2)3)39(61)49-22-36(48)59/h11-14,24-25,28-33,38H,6-10,15-23H2,1-5H3,(H2,46,57)(H2,47,58)(H2,48,59)(H,49,61)(H,50,60)(H,51,66)(H,52,62)(H,53,65)(H,54,63)(H,55,64)/t25-,28-,29-,30-,31-,32-,33-,38-/m0/s1 |
| Chemical Name | (2S)-N-[(2S)-1-[(2-amino-2-oxoethyl)amino]-4-methyl-1-oxopentan-2-yl]-1-[(3R,6S,9S,12S,15S)-6-(2-amino-2-oxoethyl)-9-(3-amino-3-oxopropyl)-12-[(2S)-butan-2-yl]-15-[(4-methoxyphenyl)methyl]-5,8,11,14,17-pentaoxo-1-thia-4,7,10,13,16-pentazacycloicosane-3-carbonyl]pyrrolidine-2-carboxamide |
| Synonyms | EINECS-253-312-6; EINECS 253-312-6; Carbetocin; EINECS253-312-6 |
| HS Tariff Code | 2934.99.9001 |
| Storage |
Powder-20°C 3 years 4°C 2 years In solvent -80°C 6 months -20°C 1 month Note: Please store this product in a sealed and protected environment (e.g. under nitrogen), avoid exposure to moisture and light. |
| Shipping Condition | Room temperature (This product is stable at ambient temperature for a few days during ordinary shipping and time spent in Customs) |
Biological Activity
| ln Vitro | Carbetocin is an agonist that has a ten-fold lower affinity for the oxytocin receptor but a much longer half-life and much greater stability. When it comes to the chimeric E1 receptor, carbetocin exhibits a greater affinity for all of the combinations of E1 with the other extracellular domains, namely E13 (Ki=13 nM), E123 (Ki=56 nM), and E1234 (Ki=37 nM)[2]. |
| ln Vivo |
Carbetocin (2-20 mg/kg; i.p.) has a significant treatment effect on the percentage of time spent swimming, climbing, and immobilizing[1]. Carbetocin (1, 10,100 μg/rat, i.c.v.) shows that when 100 μg/rat is administered acutely, there is a dose-dependent increase in the percentage of time spent swimming and a corresponding decrease in immobility[1]. |
| Animal Protocol |
Male Sprague-Dawley rats weighing between 300 and 500 g 2, 6.4, 20 mg/kg IP; single dose |
| ADME/Pharmacokinetics |
Absorption, Distribution and Excretion Bioavailability is 80% following intramuscular injection. Biological Half-Life 40 minutes |
| References |
[1]. Assessing the antidepressant-like effects of carbetocin, an oxytocin agonist, using a modification of the forced swimming test. Psychopharmacology (Berl). 2010 May;210(1):35-43. [2]. Binding domains of the oxytocin receptor for the selective oxytocin receptor antagonist barusiban in comparison to the agonists oxytocin and carbetocin. Eur J Pharmacol. 2005 Mar 7;510(1-2):9-16. [3]. The effects of oxytocin and its analog, carbetocin, on genetic deficits in sensorimotor gating. Eur Neuropsychopharmacol. 2012 May;22(5):374-8. |
| Additional Infomation |
Carbetocin is oxytocin in which the hydrogen on the phenolic hydroxy group is substituted by methyl, the amino group on the cysteine residue is substituted by hydrogen, and the sulfur of the cysteine residue is replaced by a methylene group. A synthetic carba-analogue of oxytocin, it is used to control bleeding after giving birth. Like oxytocin, it causes contraction of the uterus. It has a role as an oxytocic. Carbetocin is a drug used to control postpartum hemorrhage, bleeding after giving birth. It is an analogue of oxytocin, and its action is similar to that of oxytocin -- it causes contraction of the uterus. Carbetocin is a long-acting synthetic agonist analogue of human oxytocin, with antihemorrhagic and uterotonic activities. Upon administration, carbetocin targets, binds to and activates peripheral oxytocin receptors that are present on the smooth musculature of the uterus. This causes uterus contractions and prevents excessive bleeding after childbirth, particularly following Cesarean section, and may be used to decrease blood loss during hysteroscopic myomectomy. Drug Indication Used to control postpartum hemorrhage and bleeding after giving birth. Mechanism of Action Carbetocin binds to oxytocin receptors present on the smooth musculature of the uterus, resulting in rhythmic contractions of the uterus, increased frequency of existing contractions, and increased uterine tone. The oxytocin receptor content of the uterus is very low in the non-pregnant state, and increases during pregnancy, reaching a peak at the time of delivery. Pharmacodynamics Carbetocin is a drug used to control postpartum hemorrhage, bleeding after giving birth. It is sold under the trade name Duratocin. It is an analogue of oxytocin, and its action is similar to that of oxytocin; it causes contraction of the uterus. |
Solubility Data
| Solubility (In Vitro) |
H2O: ≥ 33.3 mg/mL (~33.7 mM) DMSO: ≥ 31 mg/mL (~31.4 mM) |
| Solubility (In Vivo) |
Solubility in Formulation 1: ≥ 2.5 mg/mL (2.53 mM) (saturation unknown) in 10% DMSO + 40% PEG300 + 5% Tween80 + 45% Saline (add these co-solvents sequentially from left to right, and one by one), clear solution. For example, if 1 mL of working solution is to be prepared, you can add 100 μL of 25.0 mg/mL clear DMSO stock solution to 400 μL PEG300 and mix evenly; then add 50 μL Tween-80 to the above solution and mix evenly; then add 450 μL normal saline to adjust the volume to 1 mL. Preparation of saline: Dissolve 0.9 g of sodium chloride in 100 mL ddH₂ O to obtain a clear solution. Solubility in Formulation 2: ≥ 2.5 mg/mL (2.53 mM) (saturation unknown) in 10% DMSO + 90% (20% SBE-β-CD in Saline) (add these co-solvents sequentially from left to right, and one by one), clear solution. For example, if 1 mL of working solution is to be prepared, you can add 100 μL of 25.0 mg/mL clear DMSO stock solution to 900 μL of 20% SBE-β-CD physiological saline solution and mix evenly. Preparation of 20% SBE-β-CD in Saline (4°C,1 week): Dissolve 2 g SBE-β-CD in 10 mL saline to obtain a clear solution. Solubility in Formulation 3: ≥ 2.5 mg/mL (2.53 mM) (saturation unknown) in 10% DMSO + 90% Corn Oil (add these co-solvents sequentially from left to right, and one by one), clear solution. For example, if 1 mL of working solution is to be prepared, you can add 100 μL of 25.0 mg/mL clear DMSO stock solution to 900 μL of corn oil and mix evenly. (Please use freshly prepared in vivo formulations for optimal results.) |
| Preparing Stock Solutions | 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | |
| 1 mM | 1.0120 mL | 5.0599 mL | 10.1197 mL | |
| 5 mM | 0.2024 mL | 1.0120 mL | 2.0239 mL | |
| 10 mM | 0.1012 mL | 0.5060 mL | 1.0120 mL |