Physicochemical Properties
| Molecular Formula | C25H27CLN2O |
| Molecular Weight | 406.95 |
| Exact Mass | 406.181 |
| CAS # | 652973-93-8 |
| PubChem CID | 11849514 |
| Appearance | Typically exists as solid at room temperature |
| Density | 1.21g/cm3 |
| Boiling Point | 597.091ºC at 760 mmHg |
| Melting Point | 53-55ºC |
| Flash Point | 314.91ºC |
| Index of Refraction | 1.638 |
| LogP | 6.666 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 2 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 2 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 5 |
| Heavy Atom Count | 29 |
| Complexity | 533 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 3 |
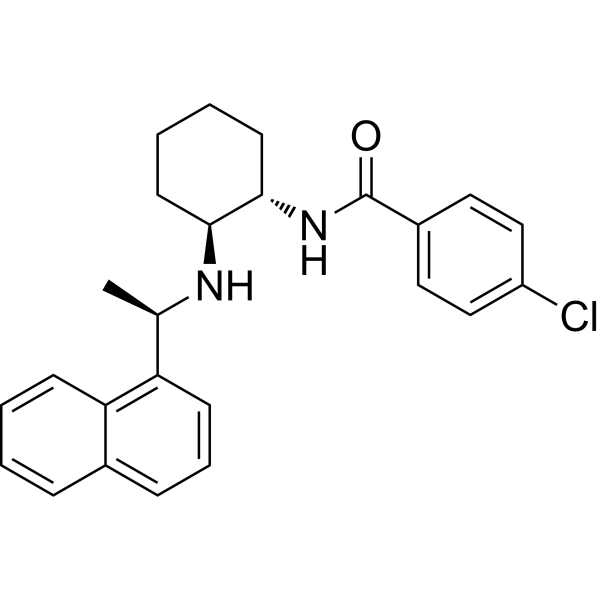
| SMILES | C[C@H](C1=CC=CC2=CC=CC=C21)N[C@H]3CCCC[C@@H]3NC(=O)C4=CC=C(C=C4)Cl |
| InChi Key | YTFUQWWKTIWYEY-CQLNOVPUSA-N |
| InChi Code | InChI=1S/C25H27ClN2O/c1-17(21-10-6-8-18-7-2-3-9-22(18)21)27-23-11-4-5-12-24(23)28-25(29)19-13-15-20(26)16-14-19/h2-3,6-10,13-17,23-24,27H,4-5,11-12H2,1H3,(H,28,29)/t17-,23+,24+/m1/s1 |
| Chemical Name | 4-chloro-N-[(1S,2S)-2-[[(1R)-1-naphthalen-1-ylethyl]amino]cyclohexyl]benzamide |
| HS Tariff Code | 2934.99.9001 |
| Storage |
Powder-20°C 3 years 4°C 2 years In solvent -80°C 6 months -20°C 1 month |
| Shipping Condition | Room temperature (This product is stable at ambient temperature for a few days during ordinary shipping and time spent in Customs) |
Biological Activity
| Targets | CaSR[1] IC50: 0.39 μM (Inositol phosphate)[1] |
| ln Vitro | Calhex 231 dose-dependently inhibited 10 mM Ca2+-induced IP responses with potency similar to that in WT receptors in T764A (IC50 = 0.28 ± 0.05 μM) and H766A (IC50 = 0.64 ± 0.03 μM) mutant receptors. [1]. Calhex 231 treatment significantly down-regulates the expression of CaSR, α-SMA, Col-I/III, and MMP2/9. Calhex 231 attenuates high glucose-induced cardiac fibrosis in cardiac fibroblasts [2]. Calhex 231 is able to inhibit Itch (atrofen-1-interacting protein 4)-ubiquitin proteasome and TGF-β1/ Smads pathway, then inhibits the proliferation of cardiac fibroblasts, reduces collagen deposition, and alleviates high glucose-induced myocardial fibrosis [2]. |
| ln Vivo | Calhex 231 (4.07 mg/kg (10 µmol/kg); intraperitoneal injection; once daily; for 12 weeks; male Wistar rats) treatment reduces diabetic myocardial fibrosis in rats with type 1 diabetes (T1D)[2]. Calhex-231 (Cal, 0.1-1 mg/kg) has an ameliorative effect on traumatic hemorrhagic shock by improving vascular hyporesponsiveness and reducing mitochondrial dysfunction[1]. |
| Cell Assay |
Cell Proliferation Assay[2] Cell Types: Primary neonatal rat cardiac fibroblasts (CFs). Tested Concentrations: 3 µM. Incubation Duration: 24 hours. Experimental Results: Significantly decreased the proliferation of cardiac fibroblasts. |
| Animal Protocol |
Animal/Disease Models: Male Wistar rats (8 weeks old) injected with Streptozotocin[2] Doses: 4.07 mg/kg (10 µmoL/kg). Route of Administration: Intraperitoneal injection; daily; for 12 weeks. Experimental Results: Ameliorated diabetic myocardial fibrosis in T1D rats. Animal/Disease Models: Four hundred and fifty Sprague-Dawley (SD) rats (half male and half female)[3]. Doses: 0.1, 1, or 5 mg/kg. Route of Administration: A continuous infusion. Experimental Results: In all groups, MAP, LVSP, and ±dp/dtmax decreased significantly after shock. Administration of 5 or 1 mg/kg Cal resulted in significantly increased values at 1 and 2 hr postadministration, compared to rats in the LR only group (or 0.01). Rats treated with 1 mg/kg Cal demonstrated the greatest recovery. LR infusion induced short-term and slightly increase of blood pressor in normal rats. Cal (1 mg/kg) without LR infusion did not restore the decreased MAP after shock. |
| References |
[1].Modeling and mutagenesis of the binding site of Calhex 231, a novel negative allosteric modulator of the extracellular Ca(2+)-sensing receptor. J Biol Chem. 2003 Dec 5;278(49):49487-94. [2].Modeling and mutagenesis of the binding site of Calhex 231, a novel negative allosteric modulator of the extracellular Ca(2+)-sensing receptor. J Biol Chem. 2003 Dec 5;278(49):49487-94. [3].The Calcilytic Drug Calhex-231 Ameliorates Vascular Hyporesponsiveness in Traumatic Hemorrhagic Shock by Inhibiting Oxidative Stress and miR-208a-Mediated Mitochondrial Fission. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2020 Dec 3:2020:4132785. |
Solubility Data
| Solubility (In Vitro) | Typically soluble in DMSO (e.g. 10 mM) |
| Solubility (In Vivo) |
Note: Listed below are some common formulations that may be used to formulate products with low water solubility (e.g. < 1 mg/mL), you may test these formulations using a minute amount of products to avoid loss of samples. Injection Formulations (e.g. IP/IV/IM/SC) Injection Formulation 1: DMSO : Tween 80: Saline = 10 : 5 : 85 (i.e. 100 μL DMSO stock solution → 50 μL Tween 80 → 850 μL Saline) *Preparation of saline: Dissolve 0.9 g of sodium chloride in 100 mL ddH ₂ O to obtain a clear solution. Injection Formulation 2: DMSO : PEG300 :Tween 80 : Saline = 10 : 40 : 5 : 45 (i.e. 100 μL DMSO → 400 μLPEG300 → 50 μL Tween 80 → 450 μL Saline) Injection Formulation 3: DMSO : Corn oil = 10 : 90 (i.e. 100 μL DMSO → 900 μL Corn oil) Example: Take the Injection Formulation 3 (DMSO : Corn oil = 10 : 90) as an example, if 1 mL of 2.5 mg/mL working solution is to be prepared, you can take 100 μL 25 mg/mL DMSO stock solution and add to 900 μL corn oil, mix well to obtain a clear or suspension solution (2.5 mg/mL, ready for use in animals). Injection Formulation 4: DMSO : 20% SBE-β-CD in saline = 10 : 90 [i.e. 100 μL DMSO → 900 μL (20% SBE-β-CD in saline)] *Preparation of 20% SBE-β-CD in Saline (4°C,1 week): Dissolve 2 g SBE-β-CD in 10 mL saline to obtain a clear solution. Injection Formulation 5: 2-Hydroxypropyl-β-cyclodextrin : Saline = 50 : 50 (i.e. 500 μL 2-Hydroxypropyl-β-cyclodextrin → 500 μL Saline) Injection Formulation 6: DMSO : PEG300 : castor oil : Saline = 5 : 10 : 20 : 65 (i.e. 50 μL DMSO → 100 μLPEG300 → 200 μL castor oil → 650 μL Saline) Injection Formulation 7: Ethanol : Cremophor : Saline = 10: 10 : 80 (i.e. 100 μL Ethanol → 100 μL Cremophor → 800 μL Saline) Injection Formulation 8: Dissolve in Cremophor/Ethanol (50 : 50), then diluted by Saline Injection Formulation 9: EtOH : Corn oil = 10 : 90 (i.e. 100 μL EtOH → 900 μL Corn oil) Injection Formulation 10: EtOH : PEG300:Tween 80 : Saline = 10 : 40 : 5 : 45 (i.e. 100 μL EtOH → 400 μLPEG300 → 50 μL Tween 80 → 450 μL Saline) Oral Formulations Oral Formulation 1: Suspend in 0.5% CMC Na (carboxymethylcellulose sodium) Oral Formulation 2: Suspend in 0.5% Carboxymethyl cellulose Example: Take the Oral Formulation 1 (Suspend in 0.5% CMC Na) as an example, if 100 mL of 2.5 mg/mL working solution is to be prepared, you can first prepare 0.5% CMC Na solution by measuring 0.5 g CMC Na and dissolve it in 100 mL ddH2O to obtain a clear solution; then add 250 mg of the product to 100 mL 0.5% CMC Na solution, to make the suspension solution (2.5 mg/mL, ready for use in animals). Oral Formulation 3: Dissolved in PEG400 Oral Formulation 4: Suspend in 0.2% Carboxymethyl cellulose Oral Formulation 5: Dissolve in 0.25% Tween 80 and 0.5% Carboxymethyl cellulose Oral Formulation 6: Mixing with food powders Note: Please be aware that the above formulations are for reference only. InvivoChem strongly recommends customers to read literature methods/protocols carefully before determining which formulation you should use for in vivo studies, as different compounds have different solubility properties and have to be formulated differently. (Please use freshly prepared in vivo formulations for optimal results.) |
| Preparing Stock Solutions | 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | |
| 1 mM | 2.4573 mL | 12.2865 mL | 24.5730 mL | |
| 5 mM | 0.4915 mL | 2.4573 mL | 4.9146 mL | |
| 10 mM | 0.2457 mL | 1.2287 mL | 2.4573 mL |