CTLA-4 inhibitor (B7/CD28 interaction inhibitor 1) is a novel and potent inhibitor of CTLA4 or CTLA-4 (cytotoxic T-lymphocyte-associated protein 4). CTLA4 is also known as CD152 (cluster of differentiation 152) and is a protein receptor that, functioning as an immune checkpoint, downregulates immune responses. CTLA4 is constitutively expressed in Tregs but only upregulated in conventional T cells after activation. It acts as an 'off' switch when bound to CD80 or CD86 on the surface of antigen-presenting cells. Polymorphisms of the CTLA-4 gene are associated with autoimmune diseases such as autoimmune thyroid disease and multiple sclerosis, though this association is often weak. In Systemic Lupus Erythematosus (SLE), the splice variant sCTLA-4 is found to be aberrantly produced and found in the serum of patients with active SLE.
Physicochemical Properties
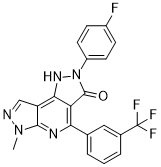
| Molecular Formula | C21H13F4N5O | |
| Molecular Weight | 427.36 | |
| Exact Mass | 427.105 | |
| CAS # | 635324-72-0 | |
| Related CAS # |
|
|
| PubChem CID | 101136468 | |
| Appearance | Off-white to light yellow solid powder | |
| Density | 1.5±0.1 g/cm3 | |
| Boiling Point | 599.5±60.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |
| Flash Point | 316.4±32.9 °C | |
| Vapour Pressure | 0.0±1.7 mmHg at 25°C | |
| Index of Refraction | 1.677 | |
| LogP | 3.8 | |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 1 | |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 8 | |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 2 | |
| Heavy Atom Count | 31 | |
| Complexity | 685 | |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 | |
| InChi Key | WQKVVTLTCHDAST-UHFFFAOYSA-N | |
| InChi Code | InChI=1S/C21H13F4N5O/c1-29-19-15(10-26-29)18-16(20(31)30(28-18)14-7-5-13(22)6-8-14)17(27-19)11-3-2-4-12(9-11)21(23,24)25/h2-10,28H,1H3 | |
| Chemical Name |
|
|
| Synonyms |
|
|
| HS Tariff Code | 2934.99.9001 | |
| Storage |
Powder-20°C 3 years 4°C 2 years In solvent -80°C 6 months -20°C 1 month |
|
| Shipping Condition | Room temperature (This product is stable at ambient temperature for a few days during ordinary shipping and time spent in Customs) |
Biological Activity
| ln Vitro | To create an exceptionally stable signaling complex, the divalent B7.1 homodimer is bridged by the divalent CTLA4 homodimer. Immunosuppression and improved allograft survival are the outcomes of blocking B7/CD28 interaction with soluble receptors or monoclonal antibodies, while B7/CTLA-4 blockage strengthens anticancer immune responses. An essential part of naive T cell activation involves the interaction between B7 molecules on antigen-presenting cells and costimulatory molecules on T cells. Drugs that interfere with these interactions might therefore be helpful in the management of autoimmune disorders and transplant rejection [1]. |
| References |
[1]. Structure-activity studies of a series of dipyrazolo[3,4-b:3',4'-d]pyridin-3-ones binding to the immune regulatory protein B7.1. Bioorg Med Chem. 2003 Jul 3;11(13):2991-3013. |
Solubility Data
| Solubility (In Vitro) |
|
|||
| Solubility (In Vivo) |
Solubility in Formulation 1: 2.08 mg/mL (4.87 mM) in 10% DMSO + 40% PEG300 +5% Tween-80 + 45% Saline (add these co-solvents sequentially from left to right, and one by one), suspension solution; with sonication. For example, if 1 mL of working solution is to be prepared, you can add 100 μL of 20.8 mg/mL clear DMSO stock solution to 400 μL PEG300 and mix evenly; then add 50 μL Tween-80 + to the above solution and mix evenly; then add 450 μL normal saline to adjust the volume to 1 mL. Preparation of saline: Dissolve 0.9 g of sodium chloride in 100 mL ddH₂ O to obtain a clear solution. (Please use freshly prepared in vivo formulations for optimal results.) |
| Preparing Stock Solutions | 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | |
| 1 mM | 2.3399 mL | 11.6997 mL | 23.3995 mL | |
| 5 mM | 0.4680 mL | 2.3399 mL | 4.6799 mL | |
| 10 mM | 0.2340 mL | 1.1700 mL | 2.3399 mL |