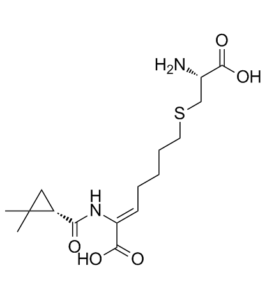
Cilastatin (formerly MK791; MK-0791; Recarbrio) is a renal dehydropeptidase inhibitor and a leukotriene D4 dipeptidase inhibitor with nephroprotective effects. Dehydropeptidase is an enzyme found in the kidney and is responsible for degrading the antibiotic imipenem.
Physicochemical Properties
| Molecular Formula | C16H26N2O5S |
| Molecular Weight | 358.45 |
| Exact Mass | 358.156 |
| Elemental Analysis | C, 53.61; H, 7.31; N, 7.82; O, 22.32; S, 8.95 |
| CAS # | 82009-34-5 |
| Related CAS # | Cilastatin sodium;81129-83-1;Cilastatin-15N,d3;2738376-83-3 |
| PubChem CID | 6435415 |
| Appearance | White to off-white solid powder |
| Density | 1.275 g/cm3 |
| Boiling Point | 655.5ºC at 760 mmHg |
| Melting Point | 156-158ºC |
| Index of Refraction | 1.569 |
| LogP | 2.523 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 4 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 7 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 11 |
| Heavy Atom Count | 24 |
| Complexity | 519 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 2 |
| SMILES | C([C@H]1CC1(C)C)(=O)N/C(/C(=O)O)=C\CCCCSC[C@H](N)C(=O)O |
| InChi Key | DHSUYTOATWAVLW-WFVMDLQDSA-N |
| InChi Code | InChI=1S/C16H26N2O5S/c1-16(2)8-10(16)13(19)18-12(15(22)23)6-4-3-5-7-24-9-11(17)14(20)21/h6,10-11H,3-5,7-9,17H2,1-2H3,(H,18,19)(H,20,21)(H,22,23)/b12-6-/t10-,11+/m1/s1 |
| Chemical Name | 2-Heptenoic acid, 7-((2-amino-2-carboxyethyl)thio)-2-(((2,2-dimethylcyclopropyl)carbonyl)amino)-, (R-(R*,S*-(Z)))- |
| Synonyms | MK 791; M K-791; MK0791; MK791;Cilastatin; MK 0791; MK-0791; |
| HS Tariff Code | 2934.99.9001 |
| Storage |
Powder-20°C 3 years 4°C 2 years In solvent -80°C 6 months -20°C 1 month |
| Shipping Condition | Room temperature (This product is stable at ambient temperature for a few days during ordinary shipping and time spent in Customs) |
Biological Activity
| Targets | β-lactam |
| ln Vitro | Without lessening the antimicrobial effect of Vancomycin, ciplastatin (200 μg/mL; 24 hours; RPTECs) treatment prevents Vancomycin-induced proximal tubule apoptosis and boosts cell viability[2]. |
| ln Vivo | In a mouse model of systemic infection (female mice, strain CD-1, 20 g), Imipenem plus Cilastatin can shield mice against infections with S. aureus, E. coli, and P. aeruginosa[3]. |
| ADME/Pharmacokinetics |
Absorption, Distribution and Excretion Cilastatin is reported by official FDA labeling to be 70% excreted in the urine, however published literature has reported values as high as 98%. Cilastatin has a volume of distribution of 14.6-20.1L. Cilastatin has a total clearance of 0.2 L/h/kg and a renal clearance of 0.10-0.16 L/h/kg. Biological Half-Life The half-life of cilastatin is approximately 1h. |
| Toxicity/Toxicokinetics |
Protein Binding Cilastatin is plasma protein binding is reported to be 35-40%. |
| References |
[1]. The renal membrane dipeptidase (dehydropeptidase I) inhibitor, cilastatin, inhibits the bacterialmetallo-beta-lactamase enzyme CphA. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1995 Jul;39(7):1629-31. [2]. Protective Effects of Cilastatin Against Vancomycin-Induced Nephrotoxicity. Biomed Res Int. 2015;2015:704382. [3]. In Vitro and in Vivo Activities of LJC10,627, a New Carbapenem With Stability to Dehydropeptidase I. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1991 Jan;35(1):203-7. |
| Additional Infomation |
Cilastatin is the thioether resulting from the formal oxidative coupling of the thiol group of L-cysteine with the 7-position of (2Z)-2-({[(1S)-2,2-dimethylcyclopropyl]carbonyl}amino)hept-2-enoic acid. It is an inhibitor of dehydropeptidase I (membrane dipeptidase, 3.4.13.19), an enzyme found in the brush border of renal tubes and responsible for degrading the antibiotic imipenem. Cilastatin is therefore administered (as the sodium salt) with imipenem to prolong the antibacterial effect of the latter by preventing its renal metabolism to inactive and potentially nephrotoxic products. Cilastatin also acts as a leukotriene D4 dipeptidase inhibitor, preventing the metabolism of leukotriene D4 to leukotriene E4. It has a role as a protease inhibitor, an EC 3.4.13.19 (membrane dipeptidase) inhibitor, a xenobiotic and an environmental contaminant. It is a non-proteinogenic L-alpha-amino acid, a L-cysteine derivative, an organic sulfide and a carboxamide. It is a conjugate acid of a cilastatin(1-). Cilastatin is an inhibitor of renal dehydropeptidase, an enzyme responsible for both the metabolism of thienamycin beta-lactam antibiotics as well as conversion of leukotriene D4 to leukotriene E4. Since the antibiotic, [imipenem], is one such antibiotic that is hydrolyzed by dehydropeptidase, cilastatin is used in combination with imipenem to prevent its metabolism. The first combination product containing both drugs was approved by the FDA in November of 1985 under the trade name Primaxin, marketed by Merck & Co. A newer triple-drug product was approved in July 2019 under the trade name Recarbrio which also contains [relebactam]. Cilastatin is a Renal Dehydropeptidase Inhibitor. The mechanism of action of cilastatin is as a Dipeptidase Inhibitor. Cilastatin has been reported in Bos taurus and Apis cerana with data available. A renal dehydropeptidase-I and leukotriene D4 dipeptidase inhibitor. Since the antibiotic, IMIPENEM, is hydrolyzed by dehydropeptidase-I, which resides in the brush border of the renal tubule, cilastatin is administered with imipenem to increase its effectiveness. The drug also inhibits the metabolism of leukotriene D4 to leukotriene E4. See also: ... View More ... Drug Indication Cilastatin is indicated, in combination with [imipenem] with or without [relebactam], for the treatment of bacterial infections including respiratory, skin, bone, gynecologic, urinary tract, and intra-abdominal as well as septicemia and endocarditis. FDA Label Mechanism of Action Cilastatin is a renal dehydropeptidase-I inhibitor. Since the antibiotic, imipenem, is hydrolyzed by dehydropeptidase-I, which resides in the brush border of the renal tubule, cilastatin is administered with imipenem to block the metabolism of imipenem. |
Solubility Data
| Solubility (In Vitro) |
DMSO : 72~100 mg/mL (200.86~278.98 mM ) 1M NaOH : ~100 mg/mL (~278.98 mM) H2O : 7~12.5 mg/mL (~34.87 mM) |
| Solubility (In Vivo) |
Solubility in Formulation 1: ≥ 2.75 mg/mL (7.67 mM) (saturation unknown) in 10% DMSO + 40% PEG300 + 5% Tween80 + 45% Saline (add these co-solvents sequentially from left to right, and one by one), clear solution. For example, if 1 mL of working solution is to be prepared, you can add 100 μL of 27.5 mg/mL clear DMSO stock solution to 400 μL PEG300 and mix evenly; then add 50 μL Tween-80 to the above solution and mix evenly; then add 450 μL normal saline to adjust the volume to 1 mL. Preparation of saline: Dissolve 0.9 g of sodium chloride in 100 mL ddH₂ O to obtain a clear solution. Solubility in Formulation 2: ≥ 2.5 mg/mL (6.97 mM) (saturation unknown) in 10% DMSO + 90% (20% SBE-β-CD in Saline) (add these co-solvents sequentially from left to right, and one by one), clear solution. For example, if 1 mL of working solution is to be prepared, you can add 100 μL of 25.0 mg/mL clear DMSO stock solution to 900 μL of 20% SBE-β-CD physiological saline solution and mix evenly. Preparation of 20% SBE-β-CD in Saline (4°C,1 week): Dissolve 2 g SBE-β-CD in 10 mL saline to obtain a clear solution. Solubility in Formulation 3: ≥ 2.5 mg/mL (6.97 mM) (saturation unknown) in 10% DMSO + 90% Corn Oil (add these co-solvents sequentially from left to right, and one by one), clear solution. For example, if 1 mL of working solution is to be prepared, you can add 100 μL of 25.0 mg/mL clear DMSO stock solution to 900 μL of corn oil and mix evenly. Solubility in Formulation 4: 10% DMSO+40% PEG300+5% Tween-80+45% Saline: ≥ 2.75 mg/mL (7.67 mM) Solubility in Formulation 5: 20 mg/mL (55.80 mM) in 50% PEG300 50% Saline (add these co-solvents sequentially from left to right, and one by one), clear solution; with ultrasonication. Preparation of saline: Dissolve 0.9 g of sodium chloride in 100 mL ddH₂ O to obtain a clear solution. (Please use freshly prepared in vivo formulations for optimal results.) |
| Preparing Stock Solutions | 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | |
| 1 mM | 2.7898 mL | 13.9489 mL | 27.8979 mL | |
| 5 mM | 0.5580 mL | 2.7898 mL | 5.5796 mL | |
| 10 mM | 0.2790 mL | 1.3949 mL | 2.7898 mL |