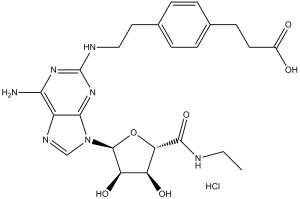
CGS 21680 HCl (CGS21680; CGS-21680), the hydrochloride salt of CGS 21680, is a potent and specific agonist of adenosine A2 receptors with potential antideppressant activity. It has 140-fold selectivity over A1 receptors and an IC50 of 22 nM for adenosine A2 receptor activation.
Physicochemical Properties
| Molecular Formula | C23H29N7O6.HCL | |
| Molecular Weight | 535.98 | |
| Exact Mass | 535.194 | |
| Elemental Analysis | C, 51.54; H, 5.64; Cl, 6.61; N, 18.29; O, 17.91 | |
| CAS # | 124431-80-7 | |
| Related CAS # | CGS 21680; 120225-54-9 | |
| PubChem CID | 10256643 | |
| Appearance | White to off-white solid powder | |
| Density | 204-206°C | |
| Melting Point | 204-206°C | |
| LogP | 1.682 | |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 7 | |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 11 | |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 10 | |
| Heavy Atom Count | 37 | |
| Complexity | 755 | |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 4 | |
| SMILES | O=C(O)CCC1=CC=C(CCNC2=NC3=C(N=CN3[C@H]4[C@H](O)[C@H](O)[C@@H](C(NCC)=O)O4)C(N)=N2)C=C1.Cl |
|
| InChi Key | QPHVMNOEKKJYJO-MJWSIIAUSA-N | |
| InChi Code | InChI=1S/C23H29N7O6.ClH/c1-2-25-21(35)18-16(33)17(34)22(36-18)30-11-27-15-19(24)28-23(29-20(15)30)26-10-9-13-5-3-12(4-6-13)7-8-14(31)32;/h3-6,11,16-18,22,33-34H,2,7-10H2,1H3,(H,25,35)(H,31,32)(H3,24,26,28,29);1H/t16-,17+,18-,22+;/m0./s1 | |
| Chemical Name | 3-[4-[2-[[6-amino-9-[(2R,3R,4S,5S)-5-(ethylcarbamoyl)-3,4-dihydroxyoxolan-2-yl]purin-2-yl]amino]ethyl]phenyl]propanoic acid;hydrochloride | |
| Synonyms |
|
|
| HS Tariff Code | 2934.99.9001 | |
| Storage |
Powder-20°C 3 years 4°C 2 years In solvent -80°C 6 months -20°C 1 month Note: Please store this product in a sealed and protected environment, avoid exposure to moisture. |
|
| Shipping Condition | Room temperature (This product is stable at ambient temperature for a few days during ordinary shipping and time spent in Customs) |
Biological Activity
| Targets | Adenosine A2A receptor ( Ki = 27 nM ) | |
| ln Vitro |
|
|
| ln Vivo |
|
|
| Enzyme Assay | CGS 21680C (2-[p-(2-carboxyethyl)phenethylamino]-5'-N-ethyl-carboxamido adenosine) a 2-substituted analog of the riboside uronamide, 5'-N-ethylcarboxamido adenosine and the related analog CGS 21577 (2-phenethylamino-5'-N-ethylcarboxamido adenosine), have high in vitro affinity for brain striatal adenosine A2 receptors (IC50 values = 22 and 13 nM, respectively). Both compounds were considerably less active at A1 receptors with CGS 21577 and CGS 21680C having respective IC50 values of 0.76 and 3.1 microM. The former compound was thus 59-fold selective for A2 receptors whereas CGS 21680C was 140-fold selective. In contrast, the reference A2 selective ligand, CV 1808 (2-phenylaminoadenosine), showed only 8-fold selectivity as an A2 ligand, having an IC50 of 115 nM in the [3H]-5'N-ethylcarboxamide adenosine assay and an IC50 of 910 nM at the N6-[3H] cyclohexyladenosine site. Further examination of CGS 21680C showed that the compound was without effect on binding to 17 other putative neurotransmitter/neuromodulator sites indicating its selectivity as an adenosine receptor ligand. In an isolated perfused working rat heart model, CGS 21680C effectively increased coronary flow with an ED25 value of 1.8 nM. The corresponding value for CGS 21577 was 3 nM whereas that for CV 1808 was 110 nM. The EC25 for eliciting bradycardia for all three compounds was greater than 1000 nM. The effects of all three compounds could be reversed by treatment with the xanthine adenosine antagonist, xanthine amine congener[1]. | |
| Cell Assay | Each group's 10×106 MNCs are re-suspended in 2 mL of RPMI 1640. Carboxy-fluorescein diacetate, succinimidyl ester (CFSE, final concentration 2.5 μM) is added to cell suspensions and well mixed. The staining process is quenched by adding 10 mL of ice-cold complete RPMI 1640 (containing 10% FBS) and incubating on ice for 5 minutes after being incubated in the dark for 15 minutes at 37°C. The cells are then given two RPMI 1640 washes. Re-suspended cell pellets are in full RPMI 1640, which contains 10% FBS. In 24-well culture plates, the stained MNCs (1×106 cells/mL, 1 mL/well) are cultured in triplicate under 37°C dark conditions. 50 μL of either P0 peptide (final concentration 10 μg/mL) or Concanavalin A (ConA, final concentration 5 μg/mL) are added to each well. After 72 hours, cells are gathered and stained for 30 minutes at 4°C using an anti-rat CD4 antibody labeled with PE. Ultimately, a flow cytometer is used to examine the cells. | |
| Animal Protocol |
In the nearby animal facility, female Lewis rats, weighing between 140 and 160 grams at birth, are kept in housing designed to prevent pathogens and provide them with unrestricted access to food and water. Day 5 p.i. is when CGS21680 administration begins (at a dose of 1 mg/kg in PBS). Until the end of the trials, rats in the experimental group receive intraperitoneal (i.p.) injections of CGS21680 every two days. The control group of rats receives the same volume of PBS in the same manner. It is decided on the dosages (1 mg/kg/i.p.) and the treatment plan (every two days, beginning on day 5 p.i.). Characterization of the adenosine A2 receptor has been limited due to the lack of available ligands which have high affinity and selectivity for this adenosine receptor subtype. In the present study, the binding of a highly A2-selective agonist radioligand, [3H]CGS 21680 (2-[p-(2-carboxyethyl)-phenethylamino]-5'-N-ethylcarboxamido adenosine) is described. [3H]CGS 21680 specific binding to rat striatal membranes was saturable, reversible and dependent upon protein concentration. Saturation studies revealed that [3H]CGS 21680 bound with high affinity (Kd = 15.5 nM) and limited capacity (apparent Bmax = 375 fmol/mg of protein) to a single class of recognition sites. Estimates of ligand affinity (16 nM) determined from association and dissociation kinetic experiments were in close agreement with the results from the saturation studies. [3H]CGS 21680 binding was greatest in striatal membranes with negligible specific binding obtained in rat cortical membranes. Adenosine agonists ligands competed for the binding of 5 nM [3H]CGS 21680 to striatal membranes with the following order of activity; CGS 21680 = 5'-N-ethylcarboxamidoadenosine greater than 2-phenylaminoadenosine (CV-1808) = 5'-N-methylcarboxamidoadenosine = 2-chloroadenosine greater than R-phenylisopropyladenosine greater than N6-cyclohexyladenosine greater than N6cyclopentyltheophylline greater than S-phenylisopropyladenosine. The nonxanthine adenosine antagonist, CGS 15943A, was the most active compound in inhibiting the binding of [3H]CGS 21680. Other adenosine antagonists inhibited binding in the following order; xanthine amine congener = (1,3-dipropyl-8-(2-amino-4-chloro)phenylxanthine greater than 1,3-dipropyl-8-cyclopentylxanthine greater than 1,3-diethyl-8-phenylxanthine greater than 8-phenyltheophylline greater than 8-cyclopentyltheophylline = xanthine carboxylic acid congener greater than 8-parasulfophenyltheophylline greater than theophylline greater than caffeine. The pharmacological profile of both adenosine agonist and antagonist compounds to compete for the binding of [3H]CGS 21680 was consistent with a selective interaction at the high affinity adenosine A2 receptor. A high positive correlation (r = 0.98, P less than .01) was observed between the pharmacological profile of adenosine ligands to inhibit the binding of [3H]CGS 21680 and the selective binding of [3H]NECA (+50 nM CPA) to high affinity A2 receptors. However, some differences between these assays were found for compounds which have moderate affinity and nonselective actions at both the A1 and A2 adenosine receptor subtypes. Unlike data obtained with nonselective adenosine ligands, the present results indicate that [3H]CGS 21680 directly labels the high affinity A2 receptor in rat brain without the need to block binding activity at the A1 receptor.[2] |
|
| References |
[1]. J Pharmacol Exp Ther . 1989 Oct;251(1):47-55. [2]. J Pharmacol Exp Ther . 1989 Dec;251(3):888-93. [3]. J Pharmacol Exp Ther . 1990 Mar;252(3):1134-41. [4]. Brain Res . 1990 Feb 19;509(2):328-30. |
|
| Additional Infomation |
Evaluation of adenosine A2 receptor function in the mammalian CNS has been impeded by the lack of highly selective A2 receptor agonists. The present investigations describe the actions of a recently introduced A2 selective adenosine agonist, CGS 21680 (2-[p-(carboxyethyl)phenylethylamino]-5'-N-ethylcarboxamidoadenosi ne), on various functional neural responses known to be affected by adenosine. In hippocampal slices, CGS 21680 appeared to be a weak agonist on pre- and postsynaptic measures of electrophysiological activity (putative A1 receptor mediated events) and was ineffective at stimulating the formation of cAMP (a putative A2b mediated response). 5'-N-ethycarboxamidoadenosine (NECA), which is known to act at both A2a and A2b receptors, increased hippocampal cAMP levels 4-fold. In striatal slices, CGS 21680 potently stimulated the formation of cAMP with an EC50 of 110 nM but was ineffective at inhibiting electrically stimulated dopamine release. In contrast, adenosine and cyclohexyladenosine both inhibited the stimulus-evoked overflow of dopamine. These results agree with previous receptor binding studies suggesting that CGS 21680 is a relatively selective agonist at the high affinity adenosine A2a receptor in striatum, with little intrinsic activity at the low affinity A2b site in hippocampus.[3] The A2 selective adenosine receptor agonist 2-p-(2-carboxyethyl)phenethylamino-5'-N-ethylcarboxamidoadenosine (CGS 21680) depressed the spontaneous, acetylcholine- and glutamate-evoked firing of rat cerebral sensorimotor cortical neurons. Iontophoretically applied CGS 21680 was equipotent with adenosine as a depressant and its actions were antagonized by 8-p-sulphophenyltheophylline applied from another barrel of the multibarrelled micropipette. The observation of a potent depressant action of a selective A2 receptor agonist suggests that A2 receptors are involved in the modulation of cerebral cortical neuronal firing by adenosine.[4] |
Solubility Data
| Solubility (In Vitro) |
|
|||
| Solubility (In Vivo) |
Solubility in Formulation 1: ≥ 2.5 mg/mL (4.66 mM) (saturation unknown) in 10% DMSO + 40% PEG300 + 5% Tween80 + 45% Saline (add these co-solvents sequentially from left to right, and one by one), clear solution. For example, if 1 mL of working solution is to be prepared, you can add 100 μL of 25.0 mg/mL clear DMSO stock solution to 400 μL PEG300 and mix evenly; then add 50 μL Tween-80 to the above solution and mix evenly; then add 450 μL normal saline to adjust the volume to 1 mL. Preparation of saline: Dissolve 0.9 g of sodium chloride in 100 mL ddH₂ O to obtain a clear solution. Solubility in Formulation 2: ≥ 2.5 mg/mL (4.66 mM) (saturation unknown) in 10% DMSO + 90% (20% SBE-β-CD in Saline) (add these co-solvents sequentially from left to right, and one by one), clear solution. For example, if 1 mL of working solution is to be prepared, you can add 100 μL of 25.0 mg/mL clear DMSO stock solution to 900 μL of 20% SBE-β-CD physiological saline solution and mix evenly. Preparation of 20% SBE-β-CD in Saline (4°C,1 week): Dissolve 2 g SBE-β-CD in 10 mL saline to obtain a clear solution. Solubility in Formulation 3: ≥ 2.5 mg/mL (4.66 mM) (saturation unknown) in 10% DMSO + 90% Corn Oil (add these co-solvents sequentially from left to right, and one by one), clear solution. For example, if 1 mL of working solution is to be prepared, you can add 100 μL of 25.0 mg/mL clear DMSO stock solution to 900 μL of corn oil and mix evenly. Solubility in Formulation 4: 30% Propylene glycol , 5% Tween 80 , 65% D5W: 30mg/mL (Please use freshly prepared in vivo formulations for optimal results.) |
| Preparing Stock Solutions | 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | |
| 1 mM | 1.8657 mL | 9.3287 mL | 18.6574 mL | |
| 5 mM | 0.3731 mL | 1.8657 mL | 3.7315 mL | |
| 10 mM | 0.1866 mL | 0.9329 mL | 1.8657 mL |