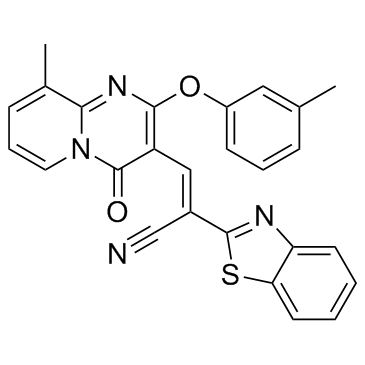
CCG-63802 is a novel, selective and reversible inhibitor of RGS4 (regulator of G-protein signaling) with IC50 value of 1.9 μM. Regulators of G protein signaling, or RGS, are multifunctional proteins that accelerate GTPase and are crucial in promoting GTP hydrolysis through the heterotrimeric G protein α subunit. A crucial function of RGS 4, also referred to as RGP4, is to negatively regulate signaling upstream or at the heterotrimeric G protein level.
Physicochemical Properties
| Molecular Formula | C26H18N4O2S |
| Molecular Weight | 450.51172 |
| Exact Mass | 450.115 |
| Elemental Analysis | C, 69.32; H, 4.03; N, 12.44; O, 7.10; S, 7.12 |
| CAS # | 620112-78-9 |
| PubChem CID | 6057678 |
| Appearance | Yellow to orange solid powder |
| Density | 1.31 |
| Boiling Point | 547.9ºC at 760 mmHg |
| Flash Point | 285.1ºC |
| Index of Refraction | 1.694 |
| LogP | 5.777 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 0 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 6 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 4 |
| Heavy Atom Count | 33 |
| Complexity | 1030 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| SMILES | N#C/C(C1=NC2=CC=CC=C2S1)=C\C3=C(N=C4C(C)=CC=CN4C3=O)OC5=CC=CC(C)=C5 |
| InChi Key | VFSVKVQMZDJFQX-NBVRZTHBSA-N |
| InChi Code | InChI=1S/C26H18N4O2S/c1-16-7-5-9-19(13-16)32-24-20(26(31)30-12-6-8-17(2)23(30)29-24)14-18(15-27)25-28-21-10-3-4-11-22(21)33-25/h3-14H,1-2H3/b18-14+ |
| Chemical Name | (E)-2-(1,3-benzothiazol-2-yl)-3-[9-methyl-2-(3-methylphenoxy)-4-oxopyrido[1,2-a]pyrimidin-3-yl]prop-2-enenitrile |
| Synonyms | CCG63802; CCG-4986; CCG-63802; CCG 63802; CCG 4986; CCG4986 |
| HS Tariff Code | 2934.99.9001 |
| Storage |
Powder-20°C 3 years 4°C 2 years In solvent -80°C 6 months -20°C 1 month |
| Shipping Condition | Room temperature (This product is stable at ambient temperature for a few days during ordinary shipping and time spent in Customs) |
Biological Activity
| Targets | RGS4 ( IC50 = 1.9 μM ) |
| ln Vitro | CCG-63802 (5 μM) iinhibits regulators of G-protein signaling (RGS) proteins, causing HEK-293 cells to depolarize once more in the presence of BK (bradykinin) and 8-Br-cGMP (membrane-permeable analogue of cGMP)[2]. |
| ln Vivo | CCG-63802 (0.05 mg/kg; intratracheal administration; once per week; 90 days) decreases the expression of the RGS4 protein, which partially abrogates the PGZ's attenuating effect on airway remodeling, inflammation, and hyperresponsiveness (AHR)[3]. |
| Animal Protocol |
Forty female BALB/c mice aged 6-8 week old 0.05 mg/kg Intratracheal administration; once per week; 90 days |
| References |
[1]. Reversible, allosteric small-molecule inhibitors of regulator of G protein signaling proteins. Mol Pharmacol. 2010 Sep;78(3):524-33. [2]. Interaction between bradykinin and natriuretic peptides via RGS protein activation in HEK-293 cells. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2012 Dec 15;303(12):C1260-8. [3]. PPARγ Agonist PGZ Attenuates OVA-Induced Airway Inflammation and Airway Remodeling via RGS4 Signaling in Mouse Model. Inflammation. 2018 Dec;41(6):2079-2089. |
Solubility Data
| Solubility (In Vitro) | DMSO: ~1.67 mg/mL (~3.7 mM) |
| Solubility (In Vivo) |
Note: Listed below are some common formulations that may be used to formulate products with low water solubility (e.g. < 1 mg/mL), you may test these formulations using a minute amount of products to avoid loss of samples. Injection Formulations (e.g. IP/IV/IM/SC) Injection Formulation 1: DMSO : Tween 80: Saline = 10 : 5 : 85 (i.e. 100 μL DMSO stock solution → 50 μL Tween 80 → 850 μL Saline) *Preparation of saline: Dissolve 0.9 g of sodium chloride in 100 mL ddH ₂ O to obtain a clear solution. Injection Formulation 2: DMSO : PEG300 :Tween 80 : Saline = 10 : 40 : 5 : 45 (i.e. 100 μL DMSO → 400 μLPEG300 → 50 μL Tween 80 → 450 μL Saline) Injection Formulation 3: DMSO : Corn oil = 10 : 90 (i.e. 100 μL DMSO → 900 μL Corn oil) Example: Take the Injection Formulation 3 (DMSO : Corn oil = 10 : 90) as an example, if 1 mL of 2.5 mg/mL working solution is to be prepared, you can take 100 μL 25 mg/mL DMSO stock solution and add to 900 μL corn oil, mix well to obtain a clear or suspension solution (2.5 mg/mL, ready for use in animals). Injection Formulation 4: DMSO : 20% SBE-β-CD in saline = 10 : 90 [i.e. 100 μL DMSO → 900 μL (20% SBE-β-CD in saline)] *Preparation of 20% SBE-β-CD in Saline (4°C,1 week): Dissolve 2 g SBE-β-CD in 10 mL saline to obtain a clear solution. Injection Formulation 5: 2-Hydroxypropyl-β-cyclodextrin : Saline = 50 : 50 (i.e. 500 μL 2-Hydroxypropyl-β-cyclodextrin → 500 μL Saline) Injection Formulation 6: DMSO : PEG300 : castor oil : Saline = 5 : 10 : 20 : 65 (i.e. 50 μL DMSO → 100 μLPEG300 → 200 μL castor oil → 650 μL Saline) Injection Formulation 7: Ethanol : Cremophor : Saline = 10: 10 : 80 (i.e. 100 μL Ethanol → 100 μL Cremophor → 800 μL Saline) Injection Formulation 8: Dissolve in Cremophor/Ethanol (50 : 50), then diluted by Saline Injection Formulation 9: EtOH : Corn oil = 10 : 90 (i.e. 100 μL EtOH → 900 μL Corn oil) Injection Formulation 10: EtOH : PEG300:Tween 80 : Saline = 10 : 40 : 5 : 45 (i.e. 100 μL EtOH → 400 μLPEG300 → 50 μL Tween 80 → 450 μL Saline) Oral Formulations Oral Formulation 1: Suspend in 0.5% CMC Na (carboxymethylcellulose sodium) Oral Formulation 2: Suspend in 0.5% Carboxymethyl cellulose Example: Take the Oral Formulation 1 (Suspend in 0.5% CMC Na) as an example, if 100 mL of 2.5 mg/mL working solution is to be prepared, you can first prepare 0.5% CMC Na solution by measuring 0.5 g CMC Na and dissolve it in 100 mL ddH2O to obtain a clear solution; then add 250 mg of the product to 100 mL 0.5% CMC Na solution, to make the suspension solution (2.5 mg/mL, ready for use in animals). Oral Formulation 3: Dissolved in PEG400 Oral Formulation 4: Suspend in 0.2% Carboxymethyl cellulose Oral Formulation 5: Dissolve in 0.25% Tween 80 and 0.5% Carboxymethyl cellulose Oral Formulation 6: Mixing with food powders Note: Please be aware that the above formulations are for reference only. InvivoChem strongly recommends customers to read literature methods/protocols carefully before determining which formulation you should use for in vivo studies, as different compounds have different solubility properties and have to be formulated differently. (Please use freshly prepared in vivo formulations for optimal results.) |
| Preparing Stock Solutions | 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | |
| 1 mM | 2.2197 mL | 11.0985 mL | 22.1971 mL | |
| 5 mM | 0.4439 mL | 2.2197 mL | 4.4394 mL | |
| 10 mM | 0.2220 mL | 1.1099 mL | 2.2197 mL |