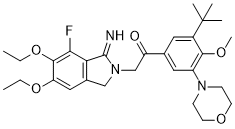
Atopaxar, formerly known as E5555, is a potent and orally -active PAR-1 inhibitor. E5555 inhibited the binding of a high-affinity thrombin receptor-activating peptide ([(3)H]haTRAP) to PAR-1 with a half maximal inhibitory concentration (IC(50)) value of 0.019μM. E5555 demonstrated strong inhibitory effects with IC(50) values of 0.064 and 0.031μM, respectively, on human platelet aggregation induced by thrombin and TRAP. With IC(50) values of 0.13 and 0.097μM, respectively, E5555 demonstrated strong and specific inhibitory effects on guinea pig platelet aggregation induced by thrombin and TRAP. E5555 may be used as a treatment for atherothrombotic illness.
Physicochemical Properties
| Molecular Formula | C29H38FN3O5 |
| Molecular Weight | 527.6374 |
| Exact Mass | 527.28 |
| Elemental Analysis | C, 66.01; H, 7.26; F, 3.60; N, 7.96; O, 15.16 |
| CAS # | 751475-53-3 |
| Related CAS # | Atopaxar hydrobromide; 474550-69-1 |
| PubChem CID | 10459564 |
| Appearance | White to off-white solid powder |
| LogP | 4.892 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 1 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 8 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 10 |
| Heavy Atom Count | 38 |
| Complexity | 817 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| SMILES | CCOC1=C(C(=C2C(=C1)CN(CC(=O)C3=CC(=C(C(=C3)N4CCOCC4)OC)C(C)(C)C)C2=N)F)OCC |
| InChi Key | QWKAUGRRIXBIPO-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
| InChi Code | InChI=1S/C29H38FN3O5/c1-7-37-23-15-19-16-33(28(31)24(19)25(30)27(23)38-8-2)17-22(34)18-13-20(29(3,4)5)26(35-6)21(14-18)32-9-11-36-12-10-32/h13-15,31H,7-12,16-17H2,1-6H3 |
| Chemical Name | 1-(3-tert-butyl-4-methoxy-5-morpholin-4-ylphenyl)-2-(5,6-diethoxy-4-fluoro-3-imino-1H-isoindol-2-yl)ethanone |
| Synonyms | ER-172594-00; ER172594-00; ER 172594-00; E5555; E-5555; E 5555; Atopaxar |
| HS Tariff Code | 2934.99.9001 |
| Storage |
Powder-20°C 3 years 4°C 2 years In solvent -80°C 6 months -20°C 1 month |
| Shipping Condition | Room temperature (This product is stable at ambient temperature for a few days during ordinary shipping and time spent in Customs) |
Biological Activity
| Targets | PAR1 |
| ln Vitro | Atopaxar (0.0001-10 μM; 1h) inhibits the binding of haTRAP (high-affinity agonist capture activating peptide) to PAR-1 on the human distal membrane in a concentration suspension manner, with an IC50 of 0.019 μM[2]. Atopaxar does not induce PRP (Rich Wheel) aggregation through ADP, U46619, collagen and PAR-4ap at concentrations up to 20 μM [2]. |
| ln Vivo | Atopaxar (30-100 mg/kg; wall) causes dose-induced prolongation of femoral artery occlusion time in a guinea pig model of photochemically induced thrombosis (PIT) [2]. At the highest dose tested, 1000 mg/kg, Atopaxar did not. Animal Model: Guinea pig, PIT model [2] Dosage: Oral Administration: 10 mg/kg, 30 mg/kg, 100 mg/kg Results: Prolonged occlusion time 1.8 -1-fold and 2.4-fold increases at doses of 30 mg/kg and 100 mg/kg, respectively, compared to the control group. |
| Animal Protocol |
Guinea pigs, PIT model Oral administration 10 mg/kg, 30 mg/kg, 100 mg/kg |
| References |
[1]. Discovery of 1,3-Diaminobenzenes as Selective Inhibitors of Platelet Activation at the PAR1 Receptor. ACS Med Chem Lett. 2012 Mar 8; 3(3): 232–237. [2]. The novel and orally active thrombin receptor antagonist E5555 (Atopaxar) inhibits arterial thrombosis without affecting bleeding time in guinea pigs. Eur J Pharmacol. 2011 Apr 25;657(1-3):131-7. |
| Additional Infomation |
Atopaxar is an aromatic ketone. Atopaxar has been investigated for the treatment of Coronary Artery Disease and Acute Coronary Syndrome. |
Solubility Data
| Solubility (In Vitro) | DMSO: ~50 mg/mL (~94.8 mM) |
| Solubility (In Vivo) |
Solubility in Formulation 1: ≥ 2.08 mg/mL (3.94 mM) (saturation unknown) in 10% DMSO + 40% PEG300 + 5% Tween80 + 45% Saline (add these co-solvents sequentially from left to right, and one by one), clear solution. For example, if 1 mL of working solution is to be prepared, you can add 100 μL of 20.8 mg/mL clear DMSO stock solution to 400 μL PEG300 and mix evenly; then add 50 μL Tween-80 to the above solution and mix evenly; then add 450 μL normal saline to adjust the volume to 1 mL. Preparation of saline: Dissolve 0.9 g of sodium chloride in 100 mL ddH₂ O to obtain a clear solution. Solubility in Formulation 2: ≥ 2.08 mg/mL (3.94 mM) (saturation unknown) in 10% DMSO + 90% Corn Oil (add these co-solvents sequentially from left to right, and one by one), clear solution. For example, if 1 mL of working solution is to be prepared, you can add 100 μL of 20.8 mg/mL clear DMSO stock solution to 900 μL of corn oil and mix evenly. Solubility in Formulation 3: 2 mg/mL (3.79 mM) in 10% DMSO + 90% (20% SBE-β-CD in Saline) (add these co-solvents sequentially from left to right, and one by one), suspension solution; with ultrasonication. For example, if 1 mL of working solution is to be prepared, you can add 100 μL of 20.0 mg/mL clear DMSO stock solution to 900 μL of 20% SBE-β-CD physiological saline solution and mix evenly. Preparation of 20% SBE-β-CD in Saline (4°C,1 week): Dissolve 2 g SBE-β-CD in 10 mL saline to obtain a clear solution. (Please use freshly prepared in vivo formulations for optimal results.) |
| Preparing Stock Solutions | 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | |
| 1 mM | 1.8952 mL | 9.4762 mL | 18.9523 mL | |
| 5 mM | 0.3790 mL | 1.8952 mL | 3.7905 mL | |
| 10 mM | 0.1895 mL | 0.9476 mL | 1.8952 mL |