AZD-9272 is a potent, selective, orally bioavailable and brain penetrant antagonist mGlu5 (metabotropic glutamate receptor 5) with IC50 values of 2.6 and 7.6 nM for rat and human receptors, respectively. Its selectivity for mGlu5 is >3900-fold greater than that of other mGlu receptors. In rats, AZD-9272 exhibits discriminative effects. A number of groups of rats trained to distinguish between cocaine, PCP, chlordiazepoxide, (-)-Δ(9)-tetrahydrocannabinol [(-)-Δ(9)-THC], or MTEP and no drug were used to evaluate AZD9272. Only MTEP and AZD9272 shared discriminative characteristics. In rats trained to separate MTEP from no drug, the discriminative half-life was 3.23 hours for MTEP and 21.93 hours for AZD9272. It was successfully taught to other rats to distinguish between AZD9272 and no medication. Because AZD9272 was in effect for a long time, discrimination training was held every other day. The amount of AZD9272-appropriate responding increased in a dose-dependent manner. In contrast to MTEP, fenobam, and the mGluR5 antagonist AZD2066, PCP did not result in AZD9272-appropriate responding. Rats trained to distinguish between AZD9272 and no drug had a discriminative half-life of 24.3 hours for AZD9272. Conclusion: AZD9272 and AZD2066 have discriminative effects that are similar to those of mGluR5 antagonists that have been studied in the past but different from those of PCP, cocaine, chlordiazepoxide, and (-)-Δ(9)-THC. Compared to MTEP, AZD9272 has a discriminative half-life that is roughly 7-fold longer. The present data provide credence to earlier discoveries indicating that mGluR5 antagonistic compounds elicit psychoactive effects that are specifically mediated by mGluR5 mechanisms.
Physicochemical Properties
| Molecular Formula | C14H6N4OF2 |
| Molecular Weight | 284.22044 |
| Exact Mass | 284.05 |
| Elemental Analysis | C, 59.16; H, 2.13; F, 13.37; N, 19.71; O, 5.63 |
| CAS # | 327056-26-8 |
| PubChem CID | 9838729 |
| Appearance | White to off-white solid powder |
| Density | 1.3±0.1 g/cm3 |
| Boiling Point | 411.4±55.0 °C at 760 mmHg |
| Flash Point | 202.6±31.5 °C |
| Vapour Pressure | 0.0±0.9 mmHg at 25°C |
| Index of Refraction | 1.558 |
| LogP | 3.99 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 0 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 7 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 2 |
| Heavy Atom Count | 21 |
| Complexity | 415 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
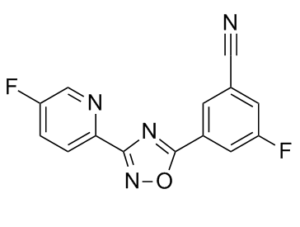
| SMILES | N#CC1=CC(F)=CC(C2=NC(C3=CC=C(F)C=N3)=NO2)=C1 |
| InChi Key | RBSPCALDSNXWEP-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
| InChi Code | InChI=1S/C14H6F2N4O/c15-10-1-2-12(18-7-10)13-19-14(21-20-13)9-3-8(6-17)4-11(16)5-9/h1-5,7H |
| Chemical Name | 3-fluoro-5-[3-(5-fluoropyridin-2-yl)-1,2,4-oxadiazol-5-yl]benzonitrile |
| Synonyms | AZD 9272; AZD-9272; AZD9272 |
| HS Tariff Code | 2934.99.9001 |
| Storage |
Powder-20°C 3 years 4°C 2 years In solvent -80°C 6 months -20°C 1 month |
| Shipping Condition | Room temperature (This product is stable at ambient temperature for a few days during ordinary shipping and time spent in Customs) |
Biological Activity
| Targets | mGluR5 |
| ln Vitro | AZD 9272 causes a concentration-dependent decrease in the magnitude of the intracellular Ca2+ response to 1.5 μM of the mGluR group I selective agonist DHPG in both human and rat mGluR5 expressing cell lines. One hundred percent inhibition is the maximum. AZD9272 has a mean IC50 (±SD) value of 7.6±1.1 nM (n=13) at the human mGluR5. 2.6±0.3 nM (n=3) is the mean IC50 value for AZD9272 at the rat mGluR5. On the other hand, the background GHEK cells' response to 10 μM ATP remains unchanged when 10 μM of AZD9272 is added. The maximal response and potency of DHPG decrease with increasing AZD9272 concentrations. In human mGluR5-GHEK cells, AZD9272 with an IC50 of 26±3 nM (n=21) completely reverses the glutamate-stimulated (EC80, 80 μM) phosphatidyl inositol hydrolysis in a concentration-dependent manner[1]. |
| ln Vivo | AZD 9272 has a low clearance after a single intravenous dose of 3 μmol/kg. Its terminal half-lives range from 2 to 6 hours, and it is eliminated from plasma. After an oral dosage, the terminal half-lives resemble those after an intravenous dosage. AZD9272 has an intermediate distribution volume at steady state [1]. At higher doses, AZD9272 results in a non-dose-dependent decrease in response rates and no cocaine-appropriate responding. Up to 20 hours after dosage, AZD9272 at 2.84 mg/kg results in more than 80% and usually more than 99% MTEP-appropriate responding; at 24 hours after dose, this number declines to about 20%, yielding a t1/2 of 21.93 hours. There are no systematic effects on response rates. Thirty minutes after dosage is when AZD9272 first induces >90% MTEP-appropriate responding[2]. |
| Enzyme Assay | Studies involving saturation binding and competition binding make use of one-hour incubations at 22°C. To perform saturation experiments, membranes derived from mGluR5-GHEK cells are subjected to varying concentrations (0.1 to 30 nM) of [3H]AZD9272, either with or without 10 μM MPEP. Saturable [3H]AZD9272 binding is found in a variant of these investigations where MPEP is present at low concentrations (10 and 20 nM). The Bmax remains constant whether MPEP is present or not, indicating that these ligands interact with a single binding site[1]. |
| Cell Assay | In media containing 10 µCi/mL [3H]myo-inositol, hmGluR5-GHEK cells are seeded at 50,000 cells/well onto 96-well plates. The cells are cultured for 16 hours, after which they are rinsed three times and left in HEPES buffered saline supplemented with 2 mM pyruvate and 1 unit/mL glutamate pyruvate transaminase for an hour at 37°C. Cells are pre-incubated in HEPES buffered saline containing 10 mM LiCl for 10 minutes after being washed once in the solution. To ascertain antagonist activity, cells are first pre-incubated with AZD9272 for 10 minutes, and then they are incubated with glutamate (EC80, 80 µM) for 30 minutes at 37°C. Ten concentrations of AZD9272, ranging from 1 nM to 30 μM, are examined in duplicate. The addition of 0.1 mL (5%) perchloric acid on ice and an incubation period of at least 30 minutes at 4°C bring the reaction to an end[1]. |
| Animal Protocol | In a colony room with lights on from 6:00 AM to 6:00 PM, about 48 male Wistar rats weighing between 240 and 250 g at the start of the experiments are housed in pairs or up to 8 rats per cage. By limiting food access, the animals are kept at about 80% of their free feeding weight. The animals are separated into distinct groups and trained to distinguish between the presence of PCP (1.6 mg/kg i.p., 30 minutes), MTEP (2 mg/kg i.p., 30 minutes), AZD9272 (1.6 mg/kg p.o., 60 minutes), and cocaine (3.4 mg/kg i.p., 15 minutes)[1]. |
| References |
[1]. AZD9272 and AZD2066: selective and highly central nervous system penetrant mGluR5 antagonists characterized by their discriminative effects. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2014 Aug;350(2):212-22. [2]. Discovery and characterization of AZD9272 and AZD6538-Two novel mGluR5 negative allosteric modulators selected for clinical development. Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 2012 Nov 15;22(22):6974-9. |
Solubility Data
| Solubility (In Vitro) | May dissolve in DMSO (in most cases), if not, try other solvents such as H2O, Ethanol, or DMF with a minute amount of products to avoid loss of samples |
| Solubility (In Vivo) |
Note: Listed below are some common formulations that may be used to formulate products with low water solubility (e.g. < 1 mg/mL), you may test these formulations using a minute amount of products to avoid loss of samples. Injection Formulations (e.g. IP/IV/IM/SC) Injection Formulation 1: DMSO : Tween 80: Saline = 10 : 5 : 85 (i.e. 100 μL DMSO stock solution → 50 μL Tween 80 → 850 μL Saline) *Preparation of saline: Dissolve 0.9 g of sodium chloride in 100 mL ddH ₂ O to obtain a clear solution. Injection Formulation 2: DMSO : PEG300 :Tween 80 : Saline = 10 : 40 : 5 : 45 (i.e. 100 μL DMSO → 400 μLPEG300 → 50 μL Tween 80 → 450 μL Saline) Injection Formulation 3: DMSO : Corn oil = 10 : 90 (i.e. 100 μL DMSO → 900 μL Corn oil) Example: Take the Injection Formulation 3 (DMSO : Corn oil = 10 : 90) as an example, if 1 mL of 2.5 mg/mL working solution is to be prepared, you can take 100 μL 25 mg/mL DMSO stock solution and add to 900 μL corn oil, mix well to obtain a clear or suspension solution (2.5 mg/mL, ready for use in animals). Injection Formulation 4: DMSO : 20% SBE-β-CD in saline = 10 : 90 [i.e. 100 μL DMSO → 900 μL (20% SBE-β-CD in saline)] *Preparation of 20% SBE-β-CD in Saline (4°C,1 week): Dissolve 2 g SBE-β-CD in 10 mL saline to obtain a clear solution. Injection Formulation 5: 2-Hydroxypropyl-β-cyclodextrin : Saline = 50 : 50 (i.e. 500 μL 2-Hydroxypropyl-β-cyclodextrin → 500 μL Saline) Injection Formulation 6: DMSO : PEG300 : castor oil : Saline = 5 : 10 : 20 : 65 (i.e. 50 μL DMSO → 100 μLPEG300 → 200 μL castor oil → 650 μL Saline) Injection Formulation 7: Ethanol : Cremophor : Saline = 10: 10 : 80 (i.e. 100 μL Ethanol → 100 μL Cremophor → 800 μL Saline) Injection Formulation 8: Dissolve in Cremophor/Ethanol (50 : 50), then diluted by Saline Injection Formulation 9: EtOH : Corn oil = 10 : 90 (i.e. 100 μL EtOH → 900 μL Corn oil) Injection Formulation 10: EtOH : PEG300:Tween 80 : Saline = 10 : 40 : 5 : 45 (i.e. 100 μL EtOH → 400 μLPEG300 → 50 μL Tween 80 → 450 μL Saline) Oral Formulations Oral Formulation 1: Suspend in 0.5% CMC Na (carboxymethylcellulose sodium) Oral Formulation 2: Suspend in 0.5% Carboxymethyl cellulose Example: Take the Oral Formulation 1 (Suspend in 0.5% CMC Na) as an example, if 100 mL of 2.5 mg/mL working solution is to be prepared, you can first prepare 0.5% CMC Na solution by measuring 0.5 g CMC Na and dissolve it in 100 mL ddH2O to obtain a clear solution; then add 250 mg of the product to 100 mL 0.5% CMC Na solution, to make the suspension solution (2.5 mg/mL, ready for use in animals). Oral Formulation 3: Dissolved in PEG400 Oral Formulation 4: Suspend in 0.2% Carboxymethyl cellulose Oral Formulation 5: Dissolve in 0.25% Tween 80 and 0.5% Carboxymethyl cellulose Oral Formulation 6: Mixing with food powders Note: Please be aware that the above formulations are for reference only. InvivoChem strongly recommends customers to read literature methods/protocols carefully before determining which formulation you should use for in vivo studies, as different compounds have different solubility properties and have to be formulated differently. (Please use freshly prepared in vivo formulations for optimal results.) |
| Preparing Stock Solutions | 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | |
| 1 mM | 3.5184 mL | 17.5920 mL | 35.1840 mL | |
| 5 mM | 0.7037 mL | 3.5184 mL | 7.0368 mL | |
| 10 mM | 0.3518 mL | 1.7592 mL | 3.5184 mL |