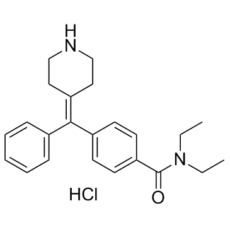
AR-M 1000390 hydrochloride (the hydrochloric acid of ARM-390; AR-M1000390) is a potent, highly selective agonist of δ opioid receptor that can induce insulin depletion in the rat and RINm5F cells. The δ opioid receptor was activated with an EC50 of 7.2±0.9 nM. After seven days of administration, AR-M100390 (600 micromol/kg) produced vacuolation in the rat pancreatic beta-cell, which was linked to insulin deficiency and hyperglycemia. The specific inhibition of rat insulin2 mRNA transcription in vivo was the cause of the insulin loss caused by AR-M100390. Hyperglycemia and insulin deficiency were reversible. Using the rat pancreatic beta-cell line RINm5F, the effects of AR-M100390 were replicated. This compound inhibited intracellular insulin content and secretion without compromising cell survival. Insulin loss in vitro was also reversible and caused by specific inhibition of insulin2 mRNA transcription. It is possible that the effects were not mediated by the delta-opioid receptor because pretreatment of cells with the pertussis toxin or the delta-opioid antagonist naltrindole did not reverse the loss of insulin in AR-M100390-treated cells. In RINm5F cells, AR-M100390 inhibited KCl-mediated calcium mobilization, indicating that L-type calcium channels present in these cells as well as in pancreatic beta-cells may contribute to this compound's partial inhibition of insulin secretion. In conclusion, research conducted both in vivo and in vitro indicates that AR-M100390'sinhibitionof insulin is caused by a combination of inhibitions of insulin release and/or synthesis.
Physicochemical Properties
| Molecular Formula | C23H29CLN2O | |
| Molecular Weight | 384.95 | |
| Exact Mass | 384.196 | |
| Elemental Analysis | C, 71.76; H, 7.59; Cl, 9.21; N, 7.28; O, 4.16 | |
| CAS # | 209808-47-9 | |
| Related CAS # |
|
|
| PubChem CID | 76848958 | |
| Appearance | White to off-white solid powder | |
| LogP | 5.484 | |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 2 | |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 2 | |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 5 | |
| Heavy Atom Count | 27 | |
| Complexity | 472 | |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 | |
| SMILES | O=C(N(CC)CC)C1=CC=C(/C(C2=CC=CC=C2)=C3CCNCC/3)C=C1.Cl |
|
| InChi Key | OTXTZCLQEGSAMW-UHFFFAOYSA-N | |
| InChi Code | InChI=1S/C23H28N2O.ClH/c1-3-25(4-2)23(26)21-12-10-19(11-13-21)22(18-8-6-5-7-9-18)20-14-16-24-17-15-20;/h5-13,24H,3-4,14-17H2,1-2H3;1H | |
| Chemical Name | N,N-diethyl-4-[phenyl(piperidin-4-ylidene)methyl]benzamide;hydrochloride | |
| Synonyms |
|
|
| HS Tariff Code | 2934.99.9001 | |
| Storage |
Powder-20°C 3 years 4°C 2 years In solvent -80°C 6 months -20°C 1 month Note: Please store this product in a sealed and protected environment, avoid exposure to moisture. |
|
| Shipping Condition | Room temperature (This product is stable at ambient temperature for a few days during ordinary shipping and time spent in Customs) |
Biological Activity
| Targets | δ opioid receptor ( EC50 = 7.2±0.9 nM ) | |
| ln Vitro |
|
|
| ln Vivo |
|
|
| Enzyme Assay | AR-M 1000390 hydrochloride (the hydrochloric acid of ARM-390) is a potent, highly selective δ opioid receptor agonist with an EC50 of 7.2±0.9 nM. | |
| Cell Assay | RINm5F cells are cultivated in 24-well plates and subjected to serum-free medium containing vehicle (DMSO), 10 μM AR-M 1000390 (AR-M100390), and 10 μM Cyclizine. Following treatment, the cells are washed with phosphate-buffered saline and kept at -80°C until further examination. The RNeasy purification system is used to isolate RNA after treating it with DNAse[2]. | |
| Animal Protocol |
|
|
| References |
[1]. N,N-Diethyl-4-(phenylpiperidin-4-ylidenemethyl)benzamide: a novel, exceptionally selective, potent delta opioid receptor agonist with oral bioavailability and its analogues. J Med Chem. 2000 Oct 19;43(21):3895-905. [2]. Mechanistic investigation of N,N-diethyl-4-(phenyl-piperidin-4-ylidenemethyl)-benzamide-inducedinsulin depletion in the rat and RINm5F cells. Toxicol Sci. 2008 Sep;105(1):221-9. |
Solubility Data
| Solubility (In Vitro) |
|
|||
| Solubility (In Vivo) |
Solubility in Formulation 1: ≥ 2.5 mg/mL (6.49 mM) (saturation unknown) in 10% DMSO + 40% PEG300 + 5% Tween80 + 45% Saline (add these co-solvents sequentially from left to right, and one by one), clear solution. For example, if 1 mL of working solution is to be prepared, you can add 100 μL of 25.0 mg/mL clear DMSO stock solution to 400 μL PEG300 and mix evenly; then add 50 μL Tween-80 to the above solution and mix evenly; then add 450 μL normal saline to adjust the volume to 1 mL. Preparation of saline: Dissolve 0.9 g of sodium chloride in 100 mL ddH₂ O to obtain a clear solution. Solubility in Formulation 2: ≥ 2.5 mg/mL (6.49 mM) (saturation unknown) in 10% DMSO + 90% (20% SBE-β-CD in Saline) (add these co-solvents sequentially from left to right, and one by one), clear solution. For example, if 1 mL of working solution is to be prepared, you can add 100 μL of 25.0 mg/mL clear DMSO stock solution to 900 μL of 20% SBE-β-CD physiological saline solution and mix evenly. Preparation of 20% SBE-β-CD in Saline (4°C,1 week): Dissolve 2 g SBE-β-CD in 10 mL saline to obtain a clear solution. Solubility in Formulation 3: ≥ 2.5 mg/mL (6.49 mM) (saturation unknown) in 10% DMSO + 90% Corn Oil (add these co-solvents sequentially from left to right, and one by one), clear solution. For example, if 1 mL of working solution is to be prepared, you can add 100 μL of 25.0 mg/mL clear DMSO stock solution to 900 μL of corn oil and mix evenly. (Please use freshly prepared in vivo formulations for optimal results.) |
| Preparing Stock Solutions | 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | |
| 1 mM | 2.5977 mL | 12.9887 mL | 25.9774 mL | |
| 5 mM | 0.5195 mL | 2.5977 mL | 5.1955 mL | |
| 10 mM | 0.2598 mL | 1.2989 mL | 2.5977 mL |