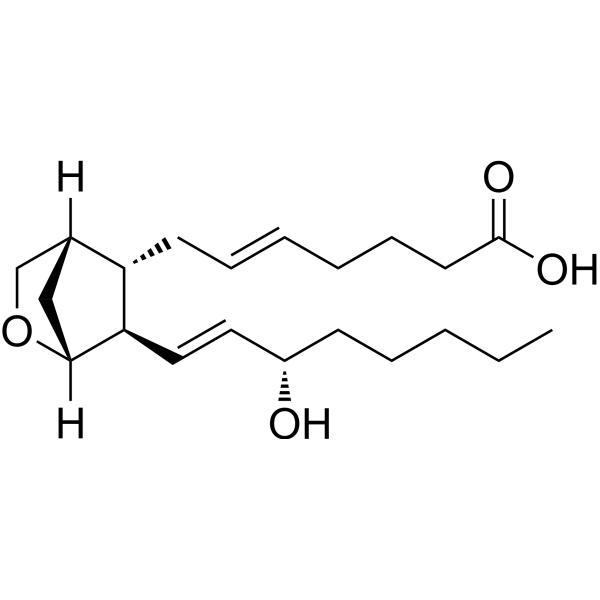
Physicochemical Properties
| Molecular Formula | C21H34O4 |
| Molecular Weight | 350.49 |
| Exact Mass | 350.245 |
| Elemental Analysis | C, 71.96; H, 9.78; O, 18.26 |
| CAS # | 330796-58-2 |
| Related CAS # | 56985-40-1 |
| PubChem CID | 44266707 |
| Appearance | Typically exists as solid at room temperature |
| Density | 1.1±0.1 g/cm3 |
| Boiling Point | 519.7±30.0 °C at 760 mmHg |
| Flash Point | 176.1±18.1 °C |
| Vapour Pressure | 0.0±3.1 mmHg at 25°C |
| Index of Refraction | 1.548 |
| LogP | 3.9 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 2 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 4 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 12 |
| Heavy Atom Count | 25 |
| Complexity | 457 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 3 |
| SMILES | CCCCC[C@@H](/C=C/[C@@H]1[C@@H](C/C=C/CCCC(=O)O)C2CC1OC2)O |
| InChi Key | LQANGKSBLPMBTJ-YTQMDITASA-N |
| InChi Code | InChI=1S/C21H34O4/c1-2-3-6-9-17(22)12-13-19-18(16-14-20(19)25-15-16)10-7-4-5-8-11-21(23)24/h4,7,12-13,16-20,22H,2-3,5-6,8-11,14-15H2,1H3,(H,23,24)/b7-4+,13-12+/t16?,17-,18-,19+,20?/m0/s1 |
| Chemical Name | (E)-7-[(5S,6R)-6-[(E,3S)-3-hydroxyoct-1-enyl]-2-oxabicyclo[2.2.1]heptan-5-yl]hept-5-enoic acid |
| Synonyms | 5-trans U-46619; 330796-58-2; (E)-7-[(5S,6R)-6-[(E,3S)-3-hydroxyoct-1-enyl]-2-oxabicyclo[2.2.1]heptan-5-yl]hept-5-enoic acid; HMS3648D04; PD021309; SR-01000946483; SR-01000946483-1; 9,11-Dideoxy-9alpha,11alpha-methanoepoxy-prosta-5E,13E-dien-1-oic acid |
| HS Tariff Code | 2934.99.9001 |
| Storage |
Powder-20°C 3 years 4°C 2 years In solvent -80°C 6 months -20°C 1 month |
| Shipping Condition | Room temperature (This product is stable at ambient temperature for a few days during ordinary shipping and time spent in Customs) |
Biological Activity
| Targets | PGE synthase; TXA2/Thromboxane A2 |
| ln Vitro |
Effects of stable PGH2 analogues and various prostaglandins on PGE synthase activity [1] Several PGs and close analogues of the PGH2 substrate were also assayed for their effects on PGE synthase activity. U-44069 and U-46619 are essentially identical to PGH2 except that each oxygen of the endoperoxide is sequentially replaced by a methylene group. These stable analogues caused only low levels of inhibition of PGE synthase (<30%) at 10 μM (Fig. 3) and thus were considerably less potent inhibitors than PUFAs. U-51605, where the endoperoxide of PGH2 is replaced by a diazo group, showed superior inhibitory activity when compared with either U-44069 or U-46619 with 70% inhibition at 10 μM. Interestingly, U-51605 also lacks the highly conserved hydroxy group at C15 found among most PGs. PGE2, 15(R)-PGE2, PGE3, PGF2α, thromboxane B2 (TXB2), PGJ2, and Δ12-PGJ2 had little effect (<30%) when tested at a concentration of 10 μM. The lack of inhibition by PGE2 suggests that the reaction is not sensitive to product inhibition under the current assay conditions. |
| References |
[1]. Inhibition of inducible prostaglandin E2 synthase by 15-deoxy-Δ12, 14-prostaglandin J2 and polyunsaturated fatty acids. Biochemical pharmacology, 2002, 63(6): 1183-1189. |
| Additional Infomation | Prostaglandin E2 synthase (PGE synthase) is one of the membrane-associated proteins in the eicosanoid and glutathione metabolism (MAPEG) family of microsomal enzymes and constitutes a novel inducible enzyme involved in inflammation and pyretic responses. We report, using a reversed-phase HPLC assay for the production of tritiated prostaglandin E2 (PGE2) by membranes from cells overexpressing human microsomal PGE synthase, that PGE synthase activity is inhibited effectively by 15-deoxy-Δ12,14-prostaglandin J2 and arachidonic acid. The anti-inflammatory compound 15-deoxy-PGJ2 was considerably more potent at inhibiting PGE synthase ( μM) than the closely related PGJ2 or Δ12-PGJ2, or the reaction product PGE2. Arachidonic acid, docosahexaenoic acid, and eicosapentaenoic acid inhibited PGE synthase with a similar potency ( μM) and were more potent inhibitors than various fatty acid analogues. The present results on the inducible PGE synthase extend observations on the ability to bind arachidonic acid to another member of the MAPEG family, and also suggest a novel mechanism of action for the anti-inflammatory effects of DHA, EPA, and 15-deoxy-PGJ2. [1] |
Solubility Data
| Solubility (In Vitro) | May dissolve in DMSO (in most cases), if not, try other solvents such as H2O, Ethanol, or DMF with a minute amount of products to avoid loss of samples |
| Solubility (In Vivo) |
Note: Listed below are some common formulations that may be used to formulate products with low water solubility (e.g. < 1 mg/mL), you may test these formulations using a minute amount of products to avoid loss of samples. Injection Formulations (e.g. IP/IV/IM/SC) Injection Formulation 1: DMSO : Tween 80: Saline = 10 : 5 : 85 (i.e. 100 μL DMSO stock solution → 50 μL Tween 80 → 850 μL Saline) *Preparation of saline: Dissolve 0.9 g of sodium chloride in 100 mL ddH ₂ O to obtain a clear solution. Injection Formulation 2: DMSO : PEG300 :Tween 80 : Saline = 10 : 40 : 5 : 45 (i.e. 100 μL DMSO → 400 μLPEG300 → 50 μL Tween 80 → 450 μL Saline) Injection Formulation 3: DMSO : Corn oil = 10 : 90 (i.e. 100 μL DMSO → 900 μL Corn oil) Example: Take the Injection Formulation 3 (DMSO : Corn oil = 10 : 90) as an example, if 1 mL of 2.5 mg/mL working solution is to be prepared, you can take 100 μL 25 mg/mL DMSO stock solution and add to 900 μL corn oil, mix well to obtain a clear or suspension solution (2.5 mg/mL, ready for use in animals). Injection Formulation 4: DMSO : 20% SBE-β-CD in saline = 10 : 90 [i.e. 100 μL DMSO → 900 μL (20% SBE-β-CD in saline)] *Preparation of 20% SBE-β-CD in Saline (4°C,1 week): Dissolve 2 g SBE-β-CD in 10 mL saline to obtain a clear solution. Injection Formulation 5: 2-Hydroxypropyl-β-cyclodextrin : Saline = 50 : 50 (i.e. 500 μL 2-Hydroxypropyl-β-cyclodextrin → 500 μL Saline) Injection Formulation 6: DMSO : PEG300 : castor oil : Saline = 5 : 10 : 20 : 65 (i.e. 50 μL DMSO → 100 μLPEG300 → 200 μL castor oil → 650 μL Saline) Injection Formulation 7: Ethanol : Cremophor : Saline = 10: 10 : 80 (i.e. 100 μL Ethanol → 100 μL Cremophor → 800 μL Saline) Injection Formulation 8: Dissolve in Cremophor/Ethanol (50 : 50), then diluted by Saline Injection Formulation 9: EtOH : Corn oil = 10 : 90 (i.e. 100 μL EtOH → 900 μL Corn oil) Injection Formulation 10: EtOH : PEG300:Tween 80 : Saline = 10 : 40 : 5 : 45 (i.e. 100 μL EtOH → 400 μLPEG300 → 50 μL Tween 80 → 450 μL Saline) Oral Formulations Oral Formulation 1: Suspend in 0.5% CMC Na (carboxymethylcellulose sodium) Oral Formulation 2: Suspend in 0.5% Carboxymethyl cellulose Example: Take the Oral Formulation 1 (Suspend in 0.5% CMC Na) as an example, if 100 mL of 2.5 mg/mL working solution is to be prepared, you can first prepare 0.5% CMC Na solution by measuring 0.5 g CMC Na and dissolve it in 100 mL ddH2O to obtain a clear solution; then add 250 mg of the product to 100 mL 0.5% CMC Na solution, to make the suspension solution (2.5 mg/mL, ready for use in animals). Oral Formulation 3: Dissolved in PEG400 Oral Formulation 4: Suspend in 0.2% Carboxymethyl cellulose Oral Formulation 5: Dissolve in 0.25% Tween 80 and 0.5% Carboxymethyl cellulose Oral Formulation 6: Mixing with food powders Note: Please be aware that the above formulations are for reference only. InvivoChem strongly recommends customers to read literature methods/protocols carefully before determining which formulation you should use for in vivo studies, as different compounds have different solubility properties and have to be formulated differently. (Please use freshly prepared in vivo formulations for optimal results.) |
| Preparing Stock Solutions | 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | |
| 1 mM | 2.8531 mL | 14.2657 mL | 28.5315 mL | |
| 5 mM | 0.5706 mL | 2.8531 mL | 5.7063 mL | |
| 10 mM | 0.2853 mL | 1.4266 mL | 2.8531 mL |