Physicochemical Properties
| Molecular Formula | C8H8O3 |
| Molecular Weight | 152.15 |
| Exact Mass | 152.047 |
| CAS # | 621-37-4 |
| PubChem CID | 12122 |
| Appearance | White to off-white solid powder |
| Density | 1.3±0.1 g/cm3 |
| Boiling Point | 349.0±17.0 °C at 760 mmHg |
| Melting Point | 129-133 °C(lit.) |
| Flash Point | 179.1±17.4 °C |
| Vapour Pressure | 0.0±0.8 mmHg at 25°C |
| Index of Refraction | 1.596 |
| LogP | 0.77 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 2 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 3 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 2 |
| Heavy Atom Count | 11 |
| Complexity | 144 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| InChi Key | FVMDYYGIDFPZAX-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
| InChi Code | InChI=1S/C8H8O3/c9-7-3-1-2-6(4-7)5-8(10)11/h1-4,9H,5H2,(H,10,11) |
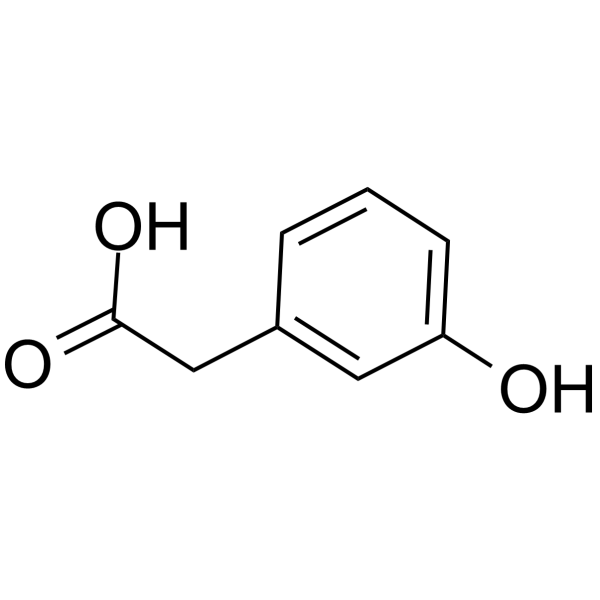
| Chemical Name | 2-(3-hydroxyphenyl)acetic acid |
| HS Tariff Code | 2934.99.9001 |
| Storage |
Powder-20°C 3 years 4°C 2 years In solvent -80°C 6 months -20°C 1 month |
| Shipping Condition | Room temperature (This product is stable at ambient temperature for a few days during ordinary shipping and time spent in Customs) |
Biological Activity
| Targets | Human Endogenous Metabolite |
| ADME/Pharmacokinetics |
Metabolism / Metabolites 3-hydroxyphenylacetic acid has known human metabolites that include 2-Phenylacetic acid. 3-hydroxyphenylacetic acid is a known human metabolite of 3,4-dihydroxyphenylacetic acid. |
| Additional Infomation |
3-hydroxyphenylacetic acid is a monocarboxylic acid that is phenylacetic acid in which the hydrogen at position 3 on the benzene ring is replaced by a hydroxy group. It has a role as a human xenobiotic metabolite. It is a monocarboxylic acid and a member of phenols. It is functionally related to an acetic acid. It is a conjugate acid of a 3-hydroxyphenylacetate. 3-Hydroxyphenylacetic acid has been reported in Homo sapiens, Rhizoctonia solani, and other organisms with data available. |
Solubility Data
| Solubility (In Vitro) | DMSO :~50 mg/mL (~328.62 mM) |
| Solubility (In Vivo) |
Solubility in Formulation 1: ≥ 2.5 mg/mL (16.43 mM) (saturation unknown) in 10% DMSO + 40% PEG300 + 5% Tween80 + 45% Saline (add these co-solvents sequentially from left to right, and one by one), clear solution. For example, if 1 mL of working solution is to be prepared, you can add 100 μL of 25.0 mg/mL clear DMSO stock solution to 400 μL PEG300 and mix evenly; then add 50 μL Tween-80 to the above solution and mix evenly; then add 450 μL normal saline to adjust the volume to 1 mL. Preparation of saline: Dissolve 0.9 g of sodium chloride in 100 mL ddH₂ O to obtain a clear solution. Solubility in Formulation 2: ≥ 2.5 mg/mL (16.43 mM) (saturation unknown) in 10% DMSO + 90% (20% SBE-β-CD in Saline) (add these co-solvents sequentially from left to right, and one by one), clear solution. For example, if 1 mL of working solution is to be prepared, you can add 100 μL of 25.0 mg/mL clear DMSO stock solution to 900 μL of 20% SBE-β-CD physiological saline solution and mix evenly. Preparation of 20% SBE-β-CD in Saline (4°C,1 week): Dissolve 2 g SBE-β-CD in 10 mL saline to obtain a clear solution. Solubility in Formulation 3: ≥ 2.5 mg/mL (16.43 mM) (saturation unknown) in 10% DMSO + 90% Corn Oil (add these co-solvents sequentially from left to right, and one by one), clear solution. For example, if 1 mL of working solution is to be prepared, you can add 100 μL of 25.0 mg/mL clear DMSO stock solution to 900 μL of corn oil and mix evenly. (Please use freshly prepared in vivo formulations for optimal results.) |
| Preparing Stock Solutions | 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | |
| 1 mM | 6.5725 mL | 32.8623 mL | 65.7246 mL | |
| 5 mM | 1.3145 mL | 6.5725 mL | 13.1449 mL | |
| 10 mM | 0.6572 mL | 3.2862 mL | 6.5725 mL |