Physicochemical Properties
| Molecular Formula | C21H26O6 |
| Molecular Weight | 374.43 |
| CAS # | 3754-05-0 |
| Appearance | Solid powder |
| LogP | 0.737 |
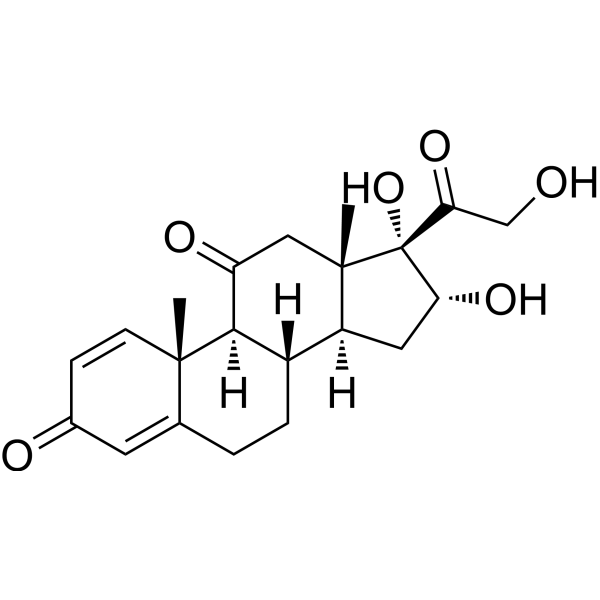
| SMILES | OC1CC2C(C)(CC(=O)C3C2CCC2C3(C)C=CC(=O)C=2)C1(O)C(=O)CO |
| Synonyms | 3754-05-0; 11-Keto-16alpha-hydroxyprednisolone; 16alpha,17,21-Trihydroxy-pregna-1,4-diene-3,11,20-trione; UNII-9UUI9HUO3Q; 9UUI9HUO3Q; (8S,9S,10R,13S,14S,16R,17S)-16,17-dihydroxy-17-(2-hydroxyacetyl)-10,13-dimethyl-6,7,8,9,12,14,15,16-octahydrocyclopenta[a]phenanthrene-3,11-dione; Pregna-1,4-diene-3,11,20-trione, 16,17,21-trihydroxy-, (16alpha)-; 16a,17,21-Trihydroxy-pregna-1,4-diene-3,11,20-trione; |
| HS Tariff Code | 2934.99.9001 |
| Storage |
Powder-20°C 3 years 4°C 2 years In solvent -80°C 6 months -20°C 1 month |
| Shipping Condition | Room temperature (This product is stable at ambient temperature for a few days during ordinary shipping and time spent in Customs) |
Biological Activity
| Targets | Glucocorticoid receptor; metabolite of Budesonide |
| ln Vivo | Budesonide (BUD) is a glucocorticoid widely used for the treatment of asthma, rhinitis, and inflammatory bowel disease. Its use in sport competitions is prohibited when administered by oral, intravenous, intramuscular, or rectal routes. However, topical preparations are not prohibited. Strategies to discriminate between legal and forbidden administrations have to be developed by doping control laboratories. For this reason, metabolism of BUD has been re-evaluated using liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry (LC-MS/MS) with different scan methods. Urine samples obtained after oral administration of 3 mg of BUD to two healthy volunteers have been analyzed for metabolite detection in free and glucuronide metabolic fractions. Structures of the metabolites have been studied by LC-MS/MS using collision induced dissociation and gas chromatography-mass spectrometry (GC/MS) in full scan mode with electron ionization. Combination of all structural information allowed the proposition of the most comprehensive picture for BUD metabolism in humans to this date. Overall, 16 metabolites including ten previously unreported compounds have been detected. The main metabolite is 16α-hydroxy-prednisolone resulting from the cleavage of the acetal group. Other metabolites without the acetal group have been identified such as those resulting from reduction of C20 carbonyl group, oxidation of the C11 hydroxyl group and reduction of the A ring. Metabolites maintaining the acetal group have also been identified, resulting from 6-hydroxylation (6α and 6β-hydroxy-budesonide), 23-hydroxylation, reduction of C6-C7, oxidation of the C11 hydroxyl group, and reduction of the C20 carbonyl group. Metabolites were mainly excreted in the free fraction. All of them were excreted in urine during the first 24 h after administration, and seven of them were still detected up to 48 h after administration for both volunteers [1]. |
| References |
[1]. Identification of budesonide metabolites in human urine after oral administration. Anal Bioanal Chem. 2012 Aug;404(2):325-40. |
| Additional Infomation | Metabolism of BUD was studied using LC-MS/MS technology, combined with GC/MS for identification of some of the metabolites. By combining all the information collected, the overall metabolism for BUD has been re-evaluated. Sixteen metabolites were detected in urine samples after oral administration of BUD. Structures of metabolites resulting from the cleavage of the acetal chain (M-I, 16α-hydroxy-prednisolone) and 6-hydroxylation (M-II and M-III, 6β-hydroxy-budesonide, and 6α-hydroxy-budesonide) were confirmed by comparison with commercially available standards. Plausible structures for the rest of metabolites were proposed based on mass spectrometric data. Some metabolites maintaining the acetal chain were generated through hydroxylation in the acetal chain (M-IVa, M-IVb, M-Va, and M-Vb), reduction of C6-C7 (M-Va, M-Vb, and M-VI), oxidation of the hydroxyl group in C11 (M-VII), or reduction in the C20 carbonyl group (M-VIII). Other metabolites were produced by cleavage of the acetal chain, as M-I, and additional modifications (reduction in the C20 carbonyl group, M-IXa and M-IXb; oxidation of the hydroxyl group in C11, M-X; or reductions in the A ring, M-XI to M-XIII). Ten of these metabolites were not reported before for BUD (M-III, M-Va, M-Vb, M-VII, MVIII, MIXa, MIXb, MXI, MXII, and MXIII). A better knowledge on the metabolism of BUD may be useful to investigate differences on the metabolites excreted in urine samples depending on the route of administration. These differences could be used in the future to define analytical strategies to discriminate between legal and forbidden use of BUD in doping control analyses.[1] |
Solubility Data
| Solubility (In Vitro) | DMSO : ~116.67 mg/mL (~311.59 mM; with ultrasonication) |
| Solubility (In Vivo) |
Note: Listed below are some common formulations that may be used to formulate products with low water solubility (e.g. < 1 mg/mL), you may test these formulations using a minute amount of products to avoid loss of samples. Injection Formulations (e.g. IP/IV/IM/SC) Injection Formulation 1: DMSO : Tween 80: Saline = 10 : 5 : 85 (i.e. 100 μL DMSO stock solution → 50 μL Tween 80 → 850 μL Saline) *Preparation of saline: Dissolve 0.9 g of sodium chloride in 100 mL ddH ₂ O to obtain a clear solution. Injection Formulation 2: DMSO : PEG300 :Tween 80 : Saline = 10 : 40 : 5 : 45 (i.e. 100 μL DMSO → 400 μLPEG300 → 50 μL Tween 80 → 450 μL Saline) Injection Formulation 3: DMSO : Corn oil = 10 : 90 (i.e. 100 μL DMSO → 900 μL Corn oil) Example: Take the Injection Formulation 3 (DMSO : Corn oil = 10 : 90) as an example, if 1 mL of 2.5 mg/mL working solution is to be prepared, you can take 100 μL 25 mg/mL DMSO stock solution and add to 900 μL corn oil, mix well to obtain a clear or suspension solution (2.5 mg/mL, ready for use in animals). Injection Formulation 4: DMSO : 20% SBE-β-CD in saline = 10 : 90 [i.e. 100 μL DMSO → 900 μL (20% SBE-β-CD in saline)] *Preparation of 20% SBE-β-CD in Saline (4°C,1 week): Dissolve 2 g SBE-β-CD in 10 mL saline to obtain a clear solution. Injection Formulation 5: 2-Hydroxypropyl-β-cyclodextrin : Saline = 50 : 50 (i.e. 500 μL 2-Hydroxypropyl-β-cyclodextrin → 500 μL Saline) Injection Formulation 6: DMSO : PEG300 : castor oil : Saline = 5 : 10 : 20 : 65 (i.e. 50 μL DMSO → 100 μLPEG300 → 200 μL castor oil → 650 μL Saline) Injection Formulation 7: Ethanol : Cremophor : Saline = 10: 10 : 80 (i.e. 100 μL Ethanol → 100 μL Cremophor → 800 μL Saline) Injection Formulation 8: Dissolve in Cremophor/Ethanol (50 : 50), then diluted by Saline Injection Formulation 9: EtOH : Corn oil = 10 : 90 (i.e. 100 μL EtOH → 900 μL Corn oil) Injection Formulation 10: EtOH : PEG300:Tween 80 : Saline = 10 : 40 : 5 : 45 (i.e. 100 μL EtOH → 400 μLPEG300 → 50 μL Tween 80 → 450 μL Saline) Oral Formulations Oral Formulation 1: Suspend in 0.5% CMC Na (carboxymethylcellulose sodium) Oral Formulation 2: Suspend in 0.5% Carboxymethyl cellulose Example: Take the Oral Formulation 1 (Suspend in 0.5% CMC Na) as an example, if 100 mL of 2.5 mg/mL working solution is to be prepared, you can first prepare 0.5% CMC Na solution by measuring 0.5 g CMC Na and dissolve it in 100 mL ddH2O to obtain a clear solution; then add 250 mg of the product to 100 mL 0.5% CMC Na solution, to make the suspension solution (2.5 mg/mL, ready for use in animals). Oral Formulation 3: Dissolved in PEG400 Oral Formulation 4: Suspend in 0.2% Carboxymethyl cellulose Oral Formulation 5: Dissolve in 0.25% Tween 80 and 0.5% Carboxymethyl cellulose Oral Formulation 6: Mixing with food powders Note: Please be aware that the above formulations are for reference only. InvivoChem strongly recommends customers to read literature methods/protocols carefully before determining which formulation you should use for in vivo studies, as different compounds have different solubility properties and have to be formulated differently. (Please use freshly prepared in vivo formulations for optimal results.) |
| Preparing Stock Solutions | 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | |
| 1 mM | 2.6707 mL | 13.3536 mL | 26.7073 mL | |
| 5 mM | 0.5341 mL | 2.6707 mL | 5.3415 mL | |
| 10 mM | 0.2671 mL | 1.3354 mL | 2.6707 mL |