Physicochemical Properties
| Molecular Formula | C20H26O3 |
| Molecular Weight | 314.418646335602 |
| CAS # | 71748-58-8 |
| Appearance | Typically exists as solids at room temperature |
| Density | 1.07g/cm3 |
| Boiling Point | 509.9ºC at 760 mmHg |
| Melting Point | 150-157ºC |
| Flash Point | 276.3ºC |
| Index of Refraction | 1.565 |
| LogP | 4.782 |
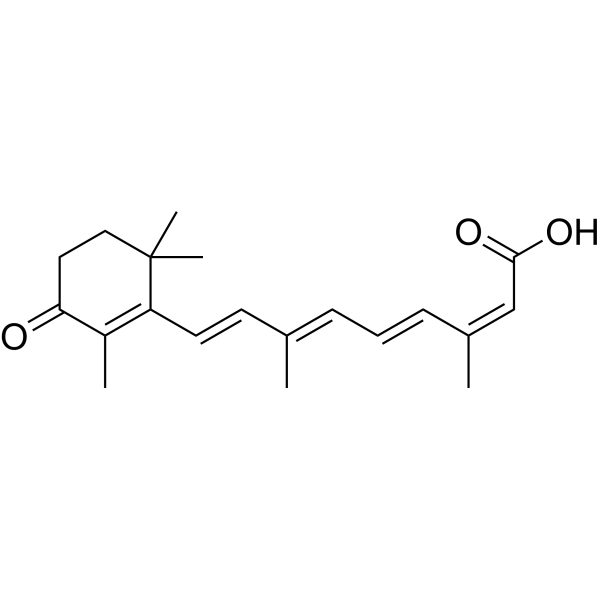
| SMILES | O=C1C(C)=C(/C=C/C(=C/C=C/C(=C\C(=O)O)/C)/C)C(C)(C)CC1 |
| Synonyms | 4-Keto 13-cis-retinoic acid; 4-Oxoisotretinoin; 71748-58-8; 13-cis-4-Oxoretinoic acid; Oxoretinoic acid; 4-Oxo-13-cis retinoic acid; Ro 22-6595; Retinoic acid, 4-oxo-, 13-cis-; DTXSID201312157; 4-Oxoiisotretinoin; Ro 22-6595 |
| HS Tariff Code | 2934.99.9001 |
| Storage |
Powder-20°C 3 years 4°C 2 years In solvent -80°C 6 months -20°C 1 month |
| Shipping Condition | Room temperature (This product is stable at ambient temperature for a few days during ordinary shipping and time spent in Customs) |
Biological Activity
| Targets | Vitamin A metabolite |
| ln Vivo | Human plasma was analyzed by high performance liquid chromatography for the presence of retinoic acid and 4-oxoretinoic acid isomers. Peaks that coeluted with the reference compounds all-trans-retinoic acid, 13-cis-retinoic acid, and 13-cis-4-oxoretinoic acid were routinely observed in human plasma. These retinoids were unequivocally identified by the following methods: comigration with reference compounds under several high performance liquid chromatographic conditions; comparison of ultraviolet spectra with those of reference compounds; derivatization with diazomethane and coelution of the methyl esters with reference compounds in a high performance liquid chromatographic system as well as in a gas chromatography system with a mass selective detector. In vitro formation of 13-cis-retinoic acid and 13-cis-4-oxoretinoic acid as artifacts during the analytical procedure was excluded by control experiments. The mean plasma concentrations of the vitamin A metabolites in ten male volunteers were: all-trans-retinoic acid: 1.32 +/- 0.46 ng/ml; 13-cis-retinoic acid: 1.63 +/- 0.85 ng/ml; and 13-cis-4-oxoretinoic acid: 3.68 +/- 0.99 ng/ml. After oral dosing with vitamin A (833 IU/kg body weight) in five male volunteers, mean plasma all-trans-retinoic acid increased to 3.92 +/- 1.40 ng/ml and 13-cis-retinoic acid increased to 9.75 +/- 2.18 ng/ml. Maximal plasma 13-cis-4-oxoretinoic acid concentrations (average 7.60 +/- 1.45 ng/ml) were observed 6 h after dosing which was the last time point in this study. Concentrations of all-trans-4-oxoretinoic acid were low or not detectable. Our findings suggest that, in addition to all-trans-retinoic acid, 13-cis-retinoic acid and 13-cis-4-oxoretinoic acid are present in normal human plasma as metabolites of vitamin A [1]. |
| Animal Protocol | Plasma samples: Blood was drawn from healthy male volunteers and plasma was prepared by centrifugating the blood in heparinized tubes for 10 min at 1500 g and 4OC. The samples were stored in polypropylene tubes at - 80°C until analysis. Dosing of vitamin A: Volunteers received retinyl palmitate (833 IU/kg body weight) as oily drops [1]. |
| References |
[1]. Identification and quantitation of all-trans- and 13-cis-retinoic acid and 13-cis-4-oxoretinoic acid in human plasma. J Lipid Res. 1990 Aug;31(8):1445-54. |
| Additional Infomation | The presented HPLC method appears to be a powerful tool for investigations concerning vitamin A metabolism. With its low limit of quantitation (0.5 ng/ml) it allows the determination of physiological concentrations of 13-cis-4- oxoRA, 13-cis-RA, and all-tram-RA in human plasma. Sample preparation with the Varian AASP is extremely easy and, together with a quick HPLC elution, allows the analysis of a large series of samples in a short time. Separation of the retinoids was achieved using a reversed phase system with an ammonium acetate buffer. Mixtures of aqueous ammonium acetate and acetonitrile or methanol are commonly used by many investigators for the analysis of retinoic acid compounds. We used a 3 pm octadecy1 silica column with column heating and a steep gradient which resulted in narrow, well-resolved peaks. For routine analysis, we use a second UV-detector (Shimadzu SPD 6-AV, flow cell: 10 x 1 mm) operating at 356 nm which is connected in series to the first detector which operates at 340 nm. Outputs of both detectors are independently processed by the C-R4A two-channel integrator. This adds the characteristics UV-absorbance ratio of the retinoid peaks as a second argument for a correct peak identification to the peak retention time argument. The assay method is successfully used for studies on the vitamin A metabolism in human as well as in monkey plasma. [1] |
Solubility Data
| Solubility (In Vitro) | May dissolve in DMSO (in most cases), if not, try other solvents such as H2O, Ethanol, or DMF with a minute amount of products to avoid loss of samples |
| Solubility (In Vivo) |
Note: Listed below are some common formulations that may be used to formulate products with low water solubility (e.g. < 1 mg/mL), you may test these formulations using a minute amount of products to avoid loss of samples. Injection Formulations (e.g. IP/IV/IM/SC) Injection Formulation 1: DMSO : Tween 80: Saline = 10 : 5 : 85 (i.e. 100 μL DMSO stock solution → 50 μL Tween 80 → 850 μL Saline) *Preparation of saline: Dissolve 0.9 g of sodium chloride in 100 mL ddH ₂ O to obtain a clear solution. Injection Formulation 2: DMSO : PEG300 :Tween 80 : Saline = 10 : 40 : 5 : 45 (i.e. 100 μL DMSO → 400 μLPEG300 → 50 μL Tween 80 → 450 μL Saline) Injection Formulation 3: DMSO : Corn oil = 10 : 90 (i.e. 100 μL DMSO → 900 μL Corn oil) Example: Take the Injection Formulation 3 (DMSO : Corn oil = 10 : 90) as an example, if 1 mL of 2.5 mg/mL working solution is to be prepared, you can take 100 μL 25 mg/mL DMSO stock solution and add to 900 μL corn oil, mix well to obtain a clear or suspension solution (2.5 mg/mL, ready for use in animals). Injection Formulation 4: DMSO : 20% SBE-β-CD in saline = 10 : 90 [i.e. 100 μL DMSO → 900 μL (20% SBE-β-CD in saline)] *Preparation of 20% SBE-β-CD in Saline (4°C,1 week): Dissolve 2 g SBE-β-CD in 10 mL saline to obtain a clear solution. Injection Formulation 5: 2-Hydroxypropyl-β-cyclodextrin : Saline = 50 : 50 (i.e. 500 μL 2-Hydroxypropyl-β-cyclodextrin → 500 μL Saline) Injection Formulation 6: DMSO : PEG300 : castor oil : Saline = 5 : 10 : 20 : 65 (i.e. 50 μL DMSO → 100 μLPEG300 → 200 μL castor oil → 650 μL Saline) Injection Formulation 7: Ethanol : Cremophor : Saline = 10: 10 : 80 (i.e. 100 μL Ethanol → 100 μL Cremophor → 800 μL Saline) Injection Formulation 8: Dissolve in Cremophor/Ethanol (50 : 50), then diluted by Saline Injection Formulation 9: EtOH : Corn oil = 10 : 90 (i.e. 100 μL EtOH → 900 μL Corn oil) Injection Formulation 10: EtOH : PEG300:Tween 80 : Saline = 10 : 40 : 5 : 45 (i.e. 100 μL EtOH → 400 μLPEG300 → 50 μL Tween 80 → 450 μL Saline) Oral Formulations Oral Formulation 1: Suspend in 0.5% CMC Na (carboxymethylcellulose sodium) Oral Formulation 2: Suspend in 0.5% Carboxymethyl cellulose Example: Take the Oral Formulation 1 (Suspend in 0.5% CMC Na) as an example, if 100 mL of 2.5 mg/mL working solution is to be prepared, you can first prepare 0.5% CMC Na solution by measuring 0.5 g CMC Na and dissolve it in 100 mL ddH2O to obtain a clear solution; then add 250 mg of the product to 100 mL 0.5% CMC Na solution, to make the suspension solution (2.5 mg/mL, ready for use in animals). Oral Formulation 3: Dissolved in PEG400 Oral Formulation 4: Suspend in 0.2% Carboxymethyl cellulose Oral Formulation 5: Dissolve in 0.25% Tween 80 and 0.5% Carboxymethyl cellulose Oral Formulation 6: Mixing with food powders Note: Please be aware that the above formulations are for reference only. InvivoChem strongly recommends customers to read literature methods/protocols carefully before determining which formulation you should use for in vivo studies, as different compounds have different solubility properties and have to be formulated differently. (Please use freshly prepared in vivo formulations for optimal results.) |
| Preparing Stock Solutions | 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | |
| 1 mM | 3.1805 mL | 15.9023 mL | 31.8046 mL | |
| 5 mM | 0.6361 mL | 3.1805 mL | 6.3609 mL | |
| 10 mM | 0.3180 mL | 1.5902 mL | 3.1805 mL |