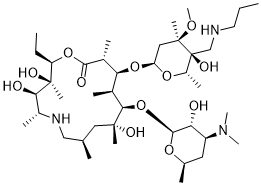
Physicochemical Properties
| Molecular Formula | C41H79N3O12 |
| Molecular Weight | 806.0789 |
| Exact Mass | 805.566 |
| Elemental Analysis | C, 61.09; H, 9.88; N, 5.21; O, 23.82 |
| CAS # | 217500-96-4 |
| PubChem CID | 9832301 |
| Appearance | Solid powder |
| Density | 1.2±0.1 g/cm3 |
| Boiling Point | 853.8±65.0 °C at 760 mmHg |
| Flash Point | 470.2±34.3 °C |
| Vapour Pressure | 0.0±0.6 mmHg at 25°C |
| Index of Refraction | 1.536 |
| LogP | 4.07 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 7 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 15 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 11 |
| Heavy Atom Count | 56 |
| Complexity | 1240 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 18 |
| SMILES | O([C@@]1([H])C([H])([H])[C@](C([H])([H])[H])([C@](C([H])([H])N([H])C([H])([H])C([H])([H])C([H])([H])[H])([C@]([H])(C([H])([H])[H])O1)O[H])OC([H])([H])[H])[C@]1([H])[C@]([H])(C(=O)O[C@]([H])(C([H])([H])C([H])([H])[H])[C@](C([H])([H])[H])([C@@]([H])([C@@]([H])(C([H])([H])[H])N([H])C([H])([H])[C@]([H])(C([H])([H])[H])C([H])([H])[C@](C([H])([H])[H])([C@@]([H])([C@@]1([H])C([H])([H])[H])O[C@@]1([H])[C@@]([H])([C@]([H])(C([H])([H])[C@@]([H])(C([H])([H])[H])O1)N(C([H])([H])[H])C([H])([H])[H])O[H])O[H])O[H])O[H])C([H])([H])[H] |
| InChi Key | GUARTUJKFNAVIK-QPTWMBCESA-N |
| InChi Code | InChI=1S/C41H79N3O12/c1-15-17-42-22-41(50)28(8)53-31(20-39(41,10)51-14)55-33-25(5)35(56-37-32(45)29(44(12)13)18-24(4)52-37)38(9,48)19-23(3)21-43-27(7)34(46)40(11,49)30(16-2)54-36(47)26(33)6/h23-35,37,42-43,45-46,48-50H,15-22H2,1-14H3/t23-,24-,25+,26-,27-,28+,29+,30-,31+,32-,33+,34-,35-,37+,38-,39-,40-,41+/m1/s1 |
| Chemical Name | (2R,3S,4R,5R,8R,10R,11R,12S,13S,14R)-11-[(2S,3R,4S,6R)-4-(Dimethylamino)-3-hydroxy-6-methyloxan-2-yl]oxy-2-ethyl-3,4,10-trihydroxy-13-[(2R,4R,5S,6S)-5-hydroxy-4-methoxy-4,6-dimethyl-5-(propylaminomethyl)oxan-2-yl]oxy-3,5,8,10,12,14-hexamethyl-1-oxa-6-azacyclopentadecan-15-one |
| Synonyms | CP-472,295; CP-472295; CP 472295; CP472295; Tulathromycin; Draxxin; Tulathromycin A; |
| HS Tariff Code | 2934.99.9001 |
| Storage |
Powder-20°C 3 years 4°C 2 years In solvent -80°C 6 months -20°C 1 month |
| Shipping Condition | Room temperature (This product is stable at ambient temperature for a few days during ordinary shipping and time spent in Customs) |
Biological Activity
| Targets | Macrolide |
| ln Vitro |
Tulathromycin A, also referred to as tulathromycin, is the first member of a recently discovered macrolide subclass called triamilides[1]. Tulathromycin A (0.02 to 2.0 mg/mL) causes neutrophils to undergo concentration- and time-dependent apoptosis, which facilitates macrophage clearance of the cells afterward[3]. |
| ln Vivo | Tulathromycin A (2.5 mg/kg, IM) in the lungs of pigs challenged with A pleuropneumoniae and zymosan inhibits the production of proinflammatory leukotriene B4 and promotes leukocyte apoptosis and efferocytosis, while simultaneously reducing leukocyte necrosis in comparison to control pigs. In pigs inoculated with A pleuropneumoniae, tulathromycin A also reduces the extent of lung damage and lesion progression[3]. |
| References |
[1]. Pharmacokinetics of tulathromycin in healthy and neutropenic mice challenged intranasally with lipopolysaccharide from Escherichia coli. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2012;56(8):4078-4086. [2]. Inhibition of protein synthesis on the ribosome by tildipirosin compared with other veterinary macrolides. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2012;56(11):6033-6036. [3]. Immunomodulatory effects of tulathromycin on apoptosis, efferocytosis, and proinflammatory leukotriene B4 production in leukocytes from Actinobacillus pleuropneumoniae-or zymosan-challenged pigs. Am J Vet Res. 2015;76(6):507-519. [4]. Vet Ther. 2005 Summer;6(2):96-112 |
| Additional Infomation |
Tulathromycin A is an aminoglycoside. See also: Ketoprofen; Tulathromycin (component of); Tulathromycin A (annotation moved to). Drug Indication Cattle: Treatment and metaphylaxis of bovine respiratory disease (BRD) associated with Mannheimia haemolytica, Pasteurella multocida, Histophilus somni and Mycoplasma bovis susceptible to tulathromycin. The presence of the disease in the herd should be established before metaphylactic treatment. Treatment of infectious bovine keratoconjunctivitis (IBK) associated with Moraxella bovis susceptible to tulathromycin. Pigs: Treatment and metaphylaxis of swine respiratory disease (SRD) associated with Actinobacillus pleuropneumoniae, Pasteurella multocida, Mycoplasma hyopneumoniae, Haemophilus parasuis and Bordetella bronchiseptica susceptible to tulathromycin. The presence of the disease in the herd should be established before metaphylactic treatment. The product should only be used if pigs are expected to develop the disease within 2â3 days. Sheep: Treatment of the early stages of infectious pododermatitis (foot rot) associated with virulent Dichelobacter nodosus requiring systemic treatment. Cattle: Treatment and metaphylaxis of bovine respiratory disease (BRD) associated with Mannheimia haemolytica, Pasteurella multocida, Histophilus somni and Mycoplasma bovis susceptible to tulathromycin. The presence of the disease in the herd should be established before metaphylactic treatment. Treatment of infectious bovine keratoconjunctivitis (IBK) associated with Moraxella bovis susceptible to tulathromycin. Pigs: Treatment and metaphylaxis of swine respiratory disease (SRD) associated with Actinobacillus pleuropneumoniae, Pasteurella multocida, Mycoplasma hyopneumoniae, Haemophilus parasuis and Bordetella bronchiseptica susceptible to tulathromycin. The presence of the disease in the herd should be established before metaphylactic treatment. The product should only be used if pigs are expected to develop the disease within 2â3 days. Sheep: Treatment of the early stages of infectious pododermatitis (foot rot) associated with virulent Dichelobacter nodosus requiring systemic treatment. Cattle: Treatment and metaphylaxis of bovine respiratory disease (BRD) associated with Mannheimia haemolytica, Pasteurella multocida, Histophilus somni and Mycoplasma bovis susceptible to tulathromycin. The presence of the disease in the herd should be established before metaphylactic treatment. Treatment of infectious bovine keratoconjunctivitis (IBK) associated with Moraxella bovis susceptible to tulathromycin. Pigs: Treatment and metaphylaxis of swine respiratory disease (SRD) associated with Actinobacillus pleuropneumoniae, Pasteurella multocida, Mycoplasma hyopneumoniae, Haemophilus parasuis and Bordetella bronchiseptica susceptible to tulathromycin. The presence of the disease in the herd should be established before metaphylactic treatment. The product should only be used if pigs are expected to develop the disease within 2â3 days. Sheep: Treatment of the early stages of infectious pododermatitis (foot rot) associated with virulent Dichelobacter nodosus requiring systemic treatment. Cattle: Treatment and metaphylaxis of bovine respiratory disease (BRD) associated with Mannheimia haemolytica, Pasteurella multocida, Histophilus somni and Mycoplasma bovis susceptible to tulathromycin. The presence of the disease in the herd should be established before metaphylactic treatment. Treatment of infectious bovine keratoconjunctivitis (IBK) associated with Moraxella bovis susceptible to tulathromycin. Pigs: Treatment and metaphylaxis of swine respiratory disease (SRD) associated with Actinobacillus pleuropneumoniae, Pasteurella multocida, Mycoplasma hyopneumoniae, Haemophilus parasuis and Bordetella bronchiseptica susceptible to tulathromycin. The presence of the disease in the herd should be established before metaphylactic treatment. The product should only be used if pigs are expected to develop the disease within 2â3 days. Sheep: Treatment of the early stages of infectious pododermatitis (foot rot) associated with virulent Dichelobacter nodosus requiring systemic treatment. Cattle: Treatment and metaphylaxis of bovine respiratory disease (BRD) associated with Mannheimia haemolytica, Pasteurella multocida, Histophilus somni and Mycoplasma bovis susceptible to tulathromycin. The presence of the disease in the herd should be established before metaphylactic treatment. Treatment of infectious bovine keratoconjunctivitis (IBK) associated with Moraxella bovis susceptible to tulathromycin. Pigs: Treatment and metaphylaxis of swine respiratory disease (SRD) associated with Actinobacillus pleuropneumoniae, Pasteurella multocida, Mycoplasma hyopneumoniae, Haemophilus parasuis and Bordetella bronchiseptica susceptible to tulathromycin. The presence of the disease in the herd should be established before metaphylactic treatment. The product should only be used if pigs are expected to develop the disease within 2â3 days. Sheep: Treatment of the early stages of infectious pododermatitis (foot rot) associated with virulent Dichelobacter nodosus requiring systemic treatment. Cattle: Treatment and metaphylaxis of bovine respiratory disease (BRD) associated with Mannheimia haemolytica, Pasteurella multocida, Histophilus somni and Mycoplasma bovis sensitive to tulathromycin. The presence of the disease in the herd should be established before metaphylactic treatment. Treatment of infectious bovine keratoconjunctivitis (IBK) associated with Moraxella bovis sensitive to tulathromycin. Pigs: Treatment and metaphylaxis of swine respiratory disease (SRD) associated with Actinobacillus pleuropneumoniae, Pasteurella multocida, Mycoplasma hyopneumoniae, Haemophilus parasuis and Bordetella bronchiseptica sensitive to tulathromycin. The presence of the disease in the herd should be established before metaphylactic treatment. Draxxin should only be used if pigs are expected to develop the disease within 2â3 days. Sheep: Treatment of the early stages of infectious pododermatitis (foot rot) associated with virulent Dichelobacter nodosus requiring systemic treatment. Cattle: Treatment and metaphylaxis of bovine respiratory disease (BRD) associated with Mannheimia haemolytica, Pasteurella multocida, Histophilus somni and Mycoplasma bovis susceptible to tulathromycin. The presence of the disease in the herd should be established before metaphylactic treatment. Treatment of infectious bovine keratoconjunctivitis (IBK) associated with Moraxella bovis susceptible to tulathromycin. Pigs: Treatment and metaphylaxis of swine respiratory disease (SRD) associated with Actinobacillus pleuropneumoniae, Pasteurella multocida, Mycoplasma hyopneumoniae, Haemophilus parasuis and Bordetella bronchiseptica susceptible to tulathromycin. The presence of the disease in the herd should be established before metaphylactic treatment. The product should only be used if pigs are expected to develop the disease within 2â3 days. Sheep: Treatment of the early stages of infectious pododermatitis (foot rot) associated with virulent Dichelobacter nodosus requiring systemic treatment. |
Solubility Data
| Solubility (In Vitro) |
DMSO : 50~100 mg/mL ( 62.03~124.05 mM ) Ethanol : ~100 mg/mL |
| Solubility (In Vivo) |
Solubility in Formulation 1: ≥ 2.5 mg/mL (3.10 mM) (saturation unknown) in 10% DMSO + 40% PEG300 + 5% Tween80 + 45% Saline (add these co-solvents sequentially from left to right, and one by one), clear solution. For example, if 1 mL of working solution is to be prepared, you can add 100 μL of 25.0 mg/mL clear DMSO stock solution to 400 μL PEG300 and mix evenly; then add 50 μL Tween-80 to the above solution and mix evenly; then add 450 μL normal saline to adjust the volume to 1 mL. Preparation of saline: Dissolve 0.9 g of sodium chloride in 100 mL ddH₂ O to obtain a clear solution. Solubility in Formulation 2: ≥ 2.5 mg/mL (3.10 mM) (saturation unknown) in 10% DMSO + 90% (20% SBE-β-CD in Saline) (add these co-solvents sequentially from left to right, and one by one), clear solution. For example, if 1 mL of working solution is to be prepared, you can add 100 μL of 25.0 mg/mL clear DMSO stock solution to 900 μL of 20% SBE-β-CD physiological saline solution and mix evenly. Preparation of 20% SBE-β-CD in Saline (4°C,1 week): Dissolve 2 g SBE-β-CD in 10 mL saline to obtain a clear solution. Solubility in Formulation 3: ≥ 2.5 mg/mL (3.10 mM) (saturation unknown) in 10% DMSO + 90% Corn Oil (add these co-solvents sequentially from left to right, and one by one), clear solution. For example, if 1 mL of working solution is to be prepared, you can add 100 μL of 25.0 mg/mL clear DMSO stock solution to 900 μL of corn oil and mix evenly. Solubility in Formulation 4: 10% DMSO+40% PEG300+5% Tween-80+45% Saline: ≥ 2.5 mg/mL (3.10 mM) (Please use freshly prepared in vivo formulations for optimal results.) |
| Preparing Stock Solutions | 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | |
| 1 mM | 1.2406 mL | 6.2029 mL | 12.4057 mL | |
| 5 mM | 0.2481 mL | 1.2406 mL | 2.4811 mL | |
| 10 mM | 0.1241 mL | 0.6203 mL | 1.2406 mL |